How much luminous flux do incandescent lamps have. Luminous flux of LED lamps
My friend, CEO Badmaev A.E., is also fond of LEDs, and for more than two years he has completely switched the lighting of his apartment to LED lamps, replacing them with old or burned-out energy-saving or incandescent lamps. Here a person sits and cannot but rejoice looking at the readings of his electric meter, because the bills for the consumed electricity have dropped significantly. Maybe it's time for all of us?
I personally bought my first LED lamp in 2009. It was a lamp with a GU 5.3 base for spotlights, with a power of 1.2 W, cold white light and then it cost 120 rubles. Since the brightness of this lamp is not very high, I had to install it in the bathroom as an emergency in addition to the halogen. For seven years, nothing happened to her, though I changed the halogen only once. Consider for yourself ... This article was written for those who call me from the store, but I am very busy and I have no time to explain the whole thing.
Characteristics of LED lamps
For right choice LED lamps you should know by what criteria they are subdivided, and as I will tell you now, it is enough to get confused.
The device of LED lamps
The LED lamp, like all others, consists of a base and a bulb. IN basement hidden printed circuit board drivers for powering the board on which the LEDs are soldered, covered with a protective and decorative plastic transparent or matte bulb. There is truth and open lamps like "corn" they are suitable for general lighting.
Here is a cool video of disassembling an LED lamp where you can clearly see the internal structure:
Dimmable LED lamps
Dimmable LED bulbs are also available. Those. lamps with the ability to change their power luminous flux using a dimmer. It is best to use a conventional dimmer for incandescent lamps for such lamps.
Everything seems to be fine, but the cost of dimmable lamps is very high and not everyone will pay for this function, and the cost of the dimmer itself should be taken into account.
Disadvantages of LED lamps
 There are LED lamps of all sizes and shapes on the market today. They are able to replace the lamps familiar to us in absolutely all lamps.
There are LED lamps of all sizes and shapes on the market today. They are able to replace the lamps familiar to us in absolutely all lamps.
Lamps of all possible socles are offered, as well as for cars, for lighting plants (phytolamps), etc.
The main problem with most LED lamps is reliability issues.
With a claimed service life of 30,000 and even 50,000 hours (we are talking about the service life of the LEDs, and not the lamp itself), in fact, the service life may be limited to a couple of days, given the cost, this is bad. The short lamp life is due to the efforts of unscrupulous manufacturers to reduce the cost of producing their products. They use cheap LEDs, the most simplified driver circuits, an unsuitable element base, and do not attach serious importance to cooling. In sum, this gives the effect that we have. You should buy products from well-known manufacturers on the market who monitor the quality of their products, although not all of them are ready to avoid the above problems.
After buying LED lamps, do not throw away the sales receipt and packaging from the lamps for warranty period this will allow you to replace a burned-out lamp. Serious manufacturers like Philips or Osram give a 3-year warranty.
Repair of LED lamps
In principle, a non-working LED lamp can be successfully repaired. A common problem with LED lamps is poor-quality drivers due to poor components that swell and even burst capacitors, one or more LEDs burn out, or they overheat due to poor cooling. Since all the LEDs are connected in series, the failure of one interrupts the operation of the entire chain. Here the task is to find and replace problematic diodes with similar ones, and electrolytic capacitors for a voltage of at least 400 V.
Of course, for the repair and alteration of LED lamps, special knowledge, skills and materials are required.
Conclusion.
The transition to LED lamps is now certainly relevant and already cost-effective. And if you also have normal hands, then you can safely take the cheapest lamps and, having slightly corrected them, rejoice like my mustachioed friend Anatoly Evgenievich. Balance price-quality - the choice is yours.
As soon as I managed to replace all the light bulbs in the house with energy-saving ones, even more economical LED ones immediately appeared. Well, I really wanted to put these at home. In fact, what attracts me in them is not so much efficiency as durability. And then the promises about the long-term service of energy saving turned out to be a fiction. With my regularly flashing light (and I’m practically in the center of civilization, well, there are 20 kilometers to the Kremlin. It’s even scary to think about the quality of the power grid where the thread is in the distant wilderness!) Light bulbs can easily burn out a month after purchase. Well, where is the benefit in comparison with conventional incandescent bulbs?
For LED, the lifespan is declared much longer than for energy-saving ones. Of course, practice will show how much they promised us about energy savings, but I want to try. There, the design, when the luminous flux is formed not by one, but by several elements, gives hope for a greater survivability of the system as a whole. That is, if one LED dies, then the light bulb does not die, but simply shines weaker. On the other hand, according to the experience of using energy-saving devices, in 90% of cases, the element base burned out in me (that is, the starter, electronic ballast, or whatever you call what is stuffed into the cartridge). The twisted luminescent tube itself is usually intact, there are no characteristic darkenings at the filament locations, the phosphor does not fall off, the sealing is not broken. But the starter in the cartridge is always very hot, up to yellowing and deformation of the plastic. It usually dies, I'm already used to reacting to the characteristic chemical smell of heated plastic - as I felt, it means it's time to change the light bulb, it will die soon.

In truth, this moment confuses me just as much in LED lamps. Judging by the presence of a well-marked ribbed radiator on most models, it has something to dissipate. This means that the base of the lamp should be warm enough, otherwise why such an expense of not cheap metal for a radiator? While this is just a theory, I still haven’t bought a single light bulb (to be honest, the price in our stores is jarring, and it’s impossible to order half the price from China), so I can be wrong. Well, in general, we'll see.
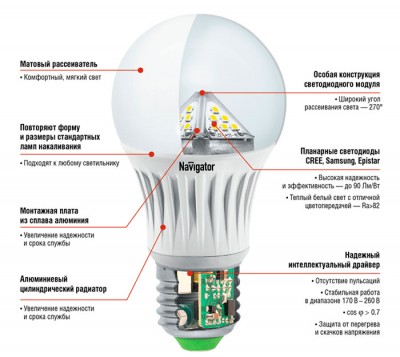 Device led light bulb. The picture is borrowed from the site www.navigator-light.ru, they release them.
Device led light bulb. The picture is borrowed from the site www.navigator-light.ru, they release them.
By the way, if you are embarrassed that the LED lamp will give directional light (like a flashlight), then you should not be afraid of this. Firstly, now most manufacturers have begun to make a "pyramid" of emitters (as in the picture above). So it shines already at least in the sector of 180 degrees. And secondly, if you really want all-round light, then they have already begun to make such light bulbs like a corn cob. I haven’t seen them in our stores yet (this doesn’t mean that they don’t exist, it means that I don’t go shopping for electrical goods a lot), but on http://ru.aliexpress.com/category/202001096/led-bulbs-tubes. html is full of them.

Well, now, actually, for the sake of which I started all this writing. When buying light bulbs, we are used to focusing on their power, that is, most people imagine how an ordinary 100W incandescent bulb shines and start from this feeling - will it be light enough for you personally if you buy a 75W light bulb, or do you still need 100? But with energy-saving ones, this method does not work - the power is completely different, a 26W bulb will shine brighter than a 100W incandescent bulb. Fortunately, physicists have foreseen everything a long time ago, having figured out how to measure the luminous flux :) And even introduced such a unit of measurement as lumen.
Designations of luminous flux in lumens appeared on lamps only very recently. Before that, they completely managed with watts, and even earlier, they just as calmly considered the luminous flux of light bulbs in candlelight. My grandmother. for example, sending me to the store, she instructed me to buy a light bulb in "60 candles". And I irritably objected to her that "watt" is correct :) In fact, it is correct - "so many lumens". I think our kids will get used to it. And for you. not yet accustomed to the numbers on the packaging, here is a small plate. it is very approximate, for example, for a 100 watt incandescent bulb, the exact figures for the luminous flux in lumens are 1340. But in order to navigate the store, it will do.
|
incandescent lamp powerTue |
Fluorescent Lamp powerTue |
LED lamp powerTue
|
Light flow |
| 20 W | 5-7W | 2-3 W | About 250 lm |
| 40 W | 10-13 W | 4-5W | About 400 lm |
| 60 W | 15-16 W | 8-10 W | About 700 lm |
| 75 W | 18-20 W | 10-12 W | About 950 lm |
| 100 W | 25-30W | 12-15W | About 1300 lm |
| 150 W | 40-50W | 18-20 W | About 1800 lm |
| 200 W | 60-80W | 25-30W | About 2500 lm |
How many lumens are in a 20 watt bulb? How many lumens are in a 40 watt bulb? How many lumens are in a 100 watt bulb? How many lumens are in a light bulb?
The most familiar lighting device for us is an ordinary incandescent light bulb. It is a source of illumination, consisting of a glass bulb, an incandescent body, electrodes, a base and an insulator.
They are simple, reliable, and can be purchased at a very low price. Despite the popularity of incandescent lamps, they have several disadvantages. The efficiency of such a device is about 2%, low light output within 20 Lm / W and a short, about 1000 hours, service life.
When connected to electrical network incandescent lamp converts electrical energy into the light, by heating the conductor (filament) of the filament. Made of refractory tungsten or its alloys, the filament is in a glass bulb filled with an inert gas or vacuum (for low-power lamps up to 25 W).
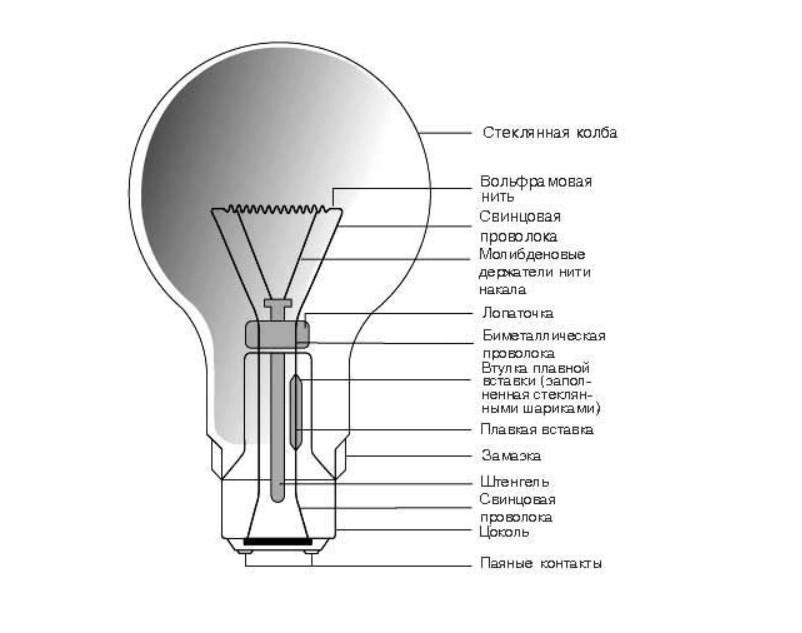 The device of the light bulb "Ilyich"
The device of the light bulb "Ilyich" The flask serves to protect against exposure external factors, and an inert gas (krypton, nitrogen, xenon, argon and their mixtures) does not allow the tungsten conductor to oxidize and reduces heat loss. The thread heats up under the action of the current passing through it to a temperature of the order of 3000ºС (such heat over time leads to thinning and burnout of the conductor).
As a result of heating, electromagnetic radiation occurs, a small fraction of which is in the visible spectrum, the main part is infrared radiation. Luminous flux occurs when the very high temperature of a filament converts electromagnetic radiation into visible light.
The energy consumed by the lamp is partially converted into radiation visible to the eye. The main part under the action of convection inside the flask is dissipated in the process of heat conduction.
The light that occurs in incandescent lamps is in the yellow and red spectrum of rays, therefore it is close to daylight.
Light flow
direct appointment of any light fixture- lighting. In an incandescent lamp, it is created by converting thermal energy into light flux.
 Luxmeter - a device for measuring light output and pulsation of a light bulb
Luxmeter - a device for measuring light output and pulsation of a light bulb Definition and measurement rules
Luminous flux - a value that characterizes the light power (light energy that is transferred through a certain surface per unit time by radiation) of visible radiation in the flux of this radiation, that is, according to the light sensation produced by the human eye.
The sensitivity of this sensation can be determined from the spectral efficiency curve, which is approved by the CIE. The unit of measure for luminous flux in the International System of Units is the lumen (lm or lm), which is calculated by the formula:
1 lm \u003d 1 cd * sr (1 lx × m2), Where:
- cd - candela;
- solid angle, 1 steradian.
The energy in a beam of light has a temporal and spatial distribution. Sources that emit a luminous flux are distinguished by the distribution of spectrum colors:
- line spectrum (separate lines);
- striped spectrum (nearby delimited lines);
- continuous spectrum.
The spectral density of a light beam is characterized by the distribution of the radiant flux over the spectrum. Measured in W/nm.
Ratio with the power of the element
The increase in luminous flux directly depends on the power of the lamp. The graph (see figure below) shows a clear dependence of the increase in brightness in proportion to the increase in power.
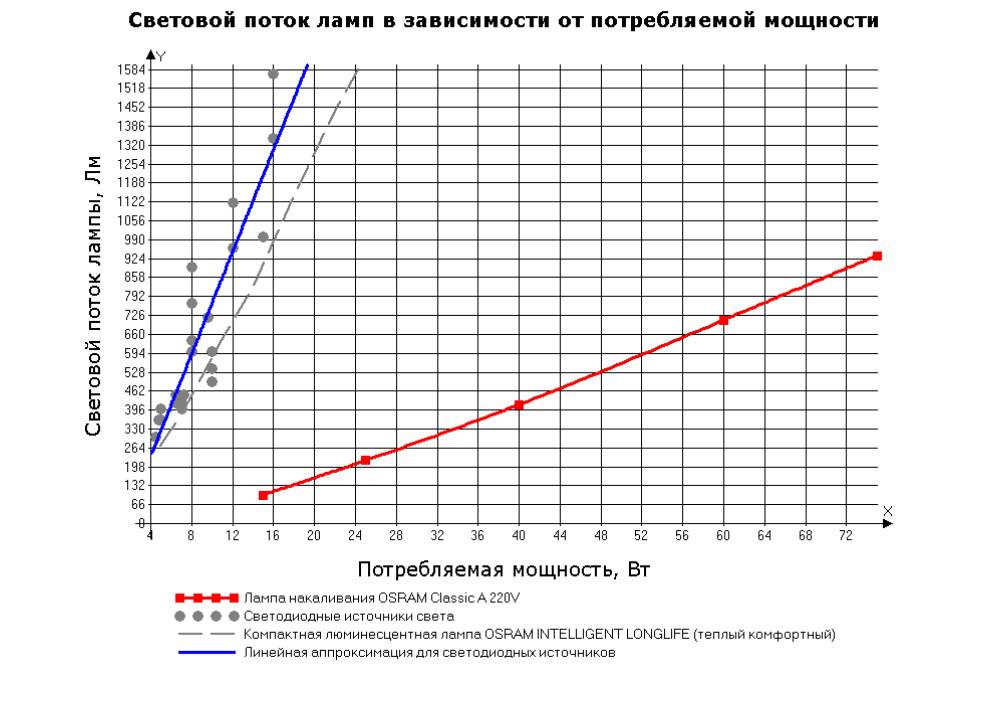 Graph of the dependence of the luminous flux of lamps of various types on power consumption
Graph of the dependence of the luminous flux of lamps of various types on power consumption | Incandescent lamp, W | Luminous flux (lm) | Lamp voltage, V |
|---|---|---|
| 40 | 610 | 12 |
| 40 | 570 | 36 |
| 40 | 340 | 230 |
| 40 | 400 | 240 |
| 60 | 955 | 36 |
| 60 | 735 | 225 |
| 60 | 645 | 230 |
| 60 | 711 | 235 |
| 60 | 670 | 240 |
| 75 | 940 | 220 |
| 75 | 960 | 225 |
| 100 | 1581 | 36 |
| 100 | 1381 | 225 |
| 100 | 1201 | 230 |
| 100 | 1361 | 235 |
| 150 | 2151 | 230 |
| 150 | 2181 | 240 |
| 200 | 2951 | 225 |
| 200 | 3051 | 230 |
| 300 | 3361 | 225 |
| 300 | 4801 | 230 |
| 300 | 4851 | 235 |
| 500 | 8401 | 220 |
| 750 | 13100 | 220 |
| 1000 | 18700 | 220 |
Incandescent lamps of the same power can emit different luminous flux. The higher the voltage, the higher the value of the luminous flux.
Comparison with other types of lamps
Comparative analysis of the luminous flux of incandescent lamps with more advanced luminescent and allows you to evaluate its effectiveness.
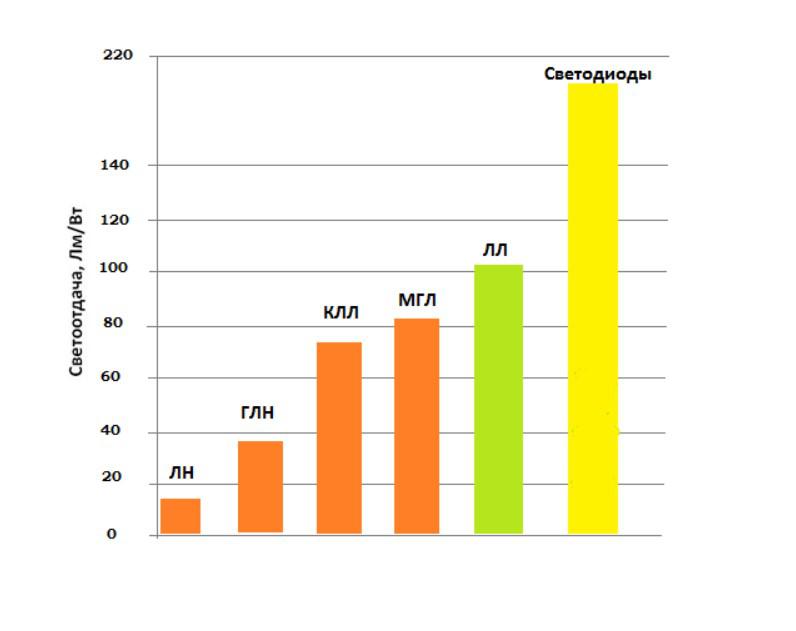 Light output level for various types lighting elements
Light output level for various types lighting elements Despite the advantages of incandescent bulbs, such as instant on, low cost, big choice shape and power, flicker-free, luminous flux efficiency in relation to power consumption is very low compared to new generation products. Abroad, the share of tungsten elements in the total flow is about 10%.
Light flow- power of light radiation, i.e. visible radiation, estimated by the light sensation that it produces on the human eye. Light output is measured in lumens.
For example, an incandescent lamp (100 W) emits a luminous flux equal to 1350 lm, and Fluorescent Lamp LB40 - 3200.
One lumen is equal to the luminous flux emitted by a point isotropic source, with a luminous intensity equal to one candela, into a solid angle, one steradian (1 lm = 1 cd sr).
The total luminous flux created by an isotropic source, with a luminous intensity of one candela, is equal to 4π lumens.
There is another definition: the unit of luminous flux is lumen(lm), equal to the flux emitted by a black body from an area of 0.5305 mm 2 at the solidification temperature of platinum (1773 ° C), or 1 candle 1 steradian.
The power of light- spatial density of the luminous flux, equal to the ratio of the luminous flux to the value of the solid angle in which the radiation is evenly distributed. The unit of light intensity is the candela.
illumination- surface density of the luminous flux incident on the surface, equal to the ratio of the luminous flux to the size of the illuminated surface, over which it is evenly distributed.
The unit of illumination is lux (lx), equal to the illumination created by a luminous flux of 1 lm, evenly distributed over an area of 1 m 2, i.e. equal to 1 lm / 1 m 2.
Brightness- the surface density of the luminous intensity in a given direction, equal to the ratio of the luminous intensity to the projection area of the luminous surface on a plane perpendicular to the same direction.
The unit of brightness is the candela per square meter(cd / m 2).
Luminosity (lightness)- surface density of the luminous flux emitted by the surface, equal to the ratio of the luminous flux to the area of the luminous surface.
The unit of luminosity is 1 lm/m 2 .
Units of light quantities in the international system of units SI (SI)
| Value name | Unit name | Expression via SI units (SI) |
Unit designation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Russian | between- folk |
|||
| The power of light | candela | cd | cd | cd |
| Light flow | lumen | cd sr | lm | lm |
| light energy | lumen second | cd sr s | lm s | lm s |
| illumination | luxury | cd sr / m 2 | OK | lx |
| Luminosity | lumens per square meter | cd sr / m 2 | lm m 2 | lm/m2 |
| Brightness | candela per square meter | cd/m2 | cd/m2 | cd/m2 |
| light exposure | lux second | cd sr s / m 2 | lx s | lx s |
| Radiation energy | joule | kg m 2 / s 2 | J | J |
| Radiation flux, radiation power | watt | kg m 2 / s 3 | Tue | W |
| Light equivalent of the radiation flux | lumens per watt | lm/W | lm/W | |
| Surface radiation flux density | watt per square meter | kg/s 3 | W/m2 | w/m2 |
| Energy power of light (radiant power) | watt per steradian | kg m2/(s 3 sr) | Tue/Wed | w/sr |
| Energy Brightness | watt per steradian square meter | kg/(s 3 sr) | W / (sr m 2) | W/(sr m 2) |
| Energy illumination (irradiance) | watt per square meter | kg/s 3 | W/m2 | w/m2 |
| Energy luminosity (radiance) | watt per square meter | kg/s 3 | W/m2 | w/m2 |
Examples:
ELECTRICAL MANUAL"
Under the general editorship. MPEI professors V.G. Gerasimova and others.
M.: MPEI Publishing House, 1998




