What color is the neutral wire. Wire color coding
Electric cables produced during the USSR period had predominantly black or white insulation, which created difficulties and inconvenience during electrical work, because. it was not always possible to identify the purpose of a particular wire quickly. Now on the shelves there are cables of various colors. This diversity has a very specific purpose. The color marking of wires of each type (zero, minus, plus, ground and various phases) is primarily designed to make electrical work safer, and finding and connecting contacts easier and faster.
In order to avoid discrepancies in colors, depending on which manufacturer manufactured this product, it is strictly standardized in the PUE (electrical installation rules) and state standards. Until 2009, GOST R 50462-92 was used, in GOST R 50462-2009, which replaced it, changes were made regarding the colors of wires in three-phase networks, the color of plus, minus and zero in DC networks, brown is recommended as the main shade for the phase in a single-phase network, the use of a combination of yellow and green for grounding is approved.
There are different types of cables:
- black
- Brown
- red
- orange
- yellow
- Green
- blue
- purple
- gray
- White
- Pink
- Turquoise
The cable is marked with the desired color at the ends (in other words, in the connection area), as well as along the entire length in the form of solid colored insulation or individual marks.
Coloring of cables of different types
Three-phase networks
In a three-phase network of transformer substations with alternating current, according to GOST 1992, phase A has a yellow wire, B is a green wire, C is red. According to the new GOST, it is preferable to use brown for phase A, black for phase B and gray for phase C. In ordinary household cables, white is used for phase A, black for phase B, and red for C.
The ground wire is usually colored in the form of yellow-green stripes in the longitudinal or transverse direction. Moreover, each color cannot occupy less than 30% and more than 70% of the surface. More rarely, the marking of the ground cable can be only yellow or only green. If such a cable is laid in an open way, then it is permissible to use black, as it improves corrosion protection. Also, the black color was used in the designation of the ground wire everywhere until changes were made to the regulatory documentation in 2009.
Zero has blue or blue wire insulation. 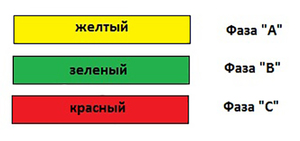
Single-phase networks
In this type of AC network, the phase insulation is most often brown, gray or black, but red, purple, pink, white and turquoise can also be used. In this case, in a single-phase network fed by a single-phase power source, wires with brown insulation are usually used. If a single-phase core is performed as a branch of a three-phase electrical circuit, then it is marked with the color that marked the phase of the three-phase circuit.
Ground wires, similar to the previous case, are marked with a combination of yellow and green.
PEN conductors, in which a protective zero and a working zero are connected along the entire length, are colored blue, and have yellow-green markings at the ends. At the same time, GOST also allows another option - yellow-green lines along the entire length of the wire and blue marks at the ends. 
DC networks
If the system with a DC network was put into operation before 2009, then the zero should be light blue, the plus should be red, the negative pole should be dark blue. According to the new GOST, brown should be used for plus, gray for minus, and blue for zero.
Labeling rules
Marking is carried out at the ends of the wires, i.e. at the points of their connection to each other or to various equipment.
It is allowed to combine the colors allowed for marking, but avoid confusion if possible. So, yellow and green can only be used in combination with each other and only for grounding, and not, for example, plus / minus.
If the wires in the system are initially labeled incorrectly or not labeled at all, then this can be corrected:
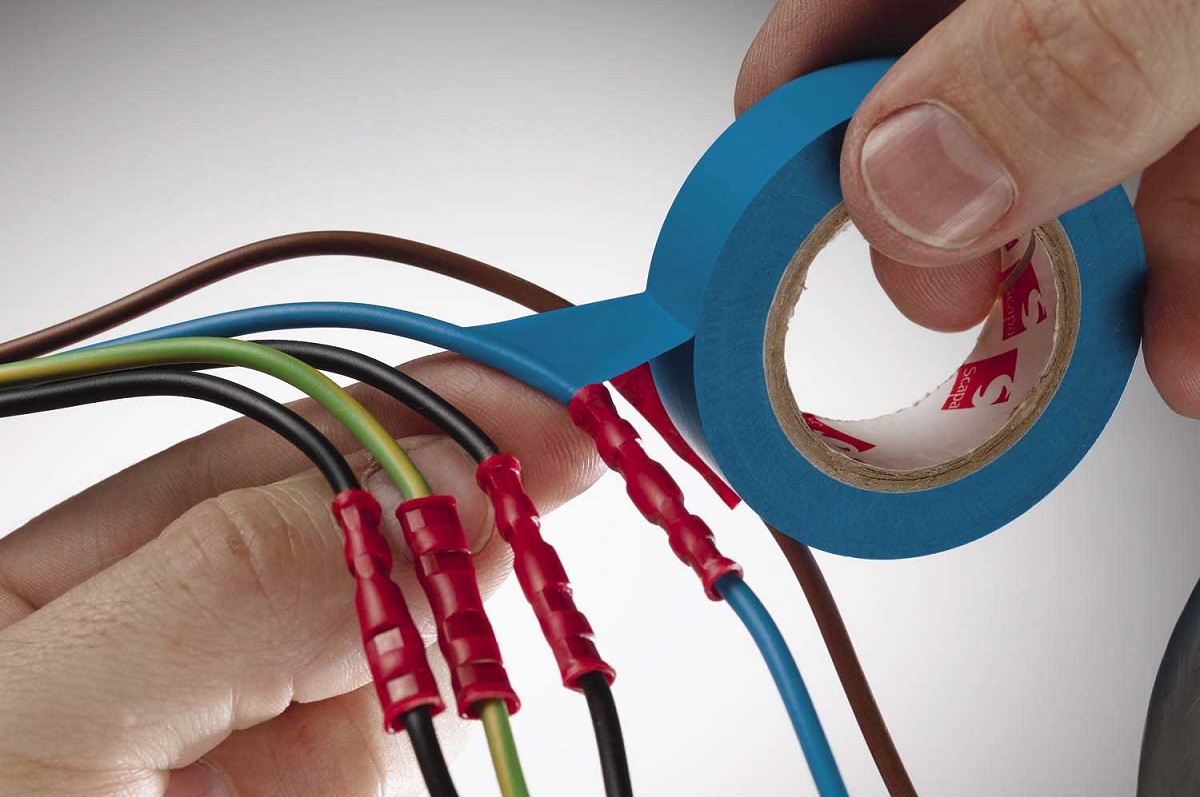
- By applying letter, symbol or color marking with indelible markers (convenient if the wire is white or at least light)
- A sticker of polyurethane labels with inscriptions
- Using heat shrink tubing or electrical tape of the desired color
Naturally, you must first determine which wire is a plus, which is a minus, etc. the purpose of each wire (in a household electrical network, this can be done using an indicator screwdriver or a multimeter).
It is not always possible to create a color circuit diagram in a paper version. Then, in black and white copies, letters are used to uniquely identify the color of each type of wire. Their complete list is given in GOST R 50462-2009. For marking cables that include several wires of different types in letter designations, different colors are separated by a plus sign.
Conclusion
Color coding of wires, depending on the purpose of each of them, allows you to make electrical work more convenient, reduces the likelihood of errors and emergencies. Therefore, it is necessary to comply with it even for an individual power supply system of an apartment or house, not to mention larger industrial, commercial, public and other facilities.
Those who have dealt with electrical wires at least once in their lives could not help but pay attention to the fact that cables always have a different color of insulation. It was not invented for beauty and bright colors. It is thanks to the color scheme in the clothes of the wire that it is easier to recognize the phases, grounding and neutral wire. All of them have their own color, which many times makes it convenient and safe to work with electrical wiring. The most important thing for the master is to know which wire should be indicated by which color.
Wire color coding
When working with electrical wiring, the wires to which the phase is connected are the most dangerous. Contact with the phase can be fatal, so the brightest warning colors, such as red, are chosen for these electrical wires.
In addition, if the wires are marked with different colors, then when repairing a particular part, you can quickly determine which of the wire bundle needs to be checked first and which of them are the most dangerous.
Most often, the following colors are used for phase wires:
- Red;
- Black;
- Brown;
- orange;
- Lilac,
- Pink;
- purple;
- White;
- Grey.
It is in these colors that the phase wires can be painted. You can deal with them easier if you exclude the neutral wire and ground. For convenience, it is customary to designate the image of a phase wire in the diagram with the Latin letter L. If there is not one phase, but several, a numerical designation should be added to the letter, which looks like this: L1, L2 and L3, for three-phase networks in 380 V. In some versions, the first phase (mass) can be indicated by the letter A, the second - B, and already the third - C.
What color is the ground wire?
In accordance with modern standards, the ground conductor should be yellow-green. In appearance, it looks like yellow insulation, on which there are two longitudinal bright green stripes. But sometimes there is also a color of transverse green-yellow stripes.
Sometimes, the cable may only have bright green or yellow conductors. In this case, the "earth" will be indicated in this color. It will also be displayed in the corresponding colors on the diagrams. Most often, engineers draw from bright green, but sometimes you can see yellow conductors. They designate “earth” on diagrams or devices in Latin (in English) letters PE. Accordingly, the contacts where the "ground" wire must be connected are also marked.
Sometimes experts call the ground wire "zero and protective", but do not confuse. If you see such a designation, then know that this is exactly the earth wire, and it is called protective because it reduces the risk of electric shock.
Zero or neutral wire has the following marking color:
- Blue;
- Blue;
- Blue with white stripe.
No colors are used in electrics to mark the neutral wire. So you will find it in any, whether it is three-core, five-core, and maybe with even more conductors. Blue and its shades are usually used to draw "zero" on various schemes. Professionals call it a working zero, because (which cannot be said about grounding), it is involved in electrical wiring with power. Some, when reading the diagram, call it a minus, while everyone considers the phase a “plus”.
How to check wire connection by color
Wire colors in electricity are designed to speed up the identification of conductors. However, relying only on the color is dangerous, because some novice, or an irresponsible worker from ZhZK, could connect them incorrectly. In this regard, before starting work, it is necessary to make sure that they are labeled or connected correctly.
In order to check the wires for polarity, we take an indicator screwdriver or a multimeter. It is worth noting that it is much easier to work with a screwdriver: when you touch the phase, the LED built into the housing lights up.
If the cable is two-core, then there are practically no problems - you have excluded the phase, which means the second conductor that remains is zero. However, three-core wires are also common. Here, to determine, you will need a tester, or a multimeter. With their help, it is also not difficult to determine which wires are phase (positive) and which are zero.
This is done as follows:
- The switch is set on the device in such a way as to select a jackal of more than 220 V.
- Then you need to pick up two probes, and holding them by the plastic handles, very carefully touch the stem of one of the probes to the found wire-phase, and lean the second to the supposed zero.
- After that, 220 V, or the voltage that is actually in the network, should be displayed on the screen. Today it may be lower.
If the display shows 220 V or something in this limit, then the other wire is zero, and the remaining one is presumably ground. If the value that appears on the display is less, it is worth continuing the test. With one probe we again touch the phase, with the other to the intended ground. If the readings of the device are lower than in the case of the first measurement, then you have a "ground". By standards, it should be green or yellow. If suddenly the readings turned out to be higher, this means that they messed up somewhere, and you have a “zero” wire in front of you. The way out of this situation is either to look for exactly where the wires were connected incorrectly, or to leave everything as it is, remembering that the wires are mixed up.
Wire designations in electrical diagrams: connection features
Starting any electrical work on lines where the network has already been laid, you must make sure that the wires are connected correctly. This is done with the help of special testing devices.
It must be remembered that when checking the phase-zero connection, the readings of the indicator multimeter will always be higher than in the case of continuity of the phase-to-ground pair.
Wires in electrical circuits are color-coded according to standards. This fact allows an electrician to find zero, ground and phase in a short period of time. If these wires are connected incorrectly to each other, a short circuit will occur. Sometimes such an oversight leads to the fact that a person receives an electric shock. Therefore, it is impossible to neglect the rules (PUE) of connection, and you need to know that the special color marking of wires is designed to ensure safety when working with electrical wiring. In addition, this systematization significantly reduces the work time of an electrician, as he has the ability to quickly find the contacts he needs.
Features of working with electrical wires of different colors:
- If you need to install a new one, or replace an old outlet, then it is not necessary to determine the phase. It doesn't matter to the plug which side you plug it in.
- In the case when you connect a switch from a chandelier, you need to know that it needs to be supplied with a specific phase, and only zero to the bulbs.
- If the color of the contacts and the phase and zero are exactly the same, then the value of the conductors is determined using an indicator screwdriver, where the handle is made of transparent plastic with a diode inside.
- Before you determine the conductor, the electrical circuit in the house or other room must be de-energized, and the wiring at the ends should be cleaned and spread apart. If this is not done, then they may accidentally touch and a short circuit will result.
The use of color coding in electrical engineering has made life much easier for people. In addition, thanks to color coding, safety has risen to a high level when working with live wires.
Designations and colors of wires in electrics (video)
Those who work with electrical wiring, whether they are qualified craftsmen or novice electricians, should be careful during the installation of the electrical wire and know which wire is designated as. When laying wiring and connecting contacts, always connect the conductors according to the color coding according to the new rules, and for your own safety and respect for those who will work with them in the future, do not confuse them. Remember that your oversight can lead to negative disastrous consequences.
Today it is difficult to imagine electrical wiring without the use of colored insulation. And these are not marketing "chips" of manufacturers seeking to present their goods in paints, and unfashionable innovations that consumers strive for. In fact, this is a simple and practical necessity, which is determined by strict state standards for compliance with the correct marking. What is it for.
Wire colors in electrical connections
Color marking
The whole variety of colors and certain colors selected from this palette are reduced to one (single) standard (PUE). Thus, wire strands are identified by color or by letter and number designations. The adoption of a single standard for the color identification of electrical wires greatly facilitated the work associated with their switching. Each core has a specific purpose and is indicated by the corresponding tone (blue, yellow, green, gray, etc.).
Color marking of wires is done along their entire length. Additionally, identification is carried out at the connection points and at the ends of the cores. To do this, use colored electrical tape or heat-shrink tubes (cambric) of the corresponding tones.
Let's look at how wiring is done and the color marking of wires for three-phase, single-phase and DC networks.
Color marking of wires and buses of alternating three-phase current
 The coloring of tires and high-voltage bushings of transformers in three-phase networks is done as follows:
The coloring of tires and high-voltage bushings of transformers in three-phase networks is done as follows:
- tires with phase "A" are painted with a yellow palette;
- tires with phase "B" - green tone;
- tires with phase "C" - in red.
Color marking of wires. Wire colors in electrical (DC busbars)
In the national economy, DC circuits are often used. They find their application in certain areas:
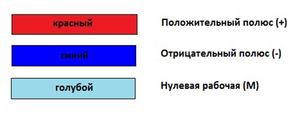
In DC networks there is no phase and zero contact. For such networks, only two contacts of different polarities are used - plus and minus. To distinguish them, respectively, two colors are used. A positive charge turns red and a negative charge turns blue. Blue color indicates the middle contact, which is marked with the letter "M".
 The "old-timers" of wiring are probably familiar with the old methods of wiring and color coding of electrical wires. The main colors of the electric cable were white and black. But that time is long gone. Each color now, and there are clearly not two of them, has its own purpose and dominant profile.
The "old-timers" of wiring are probably familiar with the old methods of wiring and color coding of electrical wires. The main colors of the electric cable were white and black. But that time is long gone. Each color now, and there are clearly not two of them, has its own purpose and dominant profile.
Contact colors in electrics indicate the purpose and belonging of the conductors to a certain group, which facilitates their switching. The possibility of an error during the installation process, which can lead to a short circuit during a test connection or an electric shock during a repair, is greatly reduced.
Color marking of wires. The color palette of the protective zero and working contact
The zero working contact is indicated by a blue tone and the letter N. The PE marking denotes a zero protective contact, which is painted in yellow-green stripes. The combination of such tones is used when marking pinching conductors.
 A blue conductor along its entire length with yellow-green stripes at the junctions indicates a combined zero working and zero protective connection (PEN). However, GOST also allows the reciprocal opposite of this color:
A blue conductor along its entire length with yellow-green stripes at the junctions indicates a combined zero working and zero protective connection (PEN). However, GOST also allows the reciprocal opposite of this color:
- Working zero contact denoted by the letter N and has a blue color.
- Protective null(PE) with yellow-green color.
- Combined(PEN) is identified by a yellow-green color and a blue mark at the ends.
Single-phase electrical circuit. Coloring of phase wires
According to PUE standards, phase contacts are usually indicated in black, red, purple, white, orange or turquoise.
Single-phase electrical circuits are created by branching a three-phase electrical network. In this case, the color of the phase contact of a single-phase circuit must match the color of the phase wire of a three-phase connection. In this case, the color marking of the phase contacts should not match the N - PE - PEN coloring. On unmarked cables, colored marks are placed at the junction. To designate them, use colored electrical tape or heat shrink tubing (cambric).
What color is the ground wire. Wire marking by color (phase - zero - earth)
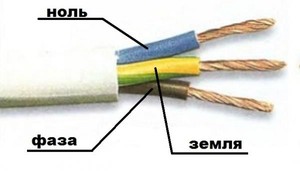 When installing lighting networks and power supply to sockets, a cable with three wires (three-core cable) is used. Using a standard color system (color of phase-zero-earth wires) significantly reduces repair time. Stranded wiring in standard multi-colored insulation greatly simplifies the laying of electrical circuits and installation work on AC wiring with its grounding. This is especially true when wiring and repairing an electrical system, which is done by different masters, but under the general guidance of GOST. Otherwise, each master would have to once again double-check the work of his predecessor.
When installing lighting networks and power supply to sockets, a cable with three wires (three-core cable) is used. Using a standard color system (color of phase-zero-earth wires) significantly reduces repair time. Stranded wiring in standard multi-colored insulation greatly simplifies the laying of electrical circuits and installation work on AC wiring with its grounding. This is especially true when wiring and repairing an electrical system, which is done by different masters, but under the general guidance of GOST. Otherwise, each master would have to once again double-check the work of his predecessor.
"Earth" is usually indicated in yellow-green and marked PE. Sometimes there is a green-yellow color and marking "P E N". In this case, there is a blue braid at the ends of the electrical wire at the attachment points and grounding is combined with neutral.
The switchboard is connected to the ground bus and to the metal door of the switchboard. The junction box is usually connected to grounded wires of fixtures or grounding pins of sockets.
Color marking of wires. Designation of zero and neutral
 "Zero" is indicated in blue. In the switchboard, it is connected to the zero bus and is indicated by the letter N. All blue wires are also connected to the bus. It is connected to the output using a meter or directly, without installing an automatic device.
"Zero" is indicated in blue. In the switchboard, it is connected to the zero bus and is indicated by the letter N. All blue wires are also connected to the bus. It is connected to the output using a meter or directly, without installing an automatic device.
The wires of the distribution box (with the exception of the wire from the switch) are indicated by a blue neutral palette. When connected, they do not take part in the switching process. "Neutral" blue wires are connected to sockets and contact N, which is indicated on the reverse side of the socket.
Color marking of wires. Phase color code
 The phase wire is usually marked in red or black. Although its coloring may not be so unambiguous. It can also be brown, but never blue, green or yellow. In automatic shields, the "phase" coming from the load of the consumer is joined to the lower contact of the meter. The switching of the phase wire is carried out in switches. In this case, the contact is closed during shutdown and voltage is supplied to the consumers. The black wire of the phase socket is connected to the contact, which is denoted by the letter L.
The phase wire is usually marked in red or black. Although its coloring may not be so unambiguous. It can also be brown, but never blue, green or yellow. In automatic shields, the "phase" coming from the load of the consumer is joined to the lower contact of the meter. The switching of the phase wire is carried out in switches. In this case, the contact is closed during shutdown and voltage is supplied to the consumers. The black wire of the phase socket is connected to the contact, which is denoted by the letter L.
Alphanumeric designation of wires by color

Knowing the elementary color markings of wires and their purpose will help any amateur electrician in installing home wiring (with grounding). If you wish, you can easily make it according to the required standards in compliance with all technical standards.




