Types and types of optical patch cords. Voltage installation types of optical connectors
Currently, it is impossible to imagine any enterprise, store or apartment without a structured cable network (SCN). Patch cords are one of the most common elements of SCS. Basically it's a piece multi-core cable, crimped at both ends with connectors. Patch cords are often called patch cords.
Their main task is to connect various devices. For user convenience, patch cords are made in different colors. Using patch cords different colors helps reduce the time to localize a problem area of a structured cable network and eliminate the problem.
What is a patch cord
Patch cord (patch cord) is an electrical or fiber optic cable for connecting or interconnecting electrical devices. They vary in type and length. Both sides of the cable must be crimped with connectors. These specific connectors are called connectors.

A crossover is often used to combine two workstations. It is also a patch cord, but with a cross connection pattern. Another name for such a connection is a “cross-connection”.
Patch cords can be of any size, but should not exceed 5 m in length according to ANSI EIA TIA 568B.1. For open offices, longer patch cords are permitted.

Application area
Most often, patch cords are used to connect workstations to SCS, as well as to connect network and server equipment.
Base from stranded wires is the main advantage of the patch cord compared to conventional solid-wire UTP cable. Cable parameters such as kink resistance and flexibility are improved. At the same time, the flexible patch cord deteriorates in the basic electrical parameters, which ultimately affects the speed of information transfer.

Depending on the area of application, there are the following types patch cords: for telephone networks, switching (for a router, switch and other similar equipment) and fiber optic (fiber optic cable terminated at both ends with optical connectors).
What are there
Patch cords can be classified according to various signs and parameters.
Most often, patch cords are classified:

The length, as well as the color, are selected taking into account personal preferences. It is important to know that the lengths of the patch cord and the main line must be summed up, and the total length must correspond existing standards structured cabling network. Now maximum length SCS segment should not exceed 100 m.

There are differences between cable and patch cord. Cables are fixed motionless and remain motionless for a long period; patch cords, on the contrary, are constantly subject to a certain mechanical load and may twist. If you handle the patch cord carelessly, the cable in it may be damaged, which will significantly reduce its parameters. Multi-core patch cords are more suitable for constant impacts.
The use of shielding for the patch cord is not required. The protection screen allows you to protect the cable from the effects of external electromagnetic waves. Grounding is mandatory for the use of FTP patch cords.
Molded patch cords are often used in computer networks. Their main difference is the presence of a plastic cap. It can be soldered directly to the cable, unlike a conventional one, in which it can move freely along its entire length. Cast patch cord can only be factory-made; it cannot be made at home.
In conditions of limited space at network facilities, flat patch cords are convenient for use due to their design.
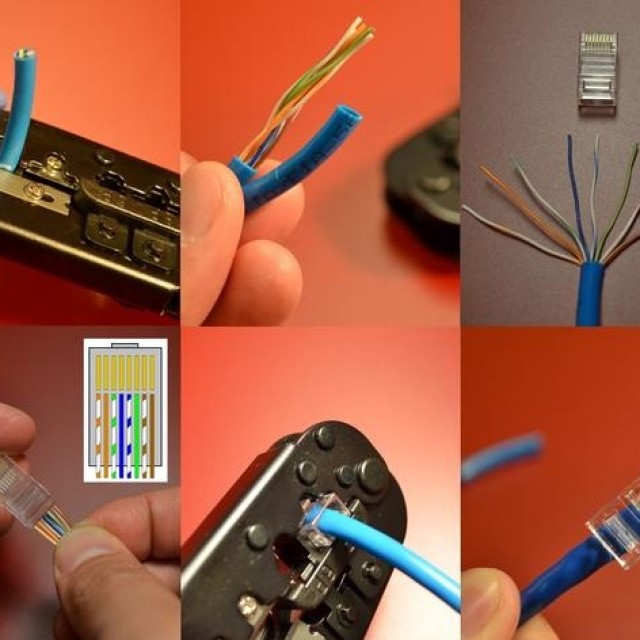
Video: Crimping UTP 5 cable
Categories of patch cords
Each factory patch cord undergoes a certification procedure, according to the results of which it is assigned a certain category. The category determines where a given patch cord can be used and what data transfer rate it can support.
Today, shielded patch cords of category 5e are mainly used. They are distinguished by providing high-quality connections to SCS of any size. They perfectly support data transfer rates of up to 100 Mbit/s, which is the minimum required nowadays.

Photo: patch cord cat. 5E shielded
To organize a gigabit local network, a category 5 patch cord is not suitable; a category 6 patch cord is required. It is based on a cable, each of the eight cores of which consists of seven copper wires, insulated in durable polyethylene. Category 6 patch cord has a slightly larger outer cable diameter (6.2 mm), which must be taken into account when laying it.


Mechanical and climatic characteristics include bending radius, permissible tensile and crushing forces, resistance to torsion and impact, operating and installation temperatures.
The values of these characteristics depend on the specific patch cord manufacturer.
Connection diagram
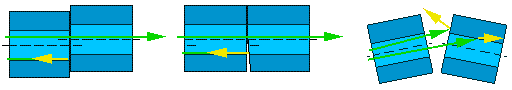
There are two main connection schemes: direct and cross.
Direct connection diagram used to connect workstations with switches, as well as to connect switches to each other via the Uplink port.
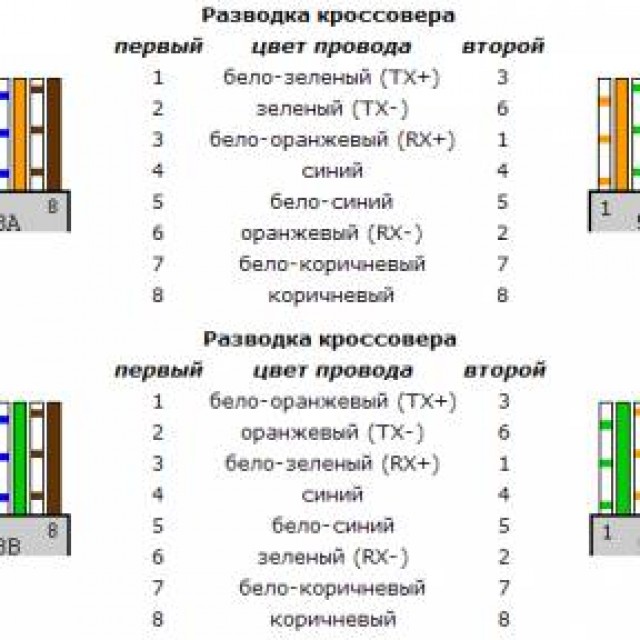
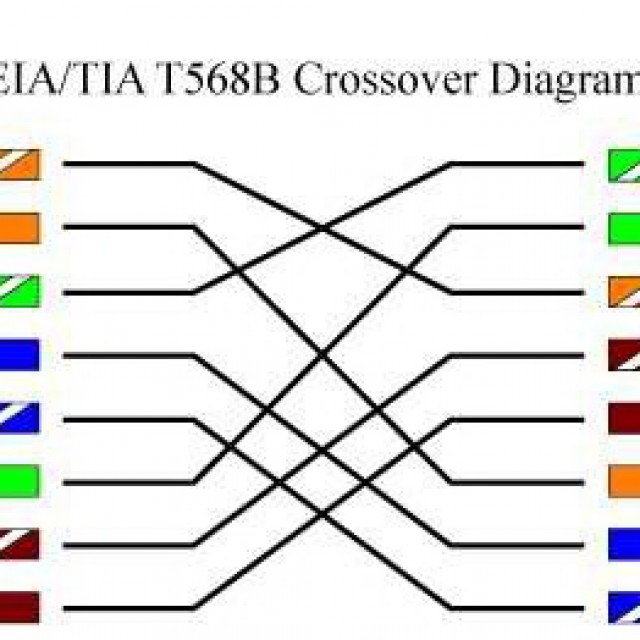
Cross or cross connection diagram necessary for direct connection of two workstations. Also, using a crossover circuit, network hubs are connected to each other without using the Uplink port. Below is a diagram of the cable connections. The numbering of contacts on the connector is from left to right, if you hold the connector up with the contacts and the cable facing you.
Why is a factory patch cord better?
Making a patch cord with your own hands is not a difficult task, and its cost will be several times less than a factory one. Strange. Is not it? Why do factory patch cords, produced in the millions, cost an order of magnitude higher than homemade patch cords?
The difference is that the manufacturer tests each patch cord for compliance with certain parameters and, based on the test results, rejects some of its products. When purchasing a factory patch cord, the client pays for confidence in the flawless functioning of the SCS.

In SCS, the main places where its parameters are lost are the connection points. And each patch cord affects two connections at once. Incorrect wiring of the wire cores can ruin the characteristics of the entire network. It is possible that if the crimping is of poor quality, interference may appear in it. After all, the eight unbraided wires of a twisted pair act as parallel antennas, as a result of which each pair creates its own interference and receives interference from neighboring pairs.
Of course, force majeure situations occur when it is necessary to as soon as possible connect a new device to the local network, or replace a damaged cable. The only way out of these situations is to make a temporary patch cord yourself.
Based on this, it is necessary to make a choice in favor of factory patch cords. Moreover, it is very important to carefully study all the manufacturers of these products and choose the manufacturer with the best quality.
Thus, patch cords play a significant role in ensuring the reliability and performance of SCS.
Experience shows that the use of low-quality patch cords (in particular homemade ones), despite the savings at the stage of creating a local network, in the future during its operation leads to significant additional costs. Failures and downtime often occur due to the use of low-quality patch cords. And one of the main qualities of SCS is reliability. Therefore, it is recommended to use patch cords only from trusted manufacturers.
Fiber optic patch cord is a structure designed to connect active equipment. Such cords are equipped with special connectors for connecting computer and other equipment. You can buy an optical patch cord in Moscow in the RACKMARLET store: we offer products from the manufacturer Cabeus at an affordable price.
Product range
In the catalog you will see optical cords with different types connectors(FC-FC, FC-ST, LC-LC, etc.). The choice depends on the characteristics of your equipment. The length of such products varies from one to 25 meters.
In the manufacture of the cable, durable and elastic optical fiber is used, as well as a protective sheath made of high-quality PVC.
Scope of application
Patch cords from this manufacturer can be used in the following areas:
organization of local networks;
connecting telecommunications equipment;
connection cable television;
connection of data networks.
Why us?
The catalog contains high-quality and original cables that are durable and have a long service life;
the product is provided with a warranty from the manufacturer;
RACKMARLET is a store where you can buy cables at an affordable price and with favorable discounts;
wide choose patch cords with various connectors;
comfortable and Fast shipping to your home or office, check delivery times with the cybermarket employees.
To order products, call us by phone: we will advise you on the assortment, select suitable option for your computer network and arrange delivery.
| Photo | Name | Code sonnet | vendor code | Unit | Price, rub.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC. | 12742 | EX9C-2P2 (ExaLan+) | set | Retail price
117.38 Price small wholesale 111.10 |
|
| PC. | 12342 | EX9L-2P2 (ExaLan+) | set | Retail price
124.90 Price small wholesale 118.22 |
|
| PC. | 12728 | EX5C-2P2 (ExaLan+) | set | Retail price
124.90 Price small wholesale 118.22 |
|
| PC. | 12714 | EX6C-2P2 (ExaLan+) | set | Retail price
124.90 Price small wholesale 118.22 |
|
| PC. | 12650 | EX9T-2P2 (ExaLan+) | set | Retail price
125.95 Price small wholesale 119.23 |
|
| PC. | 12680 | EX9F-2P2 (ExaLan+) | set | Retail price
125.95 Price small wholesale 119.23 |
|
| PC. | 12777 | EX9S-2P2a (ExaLan+) | set | Retail price
125.95 Price small wholesale 119.23 |
|
| PC. | 12782 | EX5L-2P2 (ExaLan+) | set | Retail price
130.22 Price small wholesale 123.27 |
|
| PC. | 12694 | EX9F-2P2a (ExaLan+) | set | Retail price
130.22 Price small wholesale 123.27 |
|
| PC. | 12444 | EX6L-2P2 (ExaLan+) | set | Retail price
130.22 Price small wholesale 123.27 |
Total pages: 78
The SONET product range includes optical patch cords. You can easily choose the ones that suit you.
Optical patch cord: main features
Optical patch cords provide:
- high throughput channels of various devices,
- connection stability of network equipment,
- high data transfer speed while maintaining quality.
Optical cables allow you to:
- connect patch panels together,
- connect a PC to a network device, etc.
When choosing a patch cord, pay attention to the following characteristics:
- connector type,
- component category,
- number of pairs,
- length.
To correctly select and buy a suitable optical cord, pay attention to the shape of the transmitted signal.
Contact us! We will help you order the necessary optical devices in Moscow. Specialists will provide all information about the devices. Buying a suitable patch cord is not difficult.
ARTICLES ON THE TOPIC OF THIS SECTIONProbably the most popular accessories among fiber-optic line installers are optical patch cords. A fiber optic patch cord or fiber optic cord is a piece of optical fiber in an outer sheath, usually of a standard length of 1, 1.5, 2.3 or 5 m, terminated on both sides with optical connectors of various types.
Depending on the installed type of optical connector, optical patch cords are classified into the most popular ones: optical patch cord sc sc, optical patch cord lc lc, optical patch cord fc fc, optical patch cord st st. Depending on the type of optical fiber, optical patch cords can be classified into single-mode patch cords and multimode patch cords. Fiber optic cords with single-mode fiber, as a rule, are more in demand among dealers, and therefore are more affordable in price and range.
Another important factor must be taken into account when working with patch cords or fiber optic cords. Very often, fiber optic patch cords are in demand in either simplex or duplex versions. This means that a simplex optical fiber cord or optical patch cord is made of optical fiber terminated on both sides with either the same or different types of optical connectors. Simplex optical patch cords are used in specialized single-fiber optical tasks or network applications. Sometimes such optical patch cords can be used in measurement procedures, especially when carrying out reflectometry optical fibers or in measurements of optical radiation power.
However, duplex optical patchcord is also used successfully in network applications such as structured cabling systems or MAN and WAN network transmission protocols. Very often, fiber optic patch cords are manufactured with various types of optical connectors at the ends of the fiber. This is because patch cord or fiber optic cord can be used to make patches or connect pieces of equipment with different types of optical connectors. Thus, a single-mode optical patch cord can perform the functions of a switching or cross-connection system.
It is only necessary to remember that the optical patch cord must in this case necessarily meet the requirements for compatibility of types of optical fibers when making switching. That is, no matter which of the optical patch cords is used, the type of optical fiber must be the same everywhere. When connecting two optical patch cords sc sc, optical patch cord lc lc, optical patch cord fc fc, optical patch cord lc fc or optical patch cord sc lc or optical patch cord st st through the pass-through optical adapter directly, the cores of the optical patch cords are duplex and single-mode cables must be exactly the same for both fiber optic cords.
Multimode optical fibers are a class of optical fibers that are successfully used in local area networks or LAN networks. Multimode optical fibers are used. Typically in structured cable systems(SKS). The spectrum of their action is local networks, where the line length is limited to 2 km maximum.
Multimode optical fibers have many advantages. They allow you to be practically indispensable in LAN networks. Multimode fibers are divided into classes. These are classes OM1, OM2, OM3 and OM4. Multimode optical fibers of classes OM1 and OM2 are designed for the use of optical fibers with a core of 62.5 microns, i.e. 62.5/125 µm. The broadband coefficient of such fibers is: for class OM1 – 200 MHz/km, and for class OM2 – 500 MHz/km. The most modern of multimode optical fibers are optical fibers of the OM3 and OM4 classes. Multimode optical fibers of the OM3 class are modern optical fibers that have a standard size of 50/125 microns and are designed to operate with a broadband coefficient of 2000 MHz/km. OM3 class optical fibers are designed to work with gigabit network protocols, such as 10 GBASE-T. Optical fibers of the OM3 class can transmit such a network protocol over distances of up to 350 m. If it is necessary to transmit speeds of 40 Gbit/s or even 100 Gbit/s over a network, then optical fibers of the OM3 class can be used in conjunction with bZShch (MTP) connectors, which use 8 to 10 optical fibers class OM3.
Another of the most advanced and latest known high-speed classes of optical fibers is OM4 class multimode optical fibers. OM4 class optical fibers are the fastest of all multimode optical fibers known today. The broadband coefficient of multimode optical fibers of the OM4 class is no longer 2000 MHz/km, but as much as 4700 MHz/km. Such optical fibers work excellently with laser radiation sources of the VCSEL family. These are high-speed multimode lasers that typically operate at wavelengths of 850 nm. They are especially effective at short wavelengths. Therefore, in the official literature they are often called short-wave multimode lasers.
The VCSEL laser has emission characteristics that are determined by a small aperture angle and high efficiency radiation with higher output power and lower control current. OM4 class optical fibers are capable of transmitting 10 Gbit/s over a distance of up to 400 m. Like OM3 class optical fibers, OM4 class optical fibers are used to transmit high-speed 40 Gbit/s and 100 Gbit/s protocols.
Optic patch-cord is a patch cord consisting of a piece of optical fiber terminated on both sides with optical connectors.
Optical patch cords differ in several parameters, which will be discussed further.
Types of fibers used in patchcord
SM (Single Mode)- Single-mode fiber - this type of fiber has a small core diameter (7-10 microns), due to which only one mode of electromagnetic radiation is transmitted. Currently the main type of fiber.
Also denoted as 9/125 - which should be understood as the diameters of the light-conducting core / sheath in microns).
MM (Multi Mode)- Multimode fiber - this type of fiber has a large core diameter (50 microns in the European standard and 62.5 microns in the North American and Japanese standards), due to the large diameter of the core, many modes of electromagnetic radiation are transmitted.
Also referred to as 50/125 and 62.5/125.
Number of fibers in patchcord
Simplex(Simplex) - single patch-cord (with one fiber).
Duplex(Duplex) - double patch-cord (with two fibers).

Types of connectors used in the patch cord
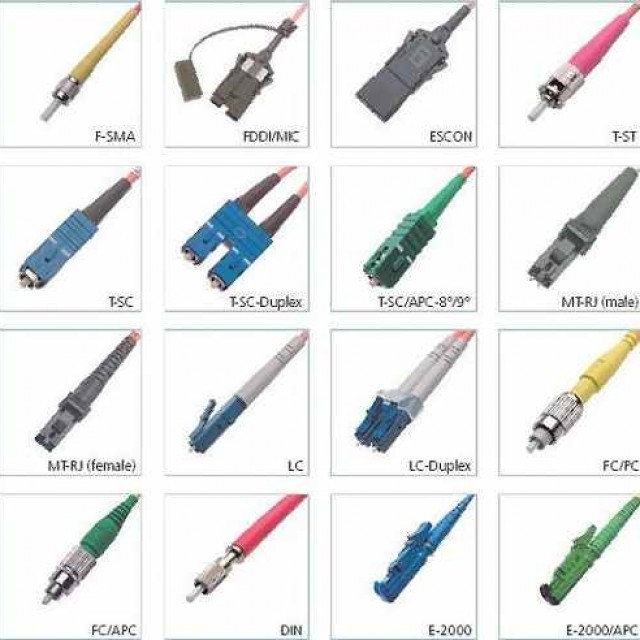
There are a huge number of connector types, most of which are obsolete and not currently used, I will list 5 main types:
FC (Fiber Channel)

ST (Straight Tip)
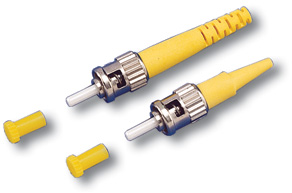
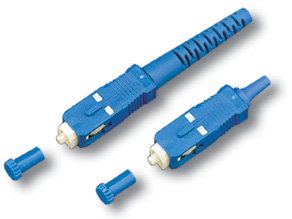
SC (Subscriber Connector)
LC (Little Connector)

MTRJ (Mechanical Transfer Registered Jack)

Types of optical connector end polishing used
When an optical connector is connected to the end of an optical fiber, signal loss occurs due to the fact that part of the transmitted light is reflected back into the fiber to the light source that created it, i.e., return loss (RL) occurs, which can disrupt the structure of the transmitted signal. To reduce return losses, use Various types polishing.
PC (Physical Contact)- Standard tip end polishing ensures return loss of -30dB. PC polishing arose first and at first provided for a flat version of the connector tip, however, operating experience has shown that an absolutely flat end of the connector cannot eliminate the formation of air gaps between the ends of the optical fibers, and this, in turn, leads to quite large back reflections, so the ends of the tips over time was replaced with a rounded one.
SPC (Super Physical Contact)- Different from PC, more high quality, machine polished end and connectors with rounded ferrules are used, which provides a return loss of -45 dB.
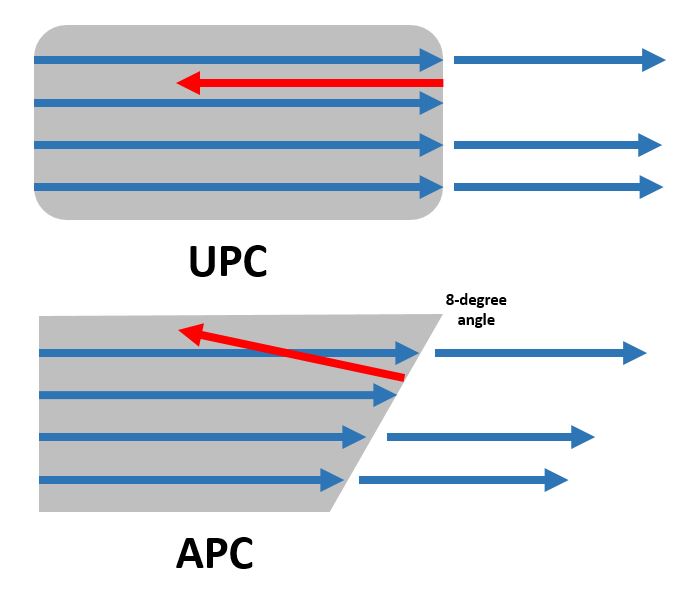
UPC (Ultra Physical Contact)– Differs from SPC in even higher quality, machine polishing is used taking into account the radius of curvature of the tip and connectors with a rounded ferrule, which provides a return loss of -55dB. Polishing types PC, SPC and UPC are compatible with each other.
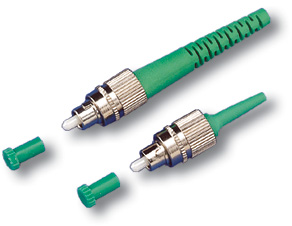
APC (Angled Physical Contact)– The highest quality type of polishing, the end of the ceramic core is beveled at an angle of 8 degrees to the axis, which provides a return loss of -65 dB. Connectors with this type of polish are incompatible with PC, SPC, UPC and are marked green.
Patchcord thickness and length
Optical patch cords vary in thickness and length. The thickness of the cord is usually 2 or 3 mm, the length of the cord is 1, 2, 3, 5, 10, 15, 20 or more meters.
That's all. Bye everyone.
One of final stages installation of fiber-optic lines - this is the wiring and connection of the incoming fiber optic cable directly at the destination: in the server room, data center, etc. To do this, the cable is inserted into the optical cross-connect and the fibers are connected to the connectors. At this stage, a group such as optical components is used - these are pigtails, and all kinds of clamps. They are also combined under the name passive fiber optic equipment.
Pigtail- this is a piece optical cable, terminated with a connector on one side only.
Patch cord has connectors at both ends, the types of connectors may differ (adapter patch cord) or be the same (connecting).
Optical adapter- this is, in fact, the outlet into which the pigtail or patch cord is connected.
What is important to consider?
It may seem that there is nothing complicated at the stage of connecting a connector to an optical adapter. How to plug a plug into a socket. However, no.
Let's look at least from a technology point of view. What is a kit - patchcord/pigtail + adapter? This is the joining of two optical fibers, the thickness of which is approximately equal to the thickness of a human hair. In this case, a connection shift of even 1 micron causes a loss of power.
That is, the cross connection must provide:
- perfectly precise contact cores (fiber optics);
- protection of this ideal contact from external influences - shifts, the appearance of an air gap, etc.;
- mechanical protection of fibers with repeated connection and disconnection;
- mechanical protection of the cable in the connector during bending, pulling, etc.
In particular, this is why so many types of optical connectors have been created. Each manufacturer strived to create the ideal connector specifically for their equipment.
But that's not all the difficulties
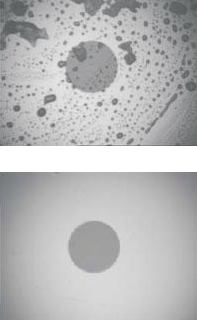
To ensure precise connection, optical connector tips should not have cracks(if a crack crosses the optical fiber, such a connector is replaced), should not be dusty or dirty. Even if you just touched it with your finger, the mark must be thoroughly wiped off with an alcohol wipe. Every speck of dust, pollution, etc. - this is weakening, attenuation of the signal, back reflections.
Therefore, optical connectors are regularly wiped with alcohol, and sockets are purged compressed air or cleaned with special sticks.
The picture on the right shows the tip of the connector after touching it with a finger. and after cleaning.
The mechanical strength of connections is ensured differently in each type of connector, but basically it is:
- especially durable material connector tip - ceramics, metal ceramics;
- protective plastic and metal caps over the connectors;
- latches and clamps positions both in optical adapters and in “plugs”;
- Kevlar and other reinforcing threads under the sheath of the cable section leading to the connector.
Types of optical patchcords, pigtails, adapters
The classification of optical pigtails, patch cords and adapters is generally the same and is based on the following parameters:
- connector standard;
- type of grinding;
- fiber type - multimode or single-mode;
- type of connectors - single or duplex.
As a result of various combinations of all these types, a huge variety of modifications of connectors and adapters are obtained. Not everything is in this picture:

What do all these letters mean?
Let's take typical optical patch cord markings. Eg, .
- S.C. And L.C.- These are the types of connectors. Here we are dealing with a patch cord - an adapter, since two different types connector;
- UPC- type of grinding;
- Multimode- type of fiber, here multimode fiber, can also be designated by the abbreviation MM. Single-mode is labeled as SingleMode or SM;
- Duplex- two connectors in one housing, for a more dense arrangement. The opposite case is Simplex, one connector.
Duplex example:

Types of polishing (grinding) of fiber optic connectors
The purpose of grinding or polishing fiber optic connectors is to ensure that the fiber optic cores are in perfect contact. There should be no air between their surfaces, as this degrades the signal quality.
Currently, the following types of polishing are used: PC, SPC, UPC and APC.
PC- the progenitor of all other types of polishing. The connector, processed using the PC method (including manually), has a rounded tip.
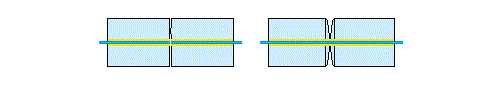
Please note that the figure shows that connecting connectors with a flat end is fraught with the occurrence of air gap. While the rounded ends are connected more tightly.
Can be used in short-range networks that require low data transfer rates.
SPC- an improved version of PC, but grinding is done only by machine.
UPC- an almost flat (but not flat) connector, which is produced using high-precision surface treatment. It provides excellent reflectivity (compared to PC and SPC), therefore it is actively used in high-speed optical networks.
Connectors with this type of connector are most often blue.

APC- a connector processed according to a completely different principle: the ends are beveled at an angle of 8 degrees. This surface polishing gives the best results. Back reflections of the signal leave the optical fiber almost immediately, and due to this, losses are reduced.
APC polished connectors are used in networks with high requirements for signal quality: transmission of voice, video data. As an example - cable TV.
Connectors with this type of connector are green.

Attention!
APC Ground Connectors unsuitable to connectors with other polishing (PC, SPC, UPC) and cause mutual damage.
PC, SPC, UPC polishes are mutually compatible.
Comparison of tip shape and reflected signal path in UPC and APC polished connectors:
The dependence of line losses on the type of polishing of the optical connector is shown in the table:
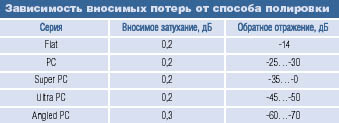
As you can see, UPC (rounded ends) and APC (beveled ends) polishing is the most effective. Therefore, patchcords and pigtails with this type of grinding are most often used.
Types of optical connectors
In practice, our fiber optic network installers work in the vast majority of cases with types FC, LC, SC. For more rare species We won’t stop with connectors just yet.
F.C.

- spring-loaded connection, due to which “pressing” and tight contact are achieved;
- metal cap - durable protection;
- the connector is screwed into the socket, which means it cannot jump out, even if accidentally pulled;
- Moving the cable does not affect the connection.
However, it is not suitable for dense placement of connectors - space is required for screwing in/unscrewing.
S.C.
![]()
Cheaper and more convenient, but a less reliable analogue of FC. Easy to connect (latch), connectors can be placed tightly.
However, the plastic shell can break, and even touching the connector affects signal attenuation and back reflections.
In general, it is used most often, but is not recommended on important highways.
L.C.

A smaller version of the SC. Due to its small size, it is used for cross connections in offices, server rooms, etc. - indoors, where required high density connector locations.
The author of the development of this type of connector - a leading manufacturer of telecommunications equipment, Lucent Technologies (USA) - initially predicted the fate of a market leader for his brainchild. In principle, this is how it is. Especially considering that this type of connector refers to connections with increased installation density.
In the following releases:
More articles on the topic "Fiber Optic Networks":
website