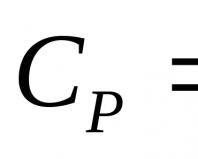Latex mattresses: main features and characteristics. What is latex? Artificial latex or natural for mattress
The term “artificial latex” refers to modern polyurethane foam with increased elasticity. Polyols are commonly used in the production of these materials.
Natural latex is a product obtained from the sap of various rubber plants, such as Hevea. Without impurities, this substance is of little use for commercial use. It's afraid sunlight, fat and easily destructible. Therefore, it is mixed with other components to improve performance. The rubber content in this mixture ranges from 45 to 85%. In the latter case, we are dealing with a material called natural latex (100%).
However, in the production of mattresses, mixtures containing more than 65% rubber are rarely used. This provides the necessary firmness and elasticity. Special additives give the material resistance to physical wear, which is why such mattresses last a very long time, but are also more expensive. More affordable models contain 20% natural rubber.
The use of natural latex in mattresses
This material can be used in mattresses different types. For example, in spring ones it is a filler. And in springless ones, a monolithic block is made from it. Also for springless mattress it can match with high elasticity latex, tough coconut coir.
 The big advantage of this material is its high strength, density and resistance to physical wear. But it also has one drawback. It does not allow air to pass through well. To get rid of this drawback, manufacturers make holes throughout the entire surface, which provide additional ventilation.
The big advantage of this material is its high strength, density and resistance to physical wear. But it also has one drawback. It does not allow air to pass through well. To get rid of this drawback, manufacturers make holes throughout the entire surface, which provide additional ventilation.
A lot is made from rubber various products, starting with chewing gum and ending balloons and bath mats.
The material is mainly obtained by processing the juice of the Brazilian Hevea. It is grown not only in Brazil, but also in Thailand, Cambodia, Vietnam, and other Asian countries, South America and Africa.
Hevea juice contains special substances that give products an antiseptic effect. The tree itself, from which sap can be extracted for decades, does not get sick from cuts. They heal quickly, and the plant does not suffer from diseases. Microbes are unable to survive in this environment. Saprophytic mites also do not take root on rubber products.
How latex furniture products are made
The technical process is quite simple and includes four stages, during which a finished product is obtained from natural raw materials.
- The latex mixture poured into a special vessel is mixed and then poured into a container for foaming.
- Then the mass is poured into molds and vulcanized. In this case, a temperature effect of 100C is used.
- After this, the blanks are removed from the molds.
- Now the product is cleaned, removing excess foam, dried at 120C, and the hardness level is checked. Then they are weighed and packaged.
One of the most best mattresses with natural latex - mattress "Multipackage Latex". In our store you can purchase it at the best price!
Latex m, Kautschukmilch f) is the general name for emulsions of dispersed polymer particles in an aqueous solution. In nature it occurs in the form of milk, which is secreted various plants, in particular, Brazilian Hevea, dandelion, etc. Products made from latex (game balls), mainly made from the milk of Castilla elastica, were widely used by the Aztecs.Latex— microheterogeneous natural (milky sap of rubber plants) or artificial systems, which represent aqueous dispersions colloidal rubber particles (globules) stabilized by surfactants and emulsifiers.
general characteristics
The shape and size of latex particles are closely related to the laws of the process of emulsion polymerization of the original monomers. Particles synthetic latexes often have a spherical or similar shape. Latex globules are stabilized by an ionic surfactant, often of the anionic type. Spontaneously, over time or as a result of special treatment (acid-base, hydrodynamic, temperature, etc.) secondary aggregates resembling bunches are formed in the latex dispersion. The primary globules in such “clusters” stuck together, but their coalescence did not take place. In most cases, latexes are not monodisperse and are characterized by varying degrees of polydispersity, which, in turn, depends on the conditions of the polymerization process. Typically, the diameter of primary latex globules is 10–200 nm. Isoprene, butadiene, styrene-butadiene, methylstyrene-butadiene, chloroprene, isobutylene-isoprene, carboxylate, acrylic, urethane and other latexes are widely used in various industries.
Obtaining latex products
A salt solution is applied to the mold, e.g. calcium chloride. The mold is then dipped into latex. The salt solution contains positively charged metal particles - cations. When a mold is introduced into latex, cations begin to diffuse from its surface into the depths of the latex. Encountering negatively charged latex particles on their way, positively charged cations discharge them. And the rubber particles settle as a thin rubber layer on the mold.
Latex based on natural rubber
Opium poppy exudes fresh latex from its cut

Commercial latex based on natural rubber (RN) is concentrated and stabilized milky juice of the Brazilian Hevea plant. The dry matter content in the original juice is 37-41%, in commercial LP its content increases to 58-75%. Methods of concentration: sedimentation and centrifugation; the latter method is the most effective and efficient.
Latex mixtures are prepared by introducing many ingredients into its composition: vulcanizing agents, accelerators and activators of vulcanization, antioxidants, powder fillers, surfactants, anti-stabilizing additives that help reduce the stability of the colloidal system, thickeners, plasticizers, defoamers or, conversely, foam stabilizers, etc. etc. When preparing mixtures, it is advisable to use freshly prepared dispersions and emulsions of ingredients. They should be stored in containers with continuous stirring, avoiding foaming. First, stabilizers are added to the latex, then the remaining ingredients and, lastly, before direct use, a zinc oxide dispersion. To mix latex with emulsions, dispersions, solutions, use enameled or rubberized containers with anti-corrosion coatings, equipped with jackets for cooling or heating and stirrers with variable frequency rotation within 30-40 rpm. The duration of preparation of the mixture is 30-60 minutes. In some cases, the mixture “ripens” for 6–24 hours at 20–60 °C with slow stirring. At the same time, the colloidal chemical characteristics of the mixture change (the pH level decreases, the viscosity increases, etc.), its homogeneity increases, the polymer in the mixture partially vulcanizes, and the technological properties of the mixture improve.
The bulk of LN is used to produce natural rubbers, about 8-10% is used to produce latex products: gloves, meteorological, radiosonde and pilot ball shells, medical products, rubber threads, sponge rubber, light rubber and sports shoes, latex adhesives for various purposes: for leather, rubber, metals, for the production of shoes, for gluing the spines of book bindings, gluing boxes, bags, gluing labels, in the manufacture of sheet plywood and others wooden products, for gluing parquet, linoleum, polymer tiles To various reasons gender; in the production of textile materials and carpets (for joining cotton, wool and linen threads without the formation of knots and thick folds), for the production of abrasive materials in combination with melamine-formaldehyde oligomers; for gluing expanded polystyrene, foam rubber, PVC materials, for gluing ceramics, glass, metals to paper, fabric, leather, polystyrene and other soft and hard materials. In addition, it is used in the production of latex mattresses, latex pillows, latex bolsters
Latexes based on synthetic rubbers
Latexes based on synthetic rubbers (SR) are colloidal aqueous dispersions of synthetic rubbers and other polymers (polystyrene, copolymers of styrene with 20-35% (by weight) butadiene), obtained in most cases by emulsion polymerization of one or more dienes, vinyl, vinylidene and others monomers. Some drugs are manufactured by dispersing in water in the presence of surfactants of “ready-made” polymers (butyl rubber, polyisoprene SKI-3, siloxane and other synthetic latexes). Drugs also include aqueous dispersions of thermoplastics (PVC, PVA) obtained by emulsion or suspension polymerization. Important Features for the consumer is the average size of the globules, pH of the medium and solids content: than larger size globule, the more content dry residue can be achieved by concentrating the drug; with small globule sizes, the stability of the drug is higher.
Prepared based on website materials - Wikipedia
Watch the video
The basis of a quality mattress is its internal filling. And one of the most popular mattress fillers is natural latex. This material is used as the main material in, and also as one of the layers in other types of mattresses. Sometimes latex is combined with coconut coir. Moreover, the ratio of these materials can be completely different: 50% to 50% (with this ratio, the layers can alternate or be divided in half); 20% to 80%; 70% to 30% and so on. Sometimes layer natural latex used as a top to soften the surface of a high-hardness mattress.
Benefits of natural latex
Natural latex is environmentally friendly and safe material. It has hypoallergenic properties, so it is recommended for allergy sufferers and asthmatics. This type of latex has a spongy structure, which allows the mattress to “breathe” and provides excellent ventilation, as well as rapid evaporation of moisture.
This type of latex has bactericidal properties, which prevents the ingress of dust and does not provide an environment for the growth of bacteria. It also does not smell and does not absorb odors.
The porous structure of a natural latex mattress allows you to retain heat in the cold and not heat up on hot summer days. It also does not absorb moisture, and therefore retains its performance properties well in rooms with high humidity.
Natural latex has good wear resistance: it will serve you for 10-15 years without loss of quality.
Thanks to excellent qualities elasticity, natural latex promotes uniform distribution of load on all areas of the body, which ensures correct work circulatory system during sleep. Your sleep on such a mattress will be more sound and relaxing.
What is natural latex made from?
Natural latex is a material belonging to the group of elastomers, which does not emit toxic and other harmful substances. This is a high-molecular compound that has the ability to undergo reversible deformations (due to the fact that the latex molecule has the shape of a twisted spiral).
Natural latex is produced from the milky sap of the rubber tree of the Brazilian rubber tree (Hevea brasiliensis). Milky, white sap is released when the bark of a tree is cut. In the process of collecting this raw material, the tree seems to cry. Interestingly, the word “rubber” itself is translated as “tears of a tree.”
Even representatives of ancient civilizations began to use the unique properties of milky juice. For example, the Mayan tribes dipped their feet in the sap collected from a tree, thus protecting their feet from contact with the ground, that is, they got a kind of prototype of rubber shoes. And the ancient Aztecs made rubber balls from collected raw materials and played with them.
Historically, this tree was native to the equatorial forests of South America. IN late XIX centuries, Hevea began to be resettled in other countries, but this plant did not take root everywhere. Today, this tree is cultivated quite successfully in tropical Asia: in Vietnam, on the island of Sri Lanka and the Malay Peninsula. But the main largest suppliers of latex are three countries: Thailand, Indonesia and Malaysia.
Natural latex production process
The basis of the raw material from which rubber (latex) is subsequently obtained is, as already mentioned, the milky juice of the Hevea plant. The final product, latex, consists of 34-37% rubber and 52-60% water. A small amount is also added to the resulting substance minerals, resins, sugar and proteins.
IN pure form natural latex can change its properties under the influence of temperatures. At high temperature it becomes sticky and plastic, at low temperature it becomes brittle or hard. At room temperature latex may undergo oxidation processes.
The work of collecting the milky juice itself is a rather lengthy and labor-intensive process. To do this, you need to make a diagonal cut in the tree bark and place containers where the sap will drain. Next, the resulting liquid undergoes a process of purification from impurities. Next, ammonia is added, which acts as a preservative. And for the latex coagulation process, an admixture of formic or acetic acid. Then the resulting raw materials are subjected to a smoking or drying process. At the final stage, rubber in the form of crumbs or sheets is packaged and sent for production.
One of them is called Dunlop - this classic way production of foam rubber, which at one time became revolutionary in the field of everyday life and hygiene. It was invented in 1929 by a company of the same name. This method of producing latex foam relies on the liquid latex itself being mixed with air (before the vulcanization process), which is then poured into a mold and heated. With this method, softness and breathability are achieved using perforations that are made on the molds for pouring. To make the foam softer and more breathable, special perforations are made in the pouring molds.
Some time later, this process was improved by the Englishman Joseph Talalay. He added a few more intermediate stages to the previous scheme. And in the 40s and 50s, his sons Leon and Anselm had already refined their father’s method: after the foamed latex solution was poured into the mold, the air was pumped out from there - this allowed the foam to evenly fill the entire cavity of the mold; This was followed by a process of rapid freezing, as a result of which the cell structure of the resulting substance partially burst; then submitted to the form carbon dioxide, it was heated before the latex vulcanization process; it was then cooled again, eventually the latex foam was washed, wrung out and dried.
The Talalay method involves a longer production process and, accordingly, it is more expensive. But this latex turns out to be softer and more breathable, its mesh structure is more uniform than the material made using the previous technology.
However, today natural latex is in kind rarely used. Today, its synthetic “colleague” is increasingly being added to it. The optimal combination of these types of latex allows you to create a material that combines the advantages of both types of raw materials.
Synthetic (artificial) latex: characteristic features
Synthetic latex (foam rubber, polyurethane foam, polyurethane foam) is similar to natural latex in its physical and chemical properties, however, differs in structure. It is used as a filler in other types (mattresses with independent spring blocks). In fact, it is highly elastic foam rubber, consisting of soft polyurethane foam (a polymer synthesized from isoprenes of other monomers (wash, butadiene, chlorprene, acrylic acid nitrile, isobutylene), which are also capable of undergoing the vulcanization process).
Benefits of artificial latex
Artificial latex has greater rigidity, and therefore is able to withstand more severe loads (suitable for fat people). Modern artificial latexes are environmentally friendly and safe for human use different ages. Its main “trump card” is its affordable price.
Like natural latex, artificial latex has hypoallergenic properties. In terms of orthopedic properties, modern foam rubbers also have excellent characteristics And the best The proof is in memory foam mattresses.
This type of mattress is classified as highly elastic polyurethane foam with cells open type. Even a small layer of this type of foam gives the mattress special comfort. And even more so, it is indispensable for people with sore joints and poor circulation. Abroad, memory foam mattresses are widely used in medical institutions: they greatly facilitate the life of patients with a wide variety of serious diseases: people with burns, those who have suffered a stroke, the paralyzed and others. Subtly responding to the weight and warmth of a person, such latex adapts to the contours of a person, which also helps to avoid complications of many diseases.
The only disadvantage of artificial latex is that it has a shorter service life. It tends to crumble or thin out after its service life (it can vary for different mattresses: from 5 to 15 years).
Production of artificial latex
Today, two methods are used for the production of artificial latex (polyurethane foam): box (batch) and conveyor (continuous).
In the first method, the components necessary for the production of foam rubber are mixed in a special box. This method of producing foam rubber is mainly used for small batches, as well as in cases where high demands are not placed on the quality of foam rubber, since from batch to batch its volume and other physical properties may differ from each other. Today, “box” devices are equipped with vacuum chambers, which help make foam rubber of less rigidity and low density.
The second - conveyor - method assumes that the chemical mixture is fed onto the conveyor belt continuously. At the same time, they can be fed into the foaming chamber at both low and low temperatures. high pressure. At the end of the conveyor, the resulting material is cut into blocks of the required size, which then undergo a curing process at a temperature of 60-90 degrees C for several hours. This method allows you to achieve a more uniform structure and quality of foam rubber.
What is artificial latex made from?
The main component for the manufacture of synthetic latex (foam rubber) is polyester foam or polyester foam. This polyurethane foam has good chemical, thermal-oxidative stability, and fire-resistant properties. This material is only afraid of exposure high humidity– under its influence the destructive process will accelerate.
Polyester foam has high elasticity and is not afraid of influence negative temperatures, as well as moisture. In most cases, this type of foam rubber is used in the production of upholstered furniture.
To make polyurethane foam, all its components are mixed with water. In some cases, for better foaming, a low-boiling liquid, freon (freon), is added. During the polymerization process, molecules that react with water begin to release carbon dioxide, which causes the mixture to foam. Also, special catalysts and emulsifiers are sometimes added to speed up these reactions to stabilize the foam. After the reaction, the curing process only takes about 10-20 minutes.
Brands of foam rubber with increased elasticity, used in expensive mattresses and upholstered furniture, are made on the basis of special polyesters and isocyanates. In this case, the density of the resulting product (15-45 kg/m3) will depend on the ratio of these components, as well as on the amount of foaming additive. Typically, foam is used to produce synthetic latex for mattresses. medium density from 25 to 35 kg/m3.
The air permeability and elasticity of foam depends on the number of open cells. The more there are, the softer the foam will be. For this purpose, the manufacturing process uses the vacuum or cyclic compression method. The same effect can be achieved by depressurizing the mold at a certain point in the curing process.
One of important criteria choosing a mattress - its filler. Today's article is about one of the best modern fillers - latex.
Today, there are two types of it: natural and artificial. Due to the difference in composition, they differ markedly from each other in price and properties.
Natural
Natural latex is a mattress filler made from the juice of the Hevea plant (this evergreen tree family Euphorbiaceae), in other words, rubber of natural origin. To produce such rubber, the juice of the Brazilian Hevea plant, which grows in the tropics, is mainly used.
Pure rubber, without impurities, is susceptible to destruction: it is afraid of ultraviolet radiation and fat. Therefore, an inhibitor (isoprene monomer) is added to it.
Production
The production of natural latex, which is widely used as a filler for mattresses and furniture, can be divided into several stages:
- From a continuous mixing container, the mixture of latex and inhibitor is sent to a special container for foaming.
- The resulting foam is poured into molds and vulcanized at 100°C.
- The resulting block is removed from the mold.
- It is cleaned of foam residues and dried at a temperature of 120°C, then tested for hardness, weighed and packaged.
Natural latex contains no more than 85% rubber. The mattress filler should contain from 45% to 65% rubber, only in this case it will be sufficiently elastic, resilient (due to rubber) and wear-resistant (due to additives).
Mattresses made from this material are considered one of the best due to their unique properties.
Increased elasticity due to the content of natural rubber:
- Thanks to this property, it provides excellent support to the body.
- Removes pressure points that cause unnecessary swaying and vibrations.
- The elastic properties of the filler provide excellent support and comfort.
- Mattresses can be used for beds with any base; they are even suitable for sleepers with adjustable lift.
Remarkable ergonomic and support qualities:
- The remarkable qualities of the filler enable it to gradually adapt to the sleeper’s body and follow his movements. This property allows you to provide comfortable and correct support to those parts of the body that need it: neck and head, lower and upper back, spine.
- To ensure maximum effective support, the latex structure is made with different additional zones comfort.
- Able to respond to even the lightest pressure, thanks to which it perfectly adapts to the anatomical features of the body and, most importantly, allows you to save correct position spine during a night's rest.

Good air exchange and humidity regulation:
- Thanks to the porous structure, it has excellent ventilation, which in turn prevents the accumulation of moisture in the mattress itself. Under the influence of the movements of the vacationer, a pulsation effect occurs, during which air is pumped and constantly circulates.
- It has excellent thermoregulation: in winter it retains heat well, and in summer it gives pleasant coolness.
Wear resistance:
- Thanks to laboratory research and scientific developments, scientists managed to achieve highest quality and strength. Latex filler is very wear-resistant and is not subject to deformation.
Hygienic and hypoallergenic:
- Not a development environment harmful bacteria and dust mites, this sets it apart from other similar fillers that have favorable soil for their habitat.
- Hypoallergenicity allows latex mattresses to be used even by people who have respiratory diseases.
Absolutely silent during use:
Quiet, so great for children and light sleepers.
Artificial

Artificial latex, or in other words, highly elastic polyurethane foam (for example, HR brand filler). This synthetic filler is made from the monomers of butadiene and styrene, both of which come from petroleum.
Compared to other brands of polyurethane foam, latex of artificial origin has increased elasticity. This material is one of the most successful attempts by manufacturers to create a synthetic analogue of natural fillers.
It has excellent restorative abilities and better wear resistance compared to other types of polyurethane foam. However, compared to natural, it has only one advantage - lower cost.
Latex is used:
- in mattresses with springs: here this highly elastic filler gives the mattress elasticity.
- as a monolithic block in mattresses without springs - high-quality ergonomic products with good elasticity are obtained.
Since cunning manufacturers often try to sell artificial latex under the guise of natural latex, every consumer should know how they differ.
How to distinguish natural latex from artificial?
Artificial Natural
Here are the basic tips, using which you can easily determine what type of filler:
- Latex filler, obtained from natural raw materials, does not absorb moisture, its surface is greasy to the touch, although it does not leave greasy marks. It is more plastic and soft, with a grayish tint.
- Artificial - very different from its counterpart. First of all, this is one of the types of foam rubber; it is capable of absorbing moisture well.
- Synthetic filler is usually yellowish-gray in color. It is tougher and if one day you are lucky enough to compare it with natural, you will always remember this difference.
- Over time, the artificial filler acquires a dirty yellow tint, becomes brittle and begins to break easily.
- And the most important difference is that natural latex filler has a strong specific smell. Particularly sensitive people may feel discomfort from its smell. Therefore, be prepared for the fact that you will have to wait about 3-4 days for it to disappear. Also, over time, it changes its shade under the influence of external factors: interaction with oxygen, temperature, time.
Mattresses

Latex mattresses are considered one of the best bedding products available today. They are able to adapt to the shape of the sleeper’s body, support the spine and evenly distribute the load. They withstand high pressure and restore shape well.
The thickness of natural latex mattresses varies from 5 to 15 cm. A fifteen-centimeter one can be placed on the bed or floor without using additional mattresses, but even with five centimeters you can feel the orthopedic effect of using the product, although for this it is better to place a latex mattress on a regular one. The sizes of models made from natural raw materials start from 100x100 cm - for cribs and up to the size of a double bed - 180x200 cm.
Watch the educational video:
So we have revealed all the production secrets, advantages and disadvantages of natural and artificial latex. We hope this information will help you buy a good quality mattress.
Send your good work in the knowledge base is simple. Use the form below
Students, graduate students, young scientists who use the knowledge base in their studies and work will be very grateful to you.
Posted on http://www.allbest.ru/
GBPOU SAMARA REGION "SAMARA SOCIAL PEDAGOGICAL COLLEGE"
Abstract on natural science
Latex and products made from it
Performed:
Galkina Kristina,
Student of group 11,
Specialty 02/44/02
Primary school teaching
Checked by the teacher:
Plottseva Svetlana Alexandrovna
Samara city, 2015
Introduction
general characteristics
Properties of latex
Obtaining latex products
Latex based on natural rubber
Latexes based on synthetic rubbers
Usage
Products made with latex
Allergy to latex
Conclusion
List of sources used
Introduction
For many people, information about the emergence of natural cotton, linen and silk is not surprising. But fabric made from tree sap? Having learned what latex is and how it appears, many people do not believe it at first. And this material doesn’t look like fabric at all; it feels and looks just like synthetic. Strictly speaking, even natural latex is not such; it is obtained in a special way from rubber - the juice of the Brazilian Hevea plant, grown on plantations around the world. By the way, a substance similar in properties is familiar to almost any European - this is the milk of the common dandelion. The raw materials are processed, various ingredients are added to it, and the output is a homogeneous, first liquid, and later a more viscous substance. This material has unique properties, which is why its use is so widespread, but there is one serious drawback - for some people it is allergenic.
general characteristics
Latex-- microheterogeneous natural (milky sap of rubber plants) or artificial systems, which are aqueous dispersions of colloidal rubber particles (globules) stabilized by surfactants and emulsifiers.
The shape and size of latex particles are closely related to the laws of the process of emulsion polymerization of the original monomers. Particles of synthetic latexes often have a spherical or similar shape. Latex globules are stabilized by an ionic surfactant, often of the anionic type. Spontaneously, over time or as a result of special treatment (acid-base, hydrodynamic, temperature, etc.) secondary aggregates resembling bunches are formed in the latex dispersion. The primary globules in such “clusters” stuck together, but their coalescence did not take place. In most cases, latexes are not monodisperse and are characterized by varying degrees of polydispersity, which, in turn, depends on the conditions of the polymerization process. Typically, the diameter of primary latex globules is 10-200 nm. Isoprene, butadiene, styrene-butadiene, methylstyrene-butadiene, chloroprene, isobutylene-isoprene, carboxylate, acrylic, urethane and other latexes are widely used in various industries.
Properties of latex
To the touch and appearance, this material is somewhat reminiscent of vinyl or rubber, but differs from them chemical composition. Basic properties characteristics that natural latex has are:
1. Elasticity. This material stretches and bends, but easily returns to its original shape.
2. Hygiene. Hevea juice initially has bactericidal properties, latex retains them, so that dust and mold do not accumulate in products made from this material for a long time, and foreign “inhabitants” do not appear.
3. Durability. When used carefully, pillows, mattresses, clothing and other latex items retain their properties for a long time.
4. Softness. Latex products, although they hold their shape, are pleasant to the body.
5. Thermoregulation. Comfort during sleep is very important, so good thermal conductivity is a valuable quality for a mattress and pillow.
6. Hydrophobicity. Natural latex does not absorb moisture at all, which often only increases its service life.
Obtaining latex products
A salt solution is applied to the mold, e.g. calcium chloride. The mold is then dipped into latex. The salt solution contains positively charged metal particles - cations. When a mold is introduced into latex, cations begin to diffuse from its surface deep into the latex. Encountering negatively charged latex particles on their way, positively charged cations discharge them. And the rubber particles settle as a thin rubber layer on the mold.
Latex based on natural rubber
Commercial latex based on natural rubber (RN) is concentrated and stabilized milky juice of the Brazilian Hevea plant. The dry matter content in the original juice is 37-41%, in commercial LP its content increases to 58-75%. Methods of concentration - settling and centrifugation; the latter method is the most effective and efficient.
Latex mixtures are prepared by introducing many ingredients into its composition: vulcanizing agents, vulcanization accelerators and activators, antioxidants, powder fillers, surfactants, anti-stabilizing additives that help reduce the stability of the colloidal system, thickeners, plasticizers, defoamers or, conversely, foam stabilizers, etc. d. When preparing mixtures, it is advisable to use freshly prepared dispersions and emulsions of ingredients. They should be stored in containers with continuous stirring, avoiding foaming. First, stabilizers are added to the latex, then the remaining ingredients and, lastly, before direct use, a zinc oxide dispersion. To mix latex with emulsions, dispersions, and solutions, containers enameled or rubberized with anti-corrosion coatings are used, equipped with jackets for cooling or heating and mixers with variable speed within 30-40 rpm. The duration of preparation of the mixture is 30-60 minutes. In some cases, the mixture “ripens” for 6–24 hours at 20–60 °C with slow stirring. At the same time, the colloidal chemical characteristics of the mixture change (the pH level decreases, the viscosity increases, etc.), its homogeneity increases, the polymer in the mixture partially vulcanizes, and the technological properties of the mixture improve.
The bulk of LN is used to produce natural rubbers, about 8-10% is used to produce latex products: gloves, meteorological, radiosonde and pilot ball shells, medical products, rubber threads, sponge rubber, light rubber and sports shoes, latex adhesives for various purposes : for leather, rubber, metals, for the production of shoes, for gluing the spines of book bindings, gluing boxes, bags, gluing labels, in the manufacture of sheet plywood and other wooden products, for gluing parquet, linoleum, polymer tiles to various floor substrates; in the production of textile materials and carpets (for joining cotton, wool and linen threads without the formation of knots and thick folds), for the production of abrasive materials in combination with melamine-formaldehyde oligomers; for gluing expanded polystyrene, foam rubber, PVC materials, for gluing ceramics, glass, metals to paper, fabric, leather, polystyrene and other soft and hard materials.
Latexes based on synthetic rubbers
Latexes based on synthetic rubbers (RS) are colloidal aqueous dispersions of synthetic rubbers and other polymers (polystyrene, copolymers of styrene with 20-35% (by weight) butadiene), obtained in most cases by emulsion polymerization of one or more diene, vinyl, vinylidene and other monomers. Some drugs are manufactured by dispersing in water in the presence of surfactants of “ready-made” polymers (butyl rubber, polyisoprene SKI-3, siloxane and other SCs - artificial latexes). Drugs also include aqueous dispersions of thermoplastics (PVC, PVA) obtained by emulsion or suspension polymerization. Important characteristics for the consumer are the average size of the globules, the pH of the medium and the dry residue content: the larger the size of the globules, the greater the dry residue content can be achieved when concentrating the drug; with small globule sizes, the higher the stability of the drug.
Usage
Latex is used in the chemical industry as a flocculant reagent in the beneficiation of minerals.
Products made with latex
Latex is used in the production of the following products: elastic bandage, medical bandage, erasers, balloons, surgical gloves, germicidal tape, some shoes and clothing, catheters, condoms, pacifiers, pacifiers, some sports equipment, some watch bands, massagers for teeth, elastic band, paints, various masks, mattresses, pillows, linoleum and others. latex synthetic rubber allergic
Allergy to latex
Proteins (proteins) contained in natural rubber latex, in rare cases (hereditary predisposition + sensitization) can cause allergies, which usually manifests itself in the form of rashes on the skin at the site of contact with products made from natural latex (and further), difficulty breathing + falling vascular pressure (anaphylactic shock), irritation of the nasal canals, in rare cases it can even lead to death. An effective way to get rid of such allergies is to avoid contact with the triggering allergen. If a person has an allergy, he should try to avoid contact with any products containing natural rubber. Instead, medical and household PPE (personal protective equipment: gloves, condoms) consisting of synthetic elastic substances: isoprene, neoprene, nitrile, vinyl (PVC), styrene-butadiene, etc. are used.
Conclusion
Latex is a wonderful material with unsurpassed elasticity properties.
An important indicator of latex quality is the ratio of the amount of natural raw materials (Hevea tree sap) and special additives. It is decisive when classifying a material into the groups of natural or synthetic latexes. The presence of certain additives affects the resistance of materials to ultraviolet rays, their specific smell, and color.
Latexes are characterized by porosity and breathability.
To create different zones of surface rigidity, latex blocks are perforated.
The material is quite expensive. Its use by small producers is practically excluded.
List of sources used
1. http://rino4ka.ru/content/naturalnyi-lateks
2. https://otvet.mail.ru/question/11715100
3. http://www.liveinternet.ru/users/chamomillia/post257787383/
4. http://dic.academic.ru/dic.nsf/enc3p/175854
5. http://www.himtrade.ru/ref_info_50.htm
Posted on Allbest.ru
...Similar documents
Rubber vulcanization process general characteristics. Classification of rubber, features of its use in Russia. Specific properties of rubber. Production technology, methods of influencing their properties. Description and properties of finished rubber products.
abstract, added 12/28/2009
Analysis of the state of the market and the range of products - dresses. Technical specifications models. Characteristics and analysis of the range of materials for the top of the product. Development of a package of product materials. Properties, requirements and characteristics of the base material.
course work, added 01/23/2011
Concept and manufacturing methods glass products, their classification and types, methods and materials used. History of ceramics and general description manufactured product, equipment. Features of the use of glass and ceramic products in design.
course work, added 11/17/2013
Types, properties and scope of rubber products (RTI). Purpose of heat-frost-acid-alkali-resistant technical plate. Methods for obtaining rubber goods: modern tendencies in the process of their manufacture. Composition of the rubber mixture, types of rubber.
course work, added 10/20/2012
Characteristics of varieties of rubber products. Indicators that determine the quality of synthetic rubber. Wear-resistant, oil- and petrol-resistant, frost-resistant, heat-resistant special rubbers. Vulcanized rubber parts. State standards.
abstract, added 10/28/2013
Technology for manufacturing plastic products by pressing. The main groups of plastics, their physical properties, disadvantages and processing methods. Special properties of rubber, depending on the type of rubber used. The essence and significance of vulcanization.
laboratory work, added 05/06/2009
Description of the product "Layrinth cover with honeycomb seal" and requirements for it. Assessment of material weldability. Scroll possible ways welding of the product, selection of its design options. Welding materials, main and auxiliary equipment.
thesis, added 04/20/2017
Characteristics of the assortment of sewing and knitwear products household use according to operating conditions, seasonality, purpose and type of material. Characteristics of clothing design and its consumer properties. Standardization of garment parts.
laboratory work, added 09/02/2013
Requirements for a sewing product. Selecting a range of quality indicators for materials. Requirements for materials for the manufacture of garments. Analysis of the range of materials for the manufacture of garments. Selection of materials.
course work, added 01/22/2007
Development technological process manufacturing the product "Ring" from fiber-reinforced composite material with an annual output of 35,000 pieces per year. Feasibility study of options for the method of obtaining products, selection of equipment.