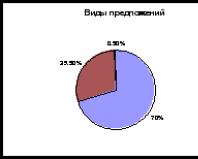
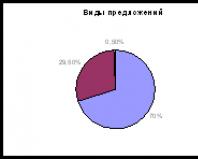
Flowers in bonsai style. Types and styles of bonsai formation. Bujingi: literary style
Bonsai culture is known to many. If earlier this art of plant formation found its admirers in Japan, now this activity has become popular all over the world. Let’s take a closer look at how to grow a Japanese bonsai tree with your own hands, and what is generally recommended to know about this culture.
The decorative dwarf plant called bonsai has a centuries-old history. According to legend, about fifteen centuries ago, one Chinese emperor wanted to see his country in a smaller copy. All kinds of specialists spent a long time creating miniature versions of structures, and talented flower growers worked on the formation of small trees. This is how the composition, called bonsai, appeared.
A bonsai tree is not just an indoor flower that will be located on your windowsill. This is a plant that is characterized by those features that are also inherent in large-growing specimens. In fact, this is their real copy: if you planted a deciduous tree, it will also grow leaves in the spring and shed them with the arrival of autumn cold weather.
Of course, growing a tree at home that will decorate your interior is not so easy. However, if you follow basic care recommendations, the plant will delight you with its greenery for many years.
Video “What is bonsai”
From this video you will learn what bonsai is and the history of its origin.
What plants can be used to make a tree?
The art of bonsai requires a lot of effort and attention from every gardener. You can replenish your flower collection with various specimens, because this composition is created from all kinds of plants (fuchsia, olive, elm, etc.).
However, in order for planting your seeds to definitely give the desired result, it is better to find out in more detail which green specimens are considered most suitable for growing in the bonsai style.
Privet or Ligustrum
This shrub is considered an evergreen deciduous, so it is perfect for creating a custom flower arrangement in your home. Typically, such a plant is cultivated in bonsai style as a smaller copy of a regular leaf tree.
It is advisable to place such a green specimen in a well-lit place. In caring for it, it is very important to moisten the substrate in time. Allow the soil to dry out a little between waterings, but it is better to avoid prolonged drought.
Olive
Types of bonsai include many names, and among them the olive plant stands out. Surely you will want to have European olive in your own home. In addition, the bonsai tree certainly blooms in the spring.
In order to grow such a shrub, it is necessary to select the nutritional composition of the soil. The best choice is a mixture of sand and clay. As for watering, it should be moderate. Take short breaks during the process so that the top layer of soil can dry noticeably.
Araucaria
Araucaria is also suitable for forming a bonsai flower. This green specimen is sure to become an elegant decoration for your interior. But its advantages do not end there. Domestic flower growers value araucaria because it is quite pliable in the process of crown formation. That is why it is best to start getting acquainted with bonsai culture with araucaria.
Boxwood
This shrub has small green leaves. It is believed that boxwood is not very suitable for long-term cultivation at home. However, with regard to resistance to pest invasion or the development of diseases, this plant is considered an ideal option for a gardener.
Podocarpus
A Chinese or Japanese tree called bonsai can be formed from podocarpus. This coniferous plant can be found in natural conditions in the subtropical region. What’s interesting is that in this specimen new shoots appear only once a year, so you don’t have to form a crown as such.
Anubias
Few people know what Anubias bonsai is. This is a slow-growing plant with small foliage. Nevertheless, feel free to root it at home, as it is easy to care for. Try to place this flower in a pot away from large shrubs: if the stem or foliage of Anubias is overly shaded, the tree may begin to rot.
Willow
Who would have thought that a classic Chinese bonsai could be created from an ordinary willow tree? You can get such a home specimen by rooting seeds, cuttings, or using air layering. This plant is considered heat-loving, but on hot summer days, try to place the flower pot in a shaded place.
Elm
Many gardeners would probably want to have an indoor small-leaved elm in their apartment. This flower can withstand both sudden temperature changes and wet or drying soil well. It is recommended to place this plant in a well-lit area of the house.
Avocado
Avocado is often used to form a bonsai composition. This shrub is a fast-growing green species. If you want to propagate it, use seed material for this. Watering should be moderate, allowing the soil mixture to develop a slight dry crust before watering again.
Other
Your imagination should have no limits. Plants such as albizia, acacia, bamboo, banana, baobab, barberry, and wisteria can also be cultivated as a bonsai tree. There are plenty of varieties suitable for decorating such a plant in modern floriculture. Let your flowering or evergreen bonsai symbolize peace and harmony in your home.
In what styles to form
A lilac, podocarpus or olive bonsai does not have to take a specific shape. Nevertheless, experts identify many styles in which modern gardeners most often create bonsai. The most popular options include fan, formal vertical, inclined, cascade, semi-cascade, etc.
Bonsai in the teachings of Feng Shui
Feng Shui culture is known to many. It is often used to create a calm, harmonious atmosphere in the house that would attract only positive energy. In order for peace to settle in your home, it is advisable to acquire one of the symbols of Feng Shui - a bonsai tree. Its form can be varied, the main thing is the result.
Some believe that bonsai is a variety of dwarf tree-like plants that are grown in standard pots. Others believe that bonsai is an art form or a movement in Eastern philosophy that the tiny Japanese tree seems to complement. In fact, bonsai are really tiny trees that are the most accurate copy of their tall relatives. They receive them - having comprehended all the intricacies of a special type of art, and for years they successfully keep them in their home - only by understanding all the intricacies of Eastern philosophy, based on contemplation, admiration and reflection. Previously, a unique Japanese tree the height of an ordinary indoor flower could only be seen at exhibitions. Now bonsai has become incredibly popular and has spread throughout the world. Many Russians have also begun to master the technique of growing it. It is simple only at first glance, but hides many secrets and features.
Where to begin
If you have firmly decided that you need a tiny tree in a pot, the question arises of how to get it. To make the task easier, you can buy ready-made bonsai in the store. Then the length of his life in the apartment will depend on knowledge and compliance with the rules of care. But many adherents of Eastern culture certainly want to grow an exotic plant from scratch on their own.
There are different types of bonsai, depending on the type of plant that will be turned into a dwarf. Almost any tree from the garden or from the nearest forest belt can be a candidate. The art of bonsai became famous thanks to Japan, but was born in China during the reign of the Tang Dynasty, when one of its rulers wanted to create a miniature copy of his empire. That’s when the smart ancient Chinese came up with the idea of making exactly the same trees out of ordinary trees, only reduced by tens of times. They called the new agricultural technology “cultivated on a tray” or bonsai. Thus, by following certain techniques, any plant can be turned into a dwarf. But in practice, success more often comes with trees that can withstand extreme living conditions, namely, develop in a miniature volume of soil, and do not get sick from changes in natural light conditions, changes in annual temperatures and watering. Therefore, no matter what type of bonsai you choose, it is important to take into account the natural living conditions of your pets and strive to get as close to them as possible.
Where to get planting material
As mentioned above, different plants are suitable for bonsai, both coniferous and deciduous. When choosing, you need to pay attention to the size of their leaf blade. Since the plant in the pot will be miniature, it is desirable that the leaf blades of its prototype are not too large. Otherwise, the small trunk simply will not be able to support them. The second condition is that the plant species from which different types of bonsai are created have a genetic tendency to form a dense crown. Having decided on a candidate, you must take into account the soil in which your future bonsai will grow in the wild, with what lighting, and at what humidity. All this will need to be exactly recreated at home in a pot. In practice, success is achieved with fruit trees, citrus trees, myrtle, maple, rhododendron, ficus and many others.

Yamadori
There are not only different types of bonsai, but also different technologies for its propagation, or, more correctly, the starting operation of cultivation. Yamadori is considered the simplest technology. It consists in the fact that in the natural habitat the desired young tree is being looked at. It is dug in a circle, roots that are too powerful (if any), cut off and left alone for three months. Next, it is removed with a lump of earth and placed in a selected flower pot (bonsai). To quickly adapt, the plant is shaded, sprayed, and a temperature regime similar to natural is created.
Toriki
This technology in Russian means trivial cuttings. It is important to comply with the timing of this process. For example, in Russia it is advisable to cut deciduous trees at the end of spring, and coniferous trees, on the contrary, at the beginning. Plants from which cuttings are taken must be five to ten years old. If you strictly follow the rules for preparing planting material for your bonsai, caring for it in the future will not bring disappointment. Cuttings should be cut only in cloudy weather, cutting off shoots that are not yet woody. Their length can vary, depending on the number of internodes. There should not be less than three and it is not desirable that there be more than five. The upper edge of the cutting is made smooth, and the lower edge is beveled, placed in water, and covered with a damp rag. Another practiced method of toriki is to carefully remove a strip of bark no more than 2 cm wide from a branch that you like, or to make an incision on the branch into which a pebble is inserted. This place is generously moistened with epin, wrapped with sphagnum, polyethylene on top, secured and wrapped on both sides to stop the air supply. Moisture is regularly added to this compress with a syringe. The twig should take root in about 60 days.

Misho
This method is ideal for beginners and means seed propagation. Maples, oaks, myrtle, pomegranate, and citrus fruits are suitable for this. You can collect ripe seeds from selected trees, which should turn into a bonsai without any problems. Only for this, the seeds must go through all phases of stratification. To make the task easier, you can carefully remove already sprouted seeds from the ground in the spring and place the finished sprouts in prepared bowls for future bonsai.
Classification according to size
Not only are there different types, but there are also styles of bonsai that vary in size. It's surprising that the world of miniature plants has its own tiny giants and midgets. The international classification distinguishes:
1. Mame. This group consists of trees up to 20 cm high. Among them:
Keshi-tsubu (midgets in the land of midgets, up to only 2.5 cm high).
Sieve (up to 7.5 cm high, maximum 8 cm).
Gafu (up to 20 cm high).
2. Shohin. This group consists of plants of intermediate sizes between very small and simply small. There are also two subgroups here:
Komono (approximately 20 cm tall).
Myabi (up to 25 cm).
3. Kifu. The group takes the middle position. The plants included in it can grow up to 40 cm.
4. Ty. Plants in this group are almost giants and reach a meter in height. Subgroups:
Tyukhin (up to 60 cm).
Omono (up to 100 cm).
5. Bonju. In the world of midget plants, these are already giants, capable of stretching up to 120 cm and higher.

Classification by crown shape
It turns out that there are also different styles of bonsai based on how the crown looks. Traditional ones include:
Tekkan (erect trunk, thickening towards the base).
Moyogi (the base and top of the stem are perpendicular to the ground, and the middle is curved).
Sokan (the tree has two stems, each with its own crown, forming something whole).
Syakan (trunk without curvature, but growing towards the ground at an angle).
Kengai (the trees resemble classic weeping trees, that is, they grow with stems inclined below the pot, as if falling down).
Khan kengai (the trunk of the tree is also cascading, but the top is always in line with the soil of the bowl, and the branching branches resemble independent plants).
Bundzingi (the tree grows with an erect stem, but with a minimum number of branches).
Sekijoju (there are stones in a bowl on the ground, and the roots of the tree seem to entwine them).
Isitsuki (a composition of figured stones is created in a bowl, and plants grow in their crevices).
Hokidachi (the stem of the plant is straight, and the branches form a beautiful spherical crown).
-Yose ue (several trees grow in a pot, not a multiple of 4, different in height and age).
Ikadabuki (imitation of a tree that seems to have fallen to the ground, with individual branches growing upward from the trunk).
Exclusive Styles
In addition to the classic ones, which are considered simpler, there are very complex ones in the art of bonsai that require high skill. This:
Netsuranari (a tree has several stems growing from one root, which are intricately intertwined with each other).
Fukinagashi (a complex composition in which the bonsai grows not just at an angle, but in such a way that its branches and leaves are arranged as if the tree is tilted by the wind).
Sakei (in a bowl an imitation of an entire corner of nature is created - a forest or a mountain area, and bonsai plants make this imitation more natural).
Growing rules
It is not very difficult to maintain a bonsai at home, the care of which is based on strict adherence to the rules. Those who believe that dwarf trees should grow only in the house as a decorative element are mistaken. Very often, bonsai compositions are placed in the fresh air and brought into the house only with the onset of cold weather. If the winters are not severe, the bonsai can be left outside, but the bowls must be placed in a container of large diameter, and covered on top with a dense layer of moss up to the very branches of the tree.

It is very important that deciduous bonsais in winter, just as in natural conditions, shed their leaves and remain dormant for some time. To do this, they are taken out to a cool room. The third condition for success is strict compliance with lighting and humidity standards. If the bonsai does not have enough natural light, additionally turn on the lamps, but take into account the heat they generate. You can maintain optimal humidity using an electric humidifier. If there is none, the bowl with the plant can be placed in a tray lined with pebbles and half filled with water. The simplest, but also the most ineffective way is to spray the crowns of plants.
Landing
When the planting material is prepared - cuttings or seeds - the bonsai needs to be placed in its home. The Japanese and Chinese use bowls and low flower pots for this purpose, coated with glaze or matte, but always having several drainage holes. To prevent soil from being washed out of them, cover the holes with a piece of tile. The shape of the pot can be any. It is best to take the same soil for indoor bonsai as that of its outdoor relative. Some masters prepare the soil separately. Everyone has their own recipes. Here are the most common:
A mixture of equal parts of clay, fine gravel, humus, stone chips or sand;
Clay, humus and gravel in ratios (3:5:2);
Clay humus, gravel (1:5:3);
Leaf soil, coke, sand, bark, volcanic soil.
In any case, the soil should easily allow water to pass through to avoid stagnation. In addition, experienced craftsmen advise disinfecting the pot and soil before planting. placed in the ground, covered with glass, the entire germination period is maintained at a warm temperature and moderate humidity. Plants that have hatched and reached the stage of 2-4 leaves dive. In order for the root system to develop, the picking operation must be carried out several more times. Cuttings and seedlings are planted in the same soil as the seeds. For better rooting, the cuttings are covered with film.

Transfer
Growing bonsai is unthinkable without replanting, which must be done every two, maximum three, years before the start of sap flow. This operation is also carried out if there is suspicion of rotting of the root system. Before transplanting, the plant is left without watering for a couple of days. Remove from the pot using a knife. The soil and all suspicious roots are carefully removed from the roots, and large roots are also removed. The pot is disinfected, filled with a couple of centimeters of new soil, the roots remaining after pruning are straightened with a wooden stick, laid out on the ground, sprinkled with earth, compacted and watered. You can fix the plant with a wire inserted into the drainage hole.
Bonsai (plant): how to care
Maintaining small trees is not very difficult. They need to be watered regularly with cool water, making sure that the soil in the pot does not remain dry or too waterlogged. During the dormant period, plants are watered less frequently, and more often during the growing season. Bonsai feeding is mandatory. This is done from the beginning of the growing season every week, adding sapropel or urea. You can also use mineral fertilizers in the form of granules or solutions. Fertilizers containing a lot of nitrogen are applied after the end of the first wave of growth. With the onset of the dormant period, feeding is stopped. Coniferous bonsai are also not fed in winter. Fertilizers should not be applied to sick or recently transplanted plants.

Bonsai formation
How to make something unusual out of ordinary wood is perhaps the main question. The technologies here are different. In our conditions, maple bonsai works well even for beginners. Having chosen the desired variety, seeds or cuttings are planted according to general rules, and the plant is allowed to grow stronger for the first year. Subsequently, the appearance of the trunk is changed by gently wrapping it with soft (copper or aluminum) wire. But with maples this does not always bring results. Most often they are formed by pruning. To stop the growth of the top, new shoots are regularly removed from it. Maple has a rather large leaf blade. To reduce it, around mid-summer, the grown leaves are removed, leaving the petiole. During this period, the tree is moved to a shaded place. In order for the maple bonsai to grow lush, when pruning, you can truncate an overly elongated trunk (cover the wound with an antiseptic), remove skeletal branches, and pinch out young shoots. To give the trunk a slope or bends, during the period of active growth you can tie a weight to it or gently bend it in the desired direction and secure it with copper wire, placing fabric under it. Several methods can be used to achieve the desired trunk thickness. In some plants, young stems are fused by planting them next to each other and fastening them together. This method is not very successful for maple. The thickness of the trunk in this case is achieved by truncation.
Bonsai is the name of a small tree with an unusual shape of trunk and crown. These trees originated in ancient China, and then in Japan they became not just plants, but turned into works of art. In the modern world, the word “bonsai” refers not only to trees, but also to methods of growing them.
The goal of gardeners who grow bonsai at home is to be able to reproduce the creation of nature. These small replicas of trees follow all natural laws and have all realistic proportions. A deciduous tree, for example, blooms, loses its leaves and becomes covered with them again, and so on.
But it must be remembered that forming a tree, growing and caring for it is a labor-intensive task that takes a lot of time and requires certain knowledge and patience.
People who have never cared for bonsai trees think that special seeds are needed to grow them, but this is not the case.
In fact, all miniature plants grow from ordinary seeds, but mankind has come up with ways to restrain the growth and change the shape of trees, and has successfully used them.
Small trees have different shapes and vary in placement in pots:

In addition to trees, the pots contain figurines and small houses. The soil is often hidden under a layer of pebbles or green moss.
Tree formation
To grow the right bonsai, you must have certain skills and knowledge.
For planting, you can use seeds, cuttings or layering of trees. To stop growth, the same techniques are used as in the wild: severe frosts, winds and droughts.
In small trees, the roots are pruned, the branches are also pruned, twisted, and additionally tied with wire. All leaves, buds and shoots must be removed. 
The trunks are bent or pulled back, depending on the chosen shape.
Growth can be slowed down in the following ways:
- squeezing tree roots;
- selection of small pots by size;
- use of rough soil, without microelements;
- exclusion of substances necessary for growth;
- influence of strong wind;
- influence of strong heating;
- the influence of strong and sharp frosts.
Trees also require rules regarding the shape chosen for the tree. To create the desired appearance, they combine naturalness and the necessary form. Trees should not exceed 30 centimeters in height.
Growing plants from a nursery
When purchasing a young tree from a nursery, you can form a bonsai fairly quickly. After all, nurseries sell plants that have been grown in a container for a long time, thanks to which they already have developed roots.
The plant is transplanted from the container into prepared bonsai soil, after cutting off the roots. Plant purchase and replanting must be done in early spring, before the growth period.
It is also necessary to trim the roots correctly and not damage them when digging. The plant is transported by placing the roots in a bag with moss, and at home it is planted in large containers and placed in a shady place, protected from drafts.
It will take about 3 years before the tree can be transplanted into a small pot. And in 5-10 years it will be possible to get a fully formed bonsai.
Trees grown in nature require a long time to take root. Therefore, sometimes preparations for replanting begin several years in advance, gradually cutting off the roots.
This option is well suited for trees from a personal garden, which you can monitor and gradually remove the length of the roots. Trees from the garden are also first planted in a container, and after three years they are transplanted into a pot. 
Rough formation can begin in the first years, then after 50 years you will get a bonsai that looks powerful and impressive.
Forming a bonsai from an almost grown tree and replanting it correctly is quite a difficult task, and beyond the power of beginners.
Bonsai from seeds
The method of growing from seeds is quite time consuming. It takes about 15 years to obtain a full-fledged bonsai. At this age it is easier to buy seedlings in a nursery.
But there are plant species whose shape can only be changed if you start the changes from the beginning, such as elms. And so they plant seeds, grow sprouts and begin the formation of more sprouts from the first year.
When the tree is fully formed, it will be very noticeable that it was formed from the very beginning.
The roots of such trees diverge in the shape of a star, and the trunks are formed smooth and beautiful. The bonsai turns out harmonious and proportional.
Sown trees at the stage of thin sprouts can be bent in any direction and given any desired shape.
Seeds can be purchased in stores or collected independently in parks or botanical gardens. Some seeds can be sown immediately, such as oaks, spruces, pines, and some must be stored in a cool place until spring, such as juniper, hornbeam and others. 
Before planting, all seeds undergo special treatment to prevent diseases.. Then they are soaked for several days and only then planted in prepared soil in containers or peat cups. After planting, the soil is compacted and watered abundantly.
Seedlings are grown following standard care standards: regular watering, ventilation, diffused light and fertilizers. When the seedling reaches 10 centimeters in height, it is transplanted and first molded.
Growing bonsai from seeds is a labor-intensive and difficult task, but the result will be excellent.
Bonsai from cuttings
Compared to the seed method, this method will speed up the formation of bonsai by a year. Cuttings must be taken from a healthy tree shoot. They are cut and rooted in the ground or in wet sand.
The final size of a bonsai is clear already at the beginning of the formation of a miniature tree. The main skeletal branches and trunk are usually already present and further growth will be limited.
In order to achieve the ideal size, you need to pay attention to the size of the leaves. If the species has small leaves, then the bonsai can be formed of any size. And if the castings have large or long needles, then it is necessary to set the size of the tree based on the proportions.
Features of growing bonsai
In order to form a certain shape of the branches and trunk, you cannot do without wire. It can be applied to the branches or trunk, and this technique is quite labor-intensive and complex.
All branches and shoots are secured with wire. In this case, it is necessary to ensure that the wire does not grow into the tree bark. It is most often applied in spring or winter, simultaneously with annual pruning. 
It usually takes about 3 weeks to stabilize the desired shape of a branch or shoot. After this, the wire is removed with wire cutters.
The wire usually used is aluminum, coated with copper. And with its help they change the direction of branches, change growth, and form trunks.
Bonsai tree care
With constant restrictions on growth, crown formation, growth in a limited space, the life of a tree changes dramatically. Its care also changes.
The most important thing to remember when growing miniature trees is that they need to be protected from drafts, and the pot should be placed away from central heating radiators. Avoid direct sunlight best.
Landing. To properly grow bonsai, it is important to choose a pot with drainage holes. An additional mesh is placed at the bottom of the pot to prevent soil from being washed out.
Before planting, the roots of the plant are trimmed. The tree is planted in a pot, fixing large roots and filling all the gaps with soil. Then the soil around the trunk is compacted and watered. The container with the plant is quarantined for 10 days in a shaded place. 
Watering. For irrigation use soft water, settled or melted. During the period of active growth, plants need to be watered frequently, and in winter watering is reduced.
You can water your bonsai using a special watering can or using the submersion method. In the modern world, drip irrigation or irrigation is widely used.
Feeding. They are carried out approximately once every two weeks, and different fertilizers are used for each type of tree or shrub. It is very important to avoid overfeeding. Therefore, a specific fertilizer application schedule is usually used.
Wintering
In winter, it is necessary to provide a period of rest for coniferous and deciduous trees. It is better to put them outside or in an unheated room.
In this case, the root system must be protected with additional means. When spring comes, the plants awaken, and the watering and fertilizing regime is restored.
Transfer
Transplantation is performed annually at the end of winter. When transplanting, the soil is removed from the roots, washed and trimmed. The pot must be larger than the previous one. When transplanting, the roots are placed horizontally, sprinkled with soil and watered. 
Crown formation. To ensure a beautiful tree crown formation, annual pruning is necessary. At the same time, it is useful in sanitary terms and rejuvenation. The crown is usually formed conical.
The first pruning is performed immediately after planting. And then every year after wintering they repeat. With the help of pruning, you can set the direction for bonsai growth and redistribute energy from strong shoots to weak ones.
Bonsai formation methods
Sometimes trees are artificially aged to make a young tree look older. One such method is to remove the bark from the trunk.
To correct the shape of the tree, you can use the air layering method. It is especially effective if the bonsai grows with a trunk that is too long.
For this method, in the spring, an incision is made on the tree trunk and the bark is removed. This place is soaked in growth stimulants and covered. 
In the fall, the incision is opened, roots should form there. Then part of the trunk is cut off below the roots. And planted as a separate plant.
Thus, you can grow a beautiful and spectacular bonsai tree at home. But this will require some effort.
Bonsai is a small, one might even say tiny tree, the fashion for growing which came to us from Japan. There, in the land of the rising sun, caring for miniature trees is considered an ancient tradition. Plants act as a kind of symbol of family happiness and prosperity, and therefore they solemnly pass from one generation to another. The trend of growing bonsai came to us relatively recently, but the main secrets and techniques of this art are already known. A small tree evokes a feeling of admiration; it attracts the eye with its unusualness, sophistication and miniature shape. It is noteworthy that this type of plant comes in different types. Each one is unique and beautiful, so it can become a decoration or a charming addition to any interior of a modern residential or office space.
Types of Bonsai Trees
A large number of bonsai trees are evergreen. Such plants create a warm environment of comfort and coziness around themselves. An evergreen tree will delight the eye all year round, regardless of the weather outside the window. The rich emerald shades of bonsai leaves will highlight the charm of the emerging spring and the lush green surroundings of summer. They can also easily create a harmonious palette with the yellow-crimson foliage of autumn and a bright contrast to the snowy white of winter. Just as the seasons change in nature, so do the types of tiny indoor trees. Some of them show themselves most impressively, dressing up the leaves in the colors of autumn, others impress with the delicate colors of spring blossoms.
There are types of bonsai, the beauty of which is fully revealed in the summer - rich shades of greenery soothe and seem to bring coziness into the house. Separately, it is worth noting the appearance of the trees, which differ from the rest in the bizarre shape of the branches and the trunk itself. The branches bending and intertwining in different directions seem to create a unique pattern, hiding a certain secret. Looking at such a bonsai, especially when the tree has shed its leaves, one imagines the violent flow of a river, the rolling sea waves, or ribbed clouds floating across the sky.
Basic shapes and styles of miniature trees
If you have fallen under the spell of miniature trees that you can grow right at home, you should pay attention to the main possible shapes and styles of this charming plant. Distribution into such categories occurred in natural conditions. Therefore, bonsai models repeat their form of growth in nature.
Syakan. Shakan is one of the most popular styles, characterized by the presence of an inclined trunk. The woody composition may have a thick or not very thick trunk inclined to the side, decorated on both sides with spreading mini-crowns. Experienced collectors like to expose the plant's roots, creating the illusion that the tree has been slightly uprooted from the ground by a ferocious hurricane. The Shakan style is suitable for growing almost all types of trees (linden, pine, maple, thuja and others).
Sozhu. The simplest, and therefore easiest to grow and shape, is the Sozhu style. To create it, just a few bonsai trees planted in one small space are enough. Different shapes and sizes of plants are harmoniously combined into a Sozhu style that is quite attractive for visual perception.
Tekkan. A tree in the Tekkan style practically does not need to be formed - it simply grows and delights others with its presence. Its main feature is the absence of features. This tree stretches upward, creating simple and clear outline lines. This form is the basis of many classic bonsai growing styles.
Bancon. Probably the Bancon style can rightfully be called the most bizarre and intricate. It is expressed in the presence of a tight knot at the base of the tree. If you choose these styles of bonsai formation, you should know that ginkgo or ficus are most suitable here. Moreover, it is necessary to form a trunk when the plant is still very young, and the trunk itself is quite flexible. View photo gallery
Bundzings. Bunjing is a style that is quite complex in terms of its level of formation. There are revolutions of the barrel, frequent bends and an inclination of the general line. Bonsai species such as pine or cedar are best suited for growing this style. An important condition for formation is the old base of the trunk and the young upper part. The lower part is freed from branches, while the upper part remains densely branched.
Moyogi. Moyogi is another name for the irregular upright style. Its main difference from the Tekkan is that the barrel can be bent in any direction at any location. Typically, such trees are grown with several bends formed at the bottom of the trunk. In this case, a prerequisite is the roots, which are visible above the surface of the earth. In this style you can grow oak and maple, pine and juniper.
Hokidachi. The broom-shaped Hokidachi is a large crown on a smooth trunk. For this style, recommended species are cypress, maple, zelkova, and elm. Oak, willow or birch, on the contrary, are absolutely not suitable. The branches and crowns of the tree should diverge in different directions, resembling the shape of a broom or a voluminous fan mounted on a handle.
Fukinagashi. The literal translation of the name of this style is a trunk in the wind. From this interpretation of the name, the shape of the plant immediately becomes clear. This style is formed in a simple, but not entirely easy way - here it is necessary that both the branches and the trunk are directed in the same direction. The ideal choice for Fukinagashi would be birch or pine.
When choosing bonsai as an indoor plant, you should know that some species require special care, need to control the level of moisture, temperature and special formation. When growing, it is necessary, depending on the type of bonsai tree and its future style, to carry out timely pruning, trimming, pinching new shoots and tops, and removing dry branches. If you follow simple rules, you can easily achieve the desired result and admire the miniature tree, the shape of which you created yourself.
The art of bonsai translated into Russian means “tree in a pot”. This art arose in 200 BC. e. in China, or rather, it originally sounded like “pan-san”. Several centuries later, the Japanese, together with Buddhism, mastered this art, brought it to perfection, and now it is considered traditionally Japanese.
The first images of bonsai, literally - hatitue, are found on scrolls of the late Kamakura period (1249-1382). The love for dwarf trees is explained simply - without a large territory and the opportunity to grow a garden near the house, the Japanese wanted to find a corner of nature at home, and small trees did not take up much space. At first it was a mass hobby, mainly among ordinary people. Much later, after the victory over China in 1885, bonsai became a subject of fashion, scientific study and collecting. Various bonsai schools and growing styles began to appear.
About 400 plant species are suitable and bred for creating bonsai. A real bonsai has dimensions from 20 cm to 1.5-2 m. A special direction is the creation of miniature landscapes, where not just one tree is grown in a bowl, but a whole piece of nature, with a lake, stones, miniature mountains and even waterfalls. The art of bonsai does not tolerate fuss; it requires patient care. Caring for bonsai is a kind of ritual and meditation. Trees have been grown for decades and centuries. In the imperial garden in Japan there are bonsai specimens that are about 300-400 years old.
Recently, bonsai-style compositions have become very fashionable. Bonsai is a miniature copy of a small part of nature. Trees with mossy roots, stones, moss - all this in a reduced form. Of course, we adapt the ancient Chinese and Japanese culture of growing dwarf trees to suit our climate and taste.
Rice. 40. Composition in bonsai style.
Russian amateurs have brought many innovations to classical compositions, but this is not about matching our compositions with the original ones, but about creating our style, which is closer to us and more consistent with our climatic conditions and cultural traditions. We have been practicing the art of bonsai, in comparison with its thousand-year history in China and then in Japan, for only about 20 years. A huge selection of indoor plants provides unlimited possibilities for growing miniature compositions.
Reference: Bonsai (from the initial "pan-san" or "pan-ching") originated in China around 200 BC. e. – 400 AD e. It is absolutely rightly considered a cultural phenomenon of Japan, since it was there, in Japan, that the art of bonsai grew, developed, experienced its formation, and has since spread widely throughout the world.
In Japanese, the word "bonsai" refers to the entire process of raising a particular species or group of plants on a tray or in a shallow pot. Obviously, if a tree can be grown on a tray, then there must be a method for cultivating miniature specimens of one species or another. Bonsai in its classic form can be imagined as a tree or any plant viewed through a miniature lens. The main elements of a bonsai are plants, soil and a pot. All this together creates a beautiful living composition that pleases the eye of its creator for a long time. So, the goal is not only to grow a healthy plant in a container, but also to create a whole from these three elements that are absolutely suitable for each other, while each of them should have its own personality and attract attention. For beginners, we can advise you to collect landscapes and make sketches, observe natural landscapes.
Bonsai has all the signs of its prototype in nature: it has a trunk, bark, branches, leaves, flowers, fruits, it also grows in the soil, exposing protruding roots, in general, it repeats the model of a living tree of a certain type of natural size. The soil should look like a natural part of the terrain. For this purpose, the selected stones - “rocks” and moss will evoke an association with the forest natural landscape. The container should be chosen more simply, that is, the color and shape should not be flashy, then it becomes a natural component of this three-dimensional design. If you follow these recommendations, the resulting bonsai will be able to create the mood that we have when we look at a wonderful landscape, grove, etc.
Bonsai culture provides some initial decisions, agricultural techniques and methods that need to be considered before moving on to the main and detailed description. Some bonsai grow and develop from seeds, others start from cuttings and layering. First of all, you should choose a specific type of plant. You need to start with the types of plants that grow in a given area. In regions with a cool climate, these can be coniferous plants, flowering and fruiting species.
Modern compositions include not only miniature trees. These are vines, ferns, and other indoor plants that are included in the composition. Many indoor plants have all the signs of original bonsai - small leaves, small trunks. The ferns seem to have been created to create an imitation of the Carboniferous landscape. Remember - plants with small foliage and graceful small flowers in a miniature bonsai look much more impressive than plants with large leaves and flowers.
Rice. 41. Composition imitating bonsai.
But let’s return to the original, “real” bonsai. There are different styles in which bonsai can be grown. Such knowledge is needed when choosing. Lovers of stately conical forms will look for a sapling whose growth pattern follows the correct upright style. Others look for irregular tree structure, which can later create the appearance of overhanging a cliff.
For beginners, it is necessary to understand the purpose of some accessories - a container, tools for decorating bonsai, tools necessary for care.
So, the first question is where to start growing bonsai. There are several methods available, and each of them has its own advantages and disadvantages. The most difficult, and at the same time, extremely satisfying way over time, is to sow a seed and watch how a seedling grows from it, then a young tree, which, with your help, turns into an elegant bonsai of a certain shape.
The second method is to grow bonsai from cuttings and layering, including air layering. This method is especially good for climbing plants - shrubs and some types of trees. You need to choose a branch in which the future bonsai can already be seen. Air layering can be done at your discretion to grow the roots of the bonsai, but the branch should be cut after the roots are well developed. Then the tree is transplanted into a container. In this model, the plant can be cultivated for several years. The difficulties lie, first of all, in finding a suitable branch, and shallow roots extending along the ground develop very slowly during natural growth.
Rice. 42. Choosing a bonsai branch and separating the cuttings.
The third method used in bonsai is the use of grafting. Its advantage is the use of a short shoot as a scion. This method is especially suitable for flowering and fruit trees. Its disadvantage is that the grafting site remains visible. However, this defect can be hidden by shaping the crown or using grafted plants in a bonsai style where it is not noticeable.
Rice. 43. Grafted tree.
The fourth method, which is definitely best suited for beginners, is to select and purchase from a nursery a suitable tree that already has a fairly thick trunk and a certain number of branches. They make it possible to give the final shape to a bonsai that has already lived in a container for several years and, therefore, has adapted to life in a limited space. After careful cutting and wrapping with wire, in just an hour the outlines of the future bonsai will appear in this plant, then another two years will be spent on bringing it to a mature state.
Fifth method. You drive out of town and look for small trees that have withstood all the storms. If you find such a tree, dig it up, shape it, and replant it, then it will be a good basis for bonsai. Perhaps the roots of the tree will not be sufficiently developed. In this case, it is helpful to replant it in the ground for a year or more to allow the plant to develop as many surface roots as possible while continuing to work on its shape. After this, the tree should be dug up and placed in a container as a bonsai.
When choosing a tree for bonsai, you must keep in mind that the size of the leaves (or needles for conifers) should initially be small, and the flowers should also not be large, since large flowers on a small tree look disproportionate.
Juniper (Juniperus prostrata) is a coniferous shrub that is very suitable for bonsai. It is hardy, easily takes shape in accordance with the chosen style, although it develops slowly. The hardy Roxburgh pine (Pinus roxburqhii) has very long needles and is only suitable as a bonsai grown in the garden, where it reaches a height of two meters. However, this resilient species can also be grown in miniature form if the needles are trimmed to the appropriate size. Cedar, spruce, fir - all these conifers are perfect for bonsai. Some types of cypress (Cupressus) and yew (Taxus) are also suitable.
Hardwood. First of all, trees of the genus Ficus (Ficus) of the mulberry family. They are stable, take a given shape well and grow so quickly that within a few years they turn into very interesting bonsai.
Ficus greenish quickly branches and forms thick, large roots protruding above the soil surface.
Ficus bengal also very quickly gives ground roots, and soon forms into an adult columnar tree, occupying an impressive area. At the same time, the leaves decrease over time, and in the future from this species you can get a small tree of a given shape that is correct, from a bonsai point of view.
Rice. 44. Ficus for bonsai.
A small tree that grows easily and freely in a container is the persimmon from the ebony family. Already in the process of growth, it is very easy to give a wonderful umbrella shape.
Ginkgo biloba, from the Ginkgo family, is one of the oldest tree species on earth. Its modern form grows on fossils dating back 175–200 million years. Fossilized imprints of the leaves of this tree have also been found in India. In Japan, this plant is called "girl's hair" because it resembles a fern and is often used in bonsai. The tree looks especially beautiful in the fall, when the leaves turn bright yellow before falling.
Camphor cinnamon, camphor laurel (Cinnamomum camphora) of the laurel family, as well as oak (Quercus) lend themselves well to cultivation.
Among deciduous trees, we note several types of maple, birch, alder and hornbeam, which are suitable for bonsai. You can try growing a plane tree, or weeping willow, in a bonsai.
Flowering and fruit trees. All trees are classified as flowering or fruit-bearing trees. The exception is a small group belonging to the family of tree ferns, the spore ferns. You should know that flowers and fruits in bonsai, if all methods are followed correctly, do not decrease in size, so it is recommended to select trees that produce small flowers and fruits so that they look proportional to the miniature tree. Some varieties of peach, plum and apricot look good if they bloom before the leaves develop.
It is also good to grow Japanese pear and almonds. Still, preference is given to the apple tree. The forest apple tree is especially good in white and pink colors or with an abundance of small red apples. Many varieties of cherries are quite suitable for our climate. Hawthorn is also suitable - a small tree covered with bunches of tiny fragrant white flowers.
The mulberry family appears to have two main types of trees. Mulberry, both wild and cultivated, is an extremely resilient species and adapts well to development in limited space. With careful pruning, a beautiful rounded crown shape with graceful branches is achieved. Small leaves are proportional to bonsai scales. The edible fruits of cultivated species of this tree are very appetizing and taste sweeter to bonsai owners than any other. The only drawback is that the leaves are difficult to reduce in size.
Dwarf guava is very suitable for bonsai. It attracts beautiful white flowers and small purple-red fruits, which is why this type of guava is sometimes called strawberry.
Some types of acacias belonging to the mimosa family are also suitable for growing bonsai. This is, first of all, the fragrant Farnesi acacia. The small leaves of this plant form a kind of graceful plumage (even not during the flowering period) of small golden spherical flowers. It grows in abundance on city streets, where it is used to create hedges.
Shrubs. Malpighia ranks first among shrubs that can be used by a bonsai lover. This stable, unpretentious plant branches heavily, leaving room for the imagination to find form. The small leaves are dark green and glossy. The shrub produces many delicate pink flowers throughout the summer. The plant is so strewn with graceful flowers that it seems as if the trunk, branches, and leaves are only visible through them. The completeness of the picture is completed by powerful roots spread across the ground. This plant requires constant pruning to maintain its desired shape.
A small shrub called Chinese lime, myrtle, also belongs to the Rutaceae family, has beautiful dark green trifoliate leaves. It blooms small white fragrant flowers, which turn red as they ripen and give the bonsai a unique charm.
A representative of the Rutaceae family is Muraya, or Chinese myrtle. It is a beautiful shrub with dark green foliage and fragrant inflorescences that appear during the rainy season. The leaves can be easily reduced with regular trimming.
Cotoneaster is adapted to even cooler climates and can produce red or yellow berries depending on the species.
There are many beautiful shrubs that are hardy in cool climates, such as the many species and varieties of azaleas that are very popular with bonsai enthusiasts in Japan.
Camellia belongs to the tea family. Some of its species and varieties are characterized by small flowers and look great in bonsai culture.
Gardenia prefers warm climates combined with cool winters. Its dwarf species, G.fortunei, with small leaves and flowers, makes an excellent bonsai base.
Also suitable for miniatures is hibiscus, or Chinese rose, from the mallow family, although its leaves are somewhat large for the size of a bonsai.
Brunfelsia, a shrub popularly called “Yesterday, Today, Tomorrow,” is an excellent subject for bonsai. The flowers, which appear several times a year, are of a deep purple hue on the first day, turn pale on the second day, and completely lose color on the third, turning white and justifying their name with these metamorphoses. Changing colors is very beautiful in bonsai.
The dwarf form of the common pomegranate, family Pomegranate, blooms and bears fruit without requiring any additional care. The flowers are bright red, small, proportional to a miniature tree. A small flowering and fruiting pomegranate tree always evokes a feeling of admiration. The twice-blooming variety of pomegranate tree is excellent for bonsai cultivation.
Euphorbia prickly is a member of the Euphorbia family, a well-known plant covered in small red flowers. It is difficult to work with because of the countless prickly thorns.
Arabic jasmine, sambac. This fairly large shrub is extremely popular due to its small white and orange flowers that bloom at night and fall off in the morning. The leaves are hard and quite coarse, but they are reduced and made more pliable by regular pruning.
Lianas. When cultivating vines in bonsai, you should know two rules:
1. Due to the large number of beautiful roots, it is better not to try to transplant into a container for the first time.
2. Shaping with wire should be done at a time when the shoots are not woody and can be easily bent.
Compact varieties are easier to keep in a small space than spreading varieties. Some double-flowered species are particularly impressive due to their abundant blooms and small flower size.
Climbing herbaceous plants can also look spectacular as bonsai, such as Japanese honeysuckle. Bonsai made from this type of plant in the “cascade” style or in the “tree hanging over a rock” style are especially impressive.
Wisteria is grown for its spectacular drooping clusters of flowers that are lilac, purple or white. The plant belongs to the subfamily of the legume family.
Bamboo can also be used in bonsai culture. First, small, tender roots are planted in a container, and then thick roots with new shoots, selected as the basis for a future grove. Next, they are watered and left in the container, allowing new stems to grow.
Cyperus umbellata, sedge family, is convenient because in a small container it does not grow to large sizes and, therefore, will look attractive, like many flowering annual plants.
Nandina domestica, a member of the barberry family, is attractive with its dark red leaves. Many succulents, particularly crassulas and milkweeds, can be a good choice for an arrangement.
As companions to the main bonsai plant, the composition usually includes herbaceous plants, mosses, and lichens in order to emphasize the advantages of the main plant.
Calamus is a dwarf plant with green and white longitudinal stripes on its leaves and looks great in a small container. The same can be said about a number of dwarf plants with small bulbs that grow well in small containers, for example muscari, mouse glacinth, zephyranthes species, and some species of oxalis.
BONSAI STYLES
Let's name the following main styles:
· “bonsai in miniature”;
· “bungin”;
· “wind-bent tree” (based on the previous style, but there are some differences);
· “broom-shaped” tree;
· a group of trees, or “grove”;
· cascade;
· compositions on the rocks;
· multi-stemmed tree;
leaning tree
· irregularly erect;
· half-cascade;
· correct erect.
In eastern countries there are many more of them, but those listed here form the basis of all other styles and their substyles. However, you should not strictly adhere to the strictest rules in relation to them, since we use species that grow in our country, and they, naturally, may differ from the species of the plant world of the East. Modern miniature arrangements come in a wide variety of styles and plants. We can highlight:
· pond and fountain in miniature;
· Latin American landscape;
· Carboniferous landscape using ferns and mosses.
And also completely fantasy compositions, for example, a cactus entwined with ivy or dracaena, on which there is a blooming fuchsia, and below, around the trunk - lichens, sedums or saxifrages. We are talking only about the design style, the landscape in miniature.
Still, you should know the main principles contained in the rules - they were developed in Japan so that everyone could be guided by them in the process of growing a miniature natural-looking tree. And success can be achieved faster by adhering to a certain style. This is much more effective than trying to guess at random how a particular tree can grow in natural conditions. By following the suggested recommendations, you will avoid many mistakes.
Correct upright style. Basic bonsai style. The tree is characterized by a straight trunk that tapers upward, thick diverging roots, and branches slightly inclined downward. The top of the tree is almost always conical or spherical in shape.
Rice. 45. Correct upright style.
The main thing is the shape of the trunk. It is divided into three parts. The lower part is without branches and foliage, so that the trunk, roots and bark structure are visible. Three main branches extend from the next third of the trunk. They are located in a three-dimensional projection, two branches to the sides, and the third deep into the composition, enhancing the impression of perspective. This branch is the main one, and it should be beautiful in shape and decorated with leaves. Two side branches complete the picture. They can be slightly turned towards the viewer, but should not obscure the main one. The third, apical, part of the trunk forms the crown. Usually the branches are raised up, and the foliage on them is developed and dense. This style of wood looks best in an oval or rectangular container.
Several important conclusions follow from the above description:
1. It should be taken into account that the front and back parts of the tree should be easily distinguishable. The foreground of the bonsai looks most impressive and creates the immediate perception of it as a naturally growing tree. The viewer can easily determine the front, most spectacular plan of the bonsai by the following features: two-thirds of the trunk are freely visible, the second or third branches are directed away from the viewer and give the bonsai spatial depth.
2. The visual age and, therefore, the “impressive” appearance of a tree is determined by overgrown roots located on the surface and going into the ground. The roots give the impression that the tree has been growing for many years and is firmly in the ground.
3. The large lower branches of many old trees bend downward, while the small ones at the top point upward. Such an arrangement in bonsai culture imitates the natural appearance of the tree and creates a visual sense of its “age”. In addition, the absence of branches in the lowest part of the trunk, their clearly visible branching in the middle part also gives the bonsai a feeling of “age”, distinguishing a miniature from a shrub or young tree.
The correct upright style is suitable for conifers and trees with a spherical crown.
Incorrect upright style. The main difference between this style is that the tree trunk must be curved. For better visual perception, the crown should be slightly turned towards the viewer. Branches, roots and leaves are arranged in the same way as in upright style compositions.
Rice. 46. Incorrect upright style.
Tilted tree style. In this case, the tree is leaning or bent in one direction and the lower branch is pointing in the opposite direction. All branches are bent towards the inclination of the trunk, the top is slightly tilted forward. The tree grows in the middle of the container so that the crown and branches do not extend beyond the container.
Rice. 47. Tilted tree.
Wind-bent tree style. The name itself speaks for itself. This type of bonsai is a tree that is bent under a strong wind that has a certain direction. The side from which the wind is supposedly blowing may have no branches at all, or this branch goes around the trunk and is directed in the same direction as the others.
Rice. 48. Tree bent by the wind.
“Semi-cascade” and “cascade” styles. The “semi-cascade” style is also called “tree on a rock”. The trunk first grows straight up, and then sharply bends to the side. In the cascade style, the trunk falls to the side while hanging below the level of the container. To do this, place the container on the edge of a table or stand. The three main branches should be visible from the back of the cascade.
Rice. 49. Cascade.
Rice. 50. Half cascade.
The composition will be more stable if the container is tall. The small branch at the top usually points away from the main body of the tree. This visually balances the composition and gives the tree a more natural look. You can also point down not the trunk, but one of the main branches.
Broom-shaped tree style. This is an upright style. There are no lower branches, and all branches are directed upward. Therefore, the tree resembles a panicle.
Rice. 51. Broom tree.
Bunzhin style (elite style). This style is quite difficult to evaluate and describe. Its peculiarity is the bend of the trunk. This is the main line of the composition, and how refined and aesthetic this line is, determines the success of the composition. This style reflects the artistic traditions of Japan. Ancient images of trees whose trunk is curved and contains few leaves. But those leaves that are visible, have clear and refined outlines, allow you to appreciate the beauty of an individual leaf.
Multi-trunk tree style. A tree can have two or more trunks, but they must grow from one point. This is usually an odd number. There are a lot of options for such a composition; the visual impression can be based on the interlacing of trunks, or the creation of a multifaceted composition. The crown can be common or separate, the trees can be the same or different in height. You can achieve interesting combinations of side branches.
Group of trees. This style includes from two or three trees to a whole “grove”. If a small number of trees are grown, they can be located close to each other. It could be an entire landscape. In such a composition, the use of additional elements is mandatory - it is they who will determine the color of the landscape and there are so many options that we will devote a separate chapter to describe them.
Rice. 52. Group of trees.
Compositions on the rocks. There are great opportunities here. The main thing is stones stacked in the form of a natural rock. You can place the plants so that the focus is on the plants themselves against the background of the rock, but other things are possible. The roots of the plant, which entangle the rocks, can themselves be decorative and interesting. In the first case, the stones and the plants themselves, which have a well-designed trunk, branches and crown, should be visible; in the second case, the lower half of the plant should be transparent, with a minimum number of branches, to allow the viewer to see the roots and stones. The crown may be smaller, but then there should be a few interesting leaves. Both of these types of compositions on rocks should be as naturalistic as possible, that is, close to natural landscapes.
Rice. 53. Trees on the rocks.
Bonsai in miniature. These are very tiny trees; the height of a mini-bonsai should not be more than 25 cm. The smaller the tree, the older it is, and the more it resembles an adult plant, the more valuable the plant. Miniature is achieved by planting in very tight containers. Growing such a plant is a long and painstaking task. There are specimens 50–70 years old. Design styles are the same as for the bonsai described above. Growth and thickening of the trunk occurs very slowly due to the small amount of soil in the tiny containers. The main thing is proper watering - a small amount of soil in a container dries out very quickly, and the plant may die.
So, we can conclude that the most important element of bonsai is the trunk of the plant. After all, every time you bend it, you can break it, and all subsequent forms of bonsai absolutely depend on the shape of the trunk. To easily develop a bonsai in accordance with the chosen style, the process of determining the shape should begin with a young trunk.