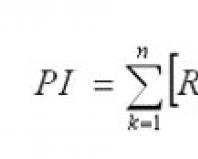What is a plug with multiple outlets called? List of plug connector standards. Standards of different countries
For connection electrical appliance With the power supply there must be a pair: a plug and a plug socket. Thus, switching is carried out with the network alternating current, and with a constant source. IN modern stores presented are household appliances designed for operation under current conditions from 6 to 10 amperes with a voltage rating of up to 250 volts. In order to install switching in a network with high current values, you need to purchase a special plug.
What is the plug made of?
The device must contain:
- contacts;
- inner insert;
- frame.
Contacts can be made of stainless steel or brass. Cases vary, but plastic examples are often seen. There are three contacts in the plug: one serves to ground the device, one provides connection to the phase, one is necessary for connection neutral wire. The design of the plug necessarily implies a special place for supplying the electrical cord. The fastening must be safe and durable. It guarantees the supply of current to the consumer device.
Variety of plugs
Modern plugs presented in hardware stores are devices that have changed significantly over the past decades. Back in the days Soviet Union they looked completely different. These days there are several manufacturing standards that influence appearance devices. Each country independently develops internal rules production and operation of plugs, which leads to numerous differences. However, they are mainly contained in the appearance, while the essence of the design remains the same.

The most common variations in internal structure forks:
- features of the case (the system can be collapsible or solid);
- presence of grounding (some plugs are designed without it).
When the plug is assembled, the ends of the wires are attached to the brass contacts. Then the connection is made to the contacts. The sequence does not matter, only the sequence is significant. correct connection grounding, if there is one in the system.
Plug and everything that comes with it
Inside the device contains wires, which are most often made of aluminum or copper. However, you can never be sure what a cheap Chinese plug is made of. Practice shows that such devices often catch fire, that is, unreliable, flammable materials were used in their manufacture. Therefore, it is better to purchase a proven model, albeit more expensive, but from a reliable manufacturer.

Among handymen and those who like to solder electronics at home, the plug is of particular interest table lamp, since the ability to handle it, replace it and repair it as needed will be useful on the farm. To figure this out, you should first understand what the lamp circuit is in general outline. In simple terms, this drawing should reflect all the elements included in a particular device. The diagram should show the actual position of the system components relative to each other, as well as the presence of electrical connections.
Types of devices
A regular plug is designed for use in a regular network, that is, at home. If the network differs in its performance, the unit must be selected that is suitable.
In some networks the voltage is low and does not exceed 42 volts. For such cases, special plugs have been developed, and there are several configurations, so you can choose the optimal one in specific case option. A special plug differs significantly from a household electric plug; it cannot even be plugged into a classic socket. And even if it were possible, such a plug would not work from a 220-volt network.

If you need to connect a portable electrical device that requires voltage up to 50 volts, you should use a plug that does not have a ground connection. This is stipulated by the rules of the PUE. According to old standards, the limitation applied to voltages up to 42 volts. However, plugs without grounding can also be used when working with conventional household network, but only if the premises are classified as safe.
Experts call grounding a “grounding knife.” Equipped with a plug (Euro) that may have a slightly protruding contact. The second design option is the inlet hole, where the “knife” of the socket will fit. Household appliance It happens:
- bipolar;
- three-pole.
Plug Features
Today everyone knows what this design is used for, but few people know what material the plug is made of or where the term “plug” comes from. It's all about the specific design of the device. The socket has holes that are recessed specifically to prevent the user from touching the pins of a plug that is not completely removed. This constructive solution regulated by the mandatory CEE 7/16 standard. This is where the name of the device comes from.

If the plug is designed to be grounded and there is a third pole, remember that this is to improve the safety of the enclosure.
How to install the plug?
The process of replacing the plug is simple, but requires compliance with safety precautions. The sequence of work is as follows:
- Use a knife to clean the ends of the wires, then solder them and make small rings;
- on the plug, on the contact legs, tighten the screws;
- attach wire rings to the contact blades with screws;
- remove the screw of one of the brackets, remove the bracket;
- insert the wires into the places intended for this purpose, turn them with a bracket, press the wire with the body and screw the screw into place;
- close the assembled fork with a nut.

Repairs to an electrical device must only be carried out when disconnected from the power source. Increasingly, modern plugs can be seen with wires soldered into the body. These cannot be repaired; if the device breaks down, it can only be replaced with a new one.
Plug connectors (from German Stöpsel - plug) are devices for detachable connection of electrical appliances to the electrical network. The plug connection consists of two parts: socket and plug
The socket is the part of the connector to which the Electric Energy from the source. The Russian name comes from a common decoration. To prevent contact with foreign objects The socket is designed as a female connector.
Plug- part of the connector for connecting the electricity consumer to the socket. The electrical contacts of a plug are usually in the form of pins, which give it some resemblance to a table fork, which is where the Russian name comes from. It can be connected to an electrical appliance with a flexible cable (cord), or be permanently attached to it.
Diffusion of standards
Widespread use of electricity in everyday life is impossible without the development of appropriate standards. Standardization of electrical installation products made it possible to make the use of electricity safer, devices more reliable, inexpensive and widespread. However, often the standards in different countries ah were developed independently of each other, which led to their great diversity and incompatibility with each other. Some standards were not widely used and disappeared. As a result of economic and political factors, some countries have changed their standards. Hotels and airports may have sockets of foreign standards for the convenience of travelers. In some countries, several connection standards, voltages and frequencies may be used simultaneously, which often leads to problems.
Standards of different countries
The two most common standards in the world are voltage and frequency. One of them - American standard 110‒127 Volt 60 Hertz, together with plugs A and B. Another standard is European, 220‒240 Volt 50 Hertz, plug types C - M.
Most countries have adopted one of these two standards, although transitional or unique standards are sometimes found.
Types currently in use
Electrical plugs and sockets vary from country to country in shape, size, maximum current rating, and other features. The type used in each country is fixed by law, by adoption national standards. In this table, each type is designated by a letter, according to the publication of the International Electrotechnical Commission.
In the pictures green the grounding contact is indicated, gray - phase, white - zero.
| Type | Standard | Denomination | Grounding | Orientation | Fuse | Pin base insulation | Appearance |
| A | NEMA 1-15 unpolarized | 15A / 125V | No | No | No | No | |
| NEMA 1-15 polarized | 15A / 125V | No | Eat | No | No | ||
| JIS C 8303, Class II | 15A/100V | No | No | No | No | ||
| B | 15A / 125V | Eat | Eat | No | No | ||
| JIS C 8303, Class I | 15 A / 100 V | Eat | Eat | No | No | ||
| 20A / 125V | Eat | Eat | No | No | |||
| C | CEE 7/16 (Euro plug) | 2.5A / 250V | No | No | No | Eat | |
| 16A / 250V | No | No¹ | No | No | |||
| Soviet plug (GOST 7396.1 Section C1) | 6A / 250V | No | No | No | No | ||
| D | 2A / 250V 5A / 250V = BS 4573 |
No | No | No | No | ||
| 2A / 250V 5A / 250V 15A / 250V = SABS 164 30A / 250V |
Eat | Eat | No | No | |||
| E | CEE 7/5 | 16A / 250V | Eat | Yes² | No | No³ | |
| F | CEE 7/4 (Schuko) | 16A / 250V | Eat | No | No | No³ | |
| E+F | CEE 7/7 | 16A / 250V | Eat | Partially² | No | No³ | |
| G | BS 1363, IS 401 & 411, MS 589, SS 145 | 13A / 230-240V | Eat | Eat | Eat | Eat | |
| H | SI 32 | 16A / 250V | Eat | Eat | No | In some modifications | |
| I | AS/NZS 3112 | 10A / 240V 20A / 240V 25A / 240V 32A / 240V |
Eat | Eat | No | Eat | |
| CPCS-CCC | 10A / 250V | Eat | Eat | No | No | ||
| IRAM 2073 | 10A / 250V | Eat | Eat | No | No | ||
| J | SEV 1011 | 10A / 250V 16A / 250V |
Eat | Eat | No | No | |
| K | Section 107-2-D1 | 13A / 250V | Eat | Eat | No | No | |
| Thailand TIS 166-2549 | 13A / 250V | Eat | Eat | No | No | ||
| L | CEI 23-16/VII | 10A / 250V 16A / 250V |
Eat | No | No | Eat | |
| N | 10A and 20A / 250V | No | No | No | Eat | ||
| 10A and 20A / 250V | Eat | Eat | No | Eat | |||
| ¹ There are specially shaped plugs that are mechanically polarized when used with an E-type receptacle (there is actually no polarization) | |||||||
| ² Plugs can only be inserted into an E-socket in one position, but insufficient wiring requirements mean that polarization is not observed in practice | |||||||
| ³ There is no need to insulate the base of the contact pins due to the recessed design of the socket | |||||||
The table shows only the most common types. In addition to them, there are many non-standard plugs and sockets. The reasons for their use are different: sometimes manufacturers developed their own connector designs, incompatible with other standards, which for some reason gained popularity for a certain time, but were never included in the standards. In houses of old construction, there are still sockets of outdated types, which have already been abandoned. Sometimes sockets were specially designed that were incompatible with popular ones in order to prevent the connection of devices to them. general purpose, or vice versa - plugs installed on devices that require a special electrical network. Examples when this may be needed:
- "clean" land for use in computer systems;
- emergency power supplies;
- sources uninterruptible power supply for critical systems or life support devices;
- isolated power supply medical instruments;
- “balanced” noise-resistant power supply for connecting studio equipment;
- theatrical lighting;
- low voltage supply in high-risk areas, kindergartens, schools, etc.
The connectors for connecting electric stoves stand out. An electric stove is usually one of the most powerful household electrical appliances, with standard household socket Only electric stoves can be connected low power(usually one- and two-burner without oven). Installing a powerful electric stove requires a special connector. And if in the USA a NEMA 14-50 connector has been developed for electric stoves, then in most other countries there are no standards for them. In these cases, industrial connectors or non-standard connectors can be used various manufacturers. Connectors for connecting electric stoves from different manufacturers are often incompatible with each other and are sold in socket-plug pairs.
As a rule, plugs are non-separable structures, where the pins and ends of the cord attached to them are fixed with PVC plastic or rubber. Most electrical appliances are equipped with these plugs. household use. Plugs with detachable housings can be found complete with non-household appliances or as a spare part to replace a failed non-separable plug.
Today the industry offers forks equipped with two or three pins. Collapsible two-pin forks come in four types: splitters, solid-pin forks, split-pin forks, and combined forks.
Forks with a collapsible body and split hollow pins can be equipped with two steel needles. Each of them comes out of the pin itself and has a plastic growth at the end - a “lamb”. Using this thumbwheel you can adjust the clearance between components pin. At the same time, it is possible to ensure close contact of the plug plugged into the socket, and removing such a plug from the socket becomes very difficult.
The plug, which consists of two detachable halves, is equipped with a special metal bracket, an insulating gasket and a pair of screws for fixing the cord at the base of the housing.

The plug body has certain insulating properties and is designed for a specific maximum permissible current that will pass through the socket. The magnitude of this current can be found out by the markings on the body of the plug, for example, 5 A, 6 A, 10 A. To determine the strength of the current that will flow from the socket to the plug of a particular electrical appliance, you need to use the following formula:
Current (A) = Power (W) / Voltage (V)
Let's say we have an electric iron with a power of 1000 W. We need to plug it into a network where the voltage is 220 V. The iron plug is designed for a current of 4.55 A.
Using plug-splitters, you can connect not one, but several devices to the network at once. As a rule, these are two or three devices. Such forks can be either with solid or carved pins.
Using a split-pin double plug, you can provide power to two appliances from one outlet. The double with solid pins also has the same capabilities: it does not have a pressing device in the sockets, and close contact is made by the split pins of the forks inserted into them.
There are split pins along the entire length of the tee plug socket that provide contact with any type of pin. Tee plugs with solid pins may have sockets that are covered with special curtains.
Small electrical appliances and radios are often combined with combined plugs. These include a rectifier for electric shavers, a power supply for an antenna amplifier, or an “Electronics” power supply.
Splitter plugs can be used in a chain if they are inserted one inside the other. At the same time, it is taken into account that the sum of the current strength that arises from the entire chain of switched on devices should not exceed the maximum mark of 6A.
Electrical engineering surrounds us everywhere. It is impossible to imagine without electrical appliances modern society. Therefore, it is quite understandable that each person in his own Everyday life interacts with devices in one way or another: opening the refrigerator, pressing the elevator call button, turning on the lighting in the room, etc.
The fine line of gradation
Conditionally everything that exists electrical equipment According to the method of interfacing with the electrical network, it can be divided into two categories:
Stationary, which is connected to a cable and Of course, if you have the tools, you can disconnect it, but only in emergency situations. An example would be equipment in production.
Relatively mobile, allowing you to disconnect without the use of specialized devices. This group includes almost all household electrical appliances. Their distinctive feature is the plug.
What is a plug
Everyone has encountered sockets and power plugs. However, few people understand where the term “plug” comes from. It's actually simple. The word "plug" - German origin. And it means nothing more than a traffic jam. Indeed, the plug, being in the socket, seems to clog the holes of the latter. Hence the term. Well, the additional word “fork” appeared due to its distant resemblance to the famous cutlery. Of course, the tasks of this device are completely different, although, it is worth recognizing, there are real plastic stoppers for sockets, protecting curious children from accidental electrical injury.
From theory to practice
If we talk in simple language about what a plug is, it is a device designed to provide the ability to make a safe detachable connection with a specially designed

Old-timers remember that something similar was previously used even in places where it is now impossible to even think about it. Thus, during the Soviet five-year plans, special lamp designs were used everywhere in lighting networks, which made it possible, through simple manipulation without tools, to disconnect the block with the socket and lamp, leaving it on the line... plug socket. True, its design was somewhat different from what is familiar to the eye. modern man decisions. Now, of course, they try to separate cable routes as much as possible, so lighting circuits, as a rule, do not allow the transmission of significant powers.
Plug device
There are several options for the design of this detachable connection element. So, there are special solutions designed for connecting fairly powerful electrical equipment to a three-phase network - they use four contacts (three for phases and a grounding one). However, in mass production, a simpler design is used - exactly the same as, for example, a plug

Externally, these are two metal (copper or chrome-plated) rods, placed parallel at a certain distance from each other and located in a housing made of dielectric material. Inside each of them there is a bolt or other clamp designed for connecting current-carrying conductors and grounding. Through such a system, electricity is supplied to the device via a cord (cable). The housing can be dismountable, in which case its parts are assembled together using a screw. There are also monolithic modifications. The thickness of the rods and the method of making the grounding contact are determined by standards. So, speaking about what a plug is, one cannot help but point out the widespread use in countries former USSR misconception that there are two types of power plugs (and sockets) - regular and euro.
Variety of modifications
The term “euro” is used in relation to the CEE 7/4 standard (Type F, or Shuko) - these are fairly large products that necessarily contain a grounding contact or rod in the design. The socket holes are deepened in such a way that when the plug is turned on, it is impossible to accidentally touch the half-extracted rods of the plug. using CEE 7/4 is designed for 16 A and 230 V. The name “euro” was given due to the fact that in Soviet times, devices from the GDR and Czechoslovakia were supplied with exactly such plugs.

In fact, the Euro fork does exist. This is a solution based on the CEE 7/16 standard. Those who have ever wondered what the structure of a table lamp plug is, know all the features of this type design. For others, let us explain: a Europlug consists of two rods with a thickness similar to Soviet (ordinary) plugs, located in a thin monolithic body made of dense rubber. There is no grounding contact. The shape is such that such a plug can be easily inserted into a socket of almost any design. Safety from accidental contact is achieved by insulating most of the rods, leaving only the outer parts, about 5 mm long, exposed. These Euro plugs are designed for connecting low-power equipment, such as table lamps. The permissible current is 2.5A, although there are modifications for 5A.
Maintainability
The design of the table lamp plug used in mass production does not allow for acceptable repairs in the event of damage. Although such monolithic plugs can be cut and the internal contacts restored by soldering, after such an operation it is impossible to ensure electrical safety while maintaining normal appearance. This applies to all monolithic solutions. In case of damage network cable cut as close to the plug as possible, strip it, identify the grounding conductor and connect it to a new collapsible plug.