What is a tube here? How to choose the required diameter of heat-shrinkable tube
Good insulation of two contacts is the key to long-term operation of electrical wiring, plus high security. Therefore, insulating tape is one of those materials that an electrician always has on hand. But it is gradually losing its position to heat-shrinkable tubes, which are superior to the former in many technical characteristics. So, let's figure out what heat shrink for wires is (dimensions, what materials it is made of, and how it is installed).
Let's start with the fact that the main property of heat shrink tube (HEET) is to shrink in size under the influence of high temperatures. That is, you put it on the contact of two wires and expose it to temperature, the tube immediately decreases in size and fits tightly around the electrical contact. What can cause fever? The best option- This is a special hair dryer that is used specifically for this operation. If there is none, then you can use a lit candle, lighter, matches, and so on. That is, the flame of an open fire is suitable for this. But keep in mind the fact that contact with fire is contraindicated, and overheating the tube will not lead to anything good. The material will become covered with bubbles, become rigid, and will quickly crack.
Specifications
Currently available on the market a large number of heat shrinkage, which differ from each other in their properties. In what ways do they differ:
- Shrinkage coefficient, that is, the ability to reduce its size (2-6 times).
- Resistance to different operating environments - heat-resistant, oil- and petrol-resistant, chemical-resistant, light-stabilized.
- With and without an adhesive layer.

In addition, we can add that heat-shrinkable tubes differ in color and the material from which they are made. Concerning color design, then there is not much variety here, because manufacturers try to approach this issue from the perspective of the color design of the cores in the cable. By the way, yellow-green tubes for grounding conductors are also available.
Now, regarding the raw material. In principle, any polymers are suitable for the manufacturing technology HERE. These include polyvinyl chloride, fluoroplastic, elastomers, polyolefins, and so on.
Main parameter
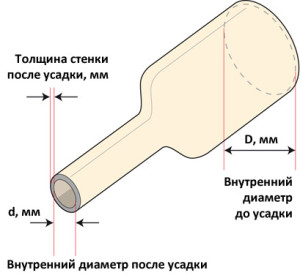
Yet the main indicator of heat shrinkage is the diameter of the tube, which indicates the size before and after shrinkage. The first size shows the diameter of the product that is supplied to the retail chain from the factory. The second shows how much the first can decrease during the heating process. This is usually how the product designation is indicated. But there is another type of marking, where only the original diameter is shown, and in addition, another indicator is the shrinkage coefficient. Eg:
- This is how heat shrinkage is marked according to the first option - 6/4 or 6 mm/4 mm.
- This is marked according to the second option - 10/2:1, that is, the shrinkage will occur twice. Essentially, this is the same as 10/5 (in the first case).

Asian manufacturers, including Russia, indicate the diameter of heat-shrinkable tubes in millimeters. European and American in inches. Converting one to the other is easy because 1 inch is equal to 25.4 mm. By the way, inch tubes are more expensive than millimeter tubes, but keep in mind that the size is in inches - this does not always mean that the product was made in America or Europe.
Attention! The higher the shrinkage factor, the better. But such products come at a higher price.
Most often, manufacturers offer the following ratios: 4:1, 3:1, 2:1. Adhesive heat shrinks do not have a standard ratio; it varies in the range from 2.8:1 or 4:1, it all depends on the diameter of the product itself.
Form
As for the shape, in stores you can find round, oval, and flat (flattened) tubes. Why such diversity? It's all about ease of storage and transportation.

- Flat and oval are thin-walled or large-diameter heat shrink.
- Round ones are thick-walled tubes and heat-shrink with an adhesive layer. Sometimes the products are thin-walled with a small diameter.
Delivery to the retail chain is made in coils and slices. By the way, it is the flat models that are supplied in coils. Depending on the diameter, pipes with a length of 10 to 100 mm are placed in coils. When cut, heat shrink comes in a length of one meter or 1.22 meters - that's four feet. But tubes with an adhesive layer have a standard length of only 1.22 m. They are not supplied in coils due to kink. The same applies to pipes with thick walls - they are not sold in coils.
How to determine the diameter
The lack of markings creates problems with determining the diameter of the heat shrink tube. But determining this parameter is not a problem. There are several options for this.
- The first option is to lay flat heat shrink on a ruler and measure it from end to end.
- The second option is to take measurements with a caliper.
These two methods are best suited for measuring large diameters. With small tubes you will not only have to take measurements, but also do some mathematical calculations. Therefore, you first need to measure the circumference, for which you will need a thread that is used to frame the tube strictly along the diameter. Then remember the formula for circumference:

L=2πR or L=πd, where R is the radius equal to half the diameter (d). And the sign “π” is an Archimedean number, approximately equal to 3.14.
That is, calculating the diameter using this formula is as easy as shelling pears. This will be the formula:
d=L/π. You measured the circumference with a thread, everything else is known.
Of course, any type of measurement gives a certain error, even in the case of calculations. Therefore, the final result will have to be adjusted to the standard one. For example, if you get, say, 20.8 mm, then it is most likely a 20 mm diameter tube.
How to use it correctly
You need to cut a piece from the product, slightly longer than the length of the open connecting section of the two wires. It is better to make the cut even. Then the cut piece is put on the joint and heated. This process can be carried out from one end of the tube to the other or from the middle to the edges.

Glue model
Heat-shrink tubing with an adhesive layer was invented in order to perform several functions at once. More specifically, the functions of waterproofing and anti-corrosion protective layer. In essence, this is ordinary heat shrinkage only with inner surface special hot melt glue.
- Firstly, the adhesive composition hermetically fills all joints and voids, thereby sealing the joint from external moisture.
- Secondly, the glue is evenly distributed throughout the joint and hardens in it. The result is a durable structure that cannot be dismantled. Therefore, this type of heat shrinkage is most often used for underground installation. electrical cables or wires.
- Thirdly, this tubular material can also be used as protection for metal and wooden products from external influence climatic conditions. For example, use a large diameter tube that is placed on wooden table, installed in the ground. Such heat shrinkage will replace hot bitumen or roofing felt, as waterproofing material. True, the tube is many times better, and its service life is a level higher.
Conclusion on the topic
So, let's summarize. Let's start with the fact that heat shrinkage in its technical characteristics exceeds conventional insulating tape. And it seems that the method of installing it is a little more complicated, but it’s high quality and long-term operation, plus a guarantee that the insulation between the two wires will not burn or crumble. But the most important thing about heat shrink for wires is the dimensions (correctly chosen). Therefore, when choosing, always focus on the diameter.
Related posts:
For the right choice heat-shrinkable tube, it is necessary to take into account a large number of parameters, depending on the conditions of its further operation as part of the equipment complex. The most important thing technical parameter Any heat shrink is its diameter. An incorrectly selected tube diameter can lead to damage during shrinkage or during operation, and will not allow you to fully use all the capabilities of the heat-shrinkable tube. In the most harmless case, the heat shrink tube simply will not fit onto the product being shrinked. A correctly selected tube is the key to reliable and durable operation of the equipment.
To correctly select the diameter of the heat shrink, you need to follow a few simple rules:
1. The minimum diameter of the product (object) on which the tube is planned to be installed must be at least 10% larger than the minimum inner diameter fully shrinked heat-shrinkable tubing in a loose state.
Comments: This is very important, since if this condition is not met, the heat-shrink tube will not fit well around the product, the elastic compression forces holding the heat shrink will be small, the tube may hold very loosely on the surface of the product and even slide off it.
The optimal result is achieved when the diameter of the insulated product is 20-40% larger than the diameter of the shrink tube. At these values, the heat-shrinkable tube will fully provide the inherent characteristics of mechanical and electrical strength, durability, and temperature resistance.
If the diameter of the insulated product is more than 50-70% of the minimum internal diameter of a fully-shrinkable heat-shrinkable tube in a free state, then such situations are allowed provided that the product is not operated at temperatures close to the maximum design temperatures for this type of heat-shrinkable tube. Otherwise, when high temperatures operation (from + 90 to + 125 ° C), the heat-shrinkable tube may rupture due to the fact that the elastic compression forces exceed its tensile strength. They can also get significantly worse performance characteristics tubes.
Tube rupture can also occur during shrinkage, especially when the shrinkage temperature exceeds the recommended one, so shrinkage of tubes on such large products must be carried out slowly, at the lowest possible heating temperature.
2. The maximum diameter of the product (object) on which it is planned to shrink the tube must be at least 10% less than the internal diameter of the heat-shrinkable tube before shrinking.
This rule is dictated primarily by the very possibility of stretching an unshrinkable heat-shrinkable tube onto an object before shrinking, so as not to damage the tube itself. For products with complex surface topography, this parameter should, if possible, be increased to 20-30%.
In addition, if the internal diameter of the tube before shrinkage is only slightly larger than the diameter of the product, it may be damaged during shrinkage or subsequent operation at elevated temperatures. (see commentary to the first rule).
Addition: Most heat shrink tubing has a compression ratio of 2x. This is usually enough to select the right size heat shrinkage for almost any product. However, there are cases when the insulated object (part) has a complex surface topography with large differences in diameters, for which it is not possible to select a tube so that all recommendations are followed.
For example, you need reliable waterproof insulation of the area between a thin cable and a thick connector attached to it. We have to face a choice: either the tube will not tightly press the surface of the cable, or we will not be able to pull the tube onto the thick connector!
Example of a simple calculation:
It is required to seat an insulating heat-shrinkable tube onto a conductive busbar round section with a diameter of 10 mm, operating at room temperature. We have tubes of the following diameters (before/after shrinkage): 20/10 mm, 19/9.5 mm, 18/9 mm, 16/8 mm, 13/6.5 mm, 12/6 mm, 11/5.5 mm, 10/5 mm.
Since we do not have temperature restrictions, we are guided by the 10% rules. Tubes 10/5 and 20/10 are discarded immediately. In the first case, we will not be able to pull the tube onto the tire, and in the second case, after the tube shrinks, its diameter will be more than 10 mm and it will not be able to compress our product.
According to Rule 1, the inner diameter of a fully loose-fitted tube must be at least 10% smaller than the tire diameter, i.e. 9 mm or more. 20/10 mm and 19/9.5 mm tubes do not correspond to this value.
According to rule 2, the inner diameter of the tube before shrinkage must be at least 10% larger than the diameter of the tire, i.e. not less than 11 mm. Thus, all the remaining tubes: 18/9 mm, 16/8 mm, 13/6.5 mm, 12/6 mm, 11/5.5 mm are formally suitable as insulation for our bus.
If we take into account additional recommendation, that the most optimal case is when the diameter of the shrinked tube is 20-40% less than the diameter of the insulated product, then the optimal diameter of the tube after free shrinkage should be from 6 to 8 mm.
Thus the best solution to insulate our tire there will be 16/8 mm, 13/6.5 mm and 12/6 mm tubes. And which one to choose is up to you to decide based on their availability, required coloring, availability, and economic feasibility, because tubes of smaller diameter are usually cheaper.
?
Heat shrink tube - a tube made of polymer materials, which shrinks in diameter after heating. The adhesive sublayer secures the tube to the wire or cable. The tube can also be produced without an adhesive sublayer. The process of combining the wire or cable and heat shrink tubing is called insulation.
For what purposes is heat shrink tubing used?
Heat shrink tubing is used to replace insulation, for protection from external influences, insulation and marking of pipes. Heat shrink tube is in a great way for guard electrical wires and cables in aggressive environments, such as water, oil, acid, as well as protection from external influences negative factors environment. Heat shrink tubing provides an alternative to conventional insulation methods and can be used in a wide variety of applications.
Why Polyolefin Tubing the best choice from the entire range of heat-shrinkable tubes?
Polyolefin heat shrink tubing is a popular choice among all heat shrink options because polyolefin is flame retardant and has good chemical, electrical and physical characteristics. Overall, polyolefin heat shrink tubing is a reliable product manufactured according to technical requirements customers guaranteed quality. Heat shrink tubing is available in a wide variety of designs for different purposes. Polyolefin heat shrink tubing is excellent choice for use in the automotive industry. However, depending on the specific application, the characteristics of a different heat shrink tubing may be more suitable for your requirements.
Is heat shrink tubing difficult to work with?
No, in most cases, heat shrink tubing is very easy to work with and install.
Heat shrink tubing comes in a huge variety of sizes and colors. The work does not require serious training, high responsibility, or expensive equipment. Only gloves and tools specified in the instructions are required.
What are the advantages of using heat shrink tubing?
In addition to providing additional strength and heat resistance, heat shrink tubing also gives perfect protection and does not come off after a certain period of time or improper use - unlike duct tape.
What important parameters should be considered when choosing?
The maximum diameter of the cable or its assembly and the temperature permissible for operation are important parameters, which should be considered when selecting heat shrink tubing. Since the parameters different manufacturers tubes HERE differ significantly, it is necessary to study the production process, cross-linking and properties source material used for the production of heat shrink, as well as the final characteristics of the product, shrinkage coefficient and other points.
What are the tube shrinkage coefficients HERE?
The shrinkage coefficient indicates the ratio of the diameter of the heat shrink at the time of delivery and the diameter of the heat shrink at the time of complete shrinkage after heating. Quantitatively, how many times the tube shrinks.
2:1 - In this case, the heat shrink tube will become half the diameter of its original size when heated.
3:1 or 6:1 - Heat shrink tubing is three to six times larger at the time of delivery, respectively, than when fully shrinked.
By the way, everywhere the moment of complete shrinkage of the tube is specified; it is better to shrink the tube not to the maximum possible size, but by a maximum of 30-60%. This condition gives the best shrinkage result.
How to choose the correct size of heat-shrinkable tubing?
Selecting the correct size of heat shrink tubing depends on the accuracy of your measurements of the material being insulated. Use precision instruments to measure the smallest and highest value diameters of cable connections, diameters of wires, steel pipes, which you intend to isolate. Choose heat shrink tubing that is twenty to thirty percent larger than most large values Your measurements. This difference is sufficient for free tension on the insulated surface. Also make sure that the heat shrink tubing has a high enough shrink rate to obtain a tight seal for the smallest diameter you intend to insulate. Finally, when buying heat shrink, you need to take 10-20% more length, because heat shrink tube when heated decreases not only in diameter, but also in length! This quality is called “longitudinal shrinkage” and depending on the diameter, the longitudinal shrinkage coefficient increases.
Posted by company
To reliably insulate the connection of electrical wires, several types of materials can be used. These include classic insulating tape made on the basis of dielectric polymers. But in Lately Heat-shrinkable tubes/couplings have become particularly popular. They are easy to install and have good performance.
Definition and Specifications
Outwardly, they resemble a plastic insulating layer. But that's where their similarities end. Heat-shrinkable sleeves (HF) are designed to create a reliable layer of protection at the junction of electrical conductors.
The principle of using TF is quite simple - it is installed on top power cable until the current-carrying wires are connected. Once they are joined, the shell is placed over the joint. In this case, the edges of the coupling must be on the cable insulation. Further using industrial hair dryer or gas burner the temperature on the surface of the TF increases, as a result of which the diameter of the product decreases and its surface is compressed with the junction of the leads.
This installation principle was made possible thanks to the manufacturing material used – a polyolefin-based polymer. Under the influence of temperature, the specific density of the material increases, as a result of which its dimensions decrease.
Main technical characteristics thermal couplings are:

To mark wires, you can use couplings of various types. color. Many models are processed adhesive composition inside. When exposed to temperature, it improves insulating properties and serves additional factor reliable fixation of the coupling on the surface of the wire.
Advantages of use and installation rules
 In addition to insulating electrical cables, heat-shrinkable tubes are used when laying sewer and water supply pipes. However, their design differs from that described above. Most often, they consist of several components, the installation of which occurs in stages.
In addition to insulating electrical cables, heat-shrinkable tubes are used when laying sewer and water supply pipes. However, their design differs from that described above. Most often, they consist of several components, the installation of which occurs in stages.
If the installation technology is followed, the TF provides the following insulation qualities:
- Mechanical strength. Due to the relatively high rigidity, breakage of the wire at the installation site is practically eliminated.
- Reliable protection against moisture. This reduces the likelihood of corrosion on the conductors, and also contributes to a lower rate of oxidation of the contacts.
- Electrical insulation.
Installation of heat shrink tubing is simple. To carry it out, you must first prepare the connecting wires. After stripping the ends from the insulating layer, measure total length wiring where it is necessary to install the TF. For stranded wires best to take advantage complete set, in which there are tubes of various thicknesses. It is selected according to the diameter of each cable. After compression, the diameter of the TF should be less than the cross-section of the rein. For example, for a core with a thickness of 2.5 mm, a coupling with a diameter of 3 mm with a coefficient of at least 2 is needed.
Each cable component must be insulated separately. For example step by step instructions you can see the order of insulation of a 3-core wire.

After completing the work, each section is checked for leaks and tight fit of the coupling to the cable.
The cost of TF directly depends on their type, size and configuration. The price of 1 set with products of various diameters will range from 600 to 1300 rubles. This is the cost of a professional set made in Europe. Piece sales are rare. On average 1 m.p. will cost from 30 (2.5 mm) to 90 (35 mm) rubles.
When choosing, you should pay attention to the geometric dimensions of the product, wall thickness and color coding. The shrinkage factor should also be taken into account.