The magnetic starter is two-pole. Contactors and magnetic starters: features and differences. Safety precautions during operation
TO category:
Crane device
Contactors and magnetic starters
It is called a contactor electrical apparatus for closing and opening power circuits, driven by an electromagnet.
Depending on the type of current, contactors are distinguished between direct and alternating current. Based on the number of simultaneously switched circuits, contactors are divided into single- and multi-pole. Contactors direct current Available in single- and double-pole, and alternating - two, three- and four-pole.
To prevent the phone from vibrating, the spring creates a pre-pressure force equal to approximately half the final pressing force. Contacts can sometimes be made of copper if the oxide film that forms on work surface contacts, periodically removed for self-cleaning. The arcing system of DC contactors is usually made in the form of a chamber with longitudinal slots, into which the arc is forced out using magnetic force. The arcing system of AC contactors, as a rule, has the form of a chamber with steel arcing plates and a double arc break in each phase.
The three-pole AC contactor consists of a magnetic system, a main contact system and a block contact system. The magnetic system includes a stationary part (core), a coil and a moving part (armature). The armature and core are riveted from thin plates of electrical steel to reduce heat and losses from eddy currents. The main contact system consists of fixed and moving contacts, to which the wires of the switched circuit are connected. The moving contacts are mounted on the same shaft with the armature. Block contacts are used for various electrical switching in the control circuit, which includes the contactor coil. The main contacts are made massive, designed for high current, and the block contacts are made small, since the current in the control circuit does not exceed 5 ... 10 A.
Blocking or auxiliary contacts are used for switching in control and signaling circuits, therefore they have the same design as relay contacts. As a rule, the type of current in the control circuit that powers the contactor coil coincides with the type of current in the main circuit. Therefore, DC contactors designed to switch DC motors have an electromagnetic mechanism that is powered by DC current. According to AC contactors, designed to switch AC motors, have an electromagnetic mechanism powered by AC current.
When opening electrical circuits When under load, an electric arc occurs between the power contacts of the contactor, which causes accelerated wear of the contacts and even destroys them. To reduce arc burning time, use various systems forced arc extinguishing. The power contacts of the contactor are enclosed in an arc-extinguishing chamber made of fire-resistant material. The chamber serves to cool and extinguish the arc and prevents its transfer to adjacent devices or grounded parts.
There are, for example, cases where the coils of AC contactors are powered by a DC circuit. The structure of a DC contactor is shown in Fig. The rotary-type electromagnetic mechanism consists of a core 1 with a coil 2, an armature 3 and a return spring. Cores 1 have a pole piece necessary to increase the magnetic conductivity of the working gap of the electromagnet.
Constant contactor Fig. Current electromagnetic blowing. Non-magnetic gasket 5 serves to predict armature sticking. The power contact unit consists of 6 fixed and 7 movable contacts. Contact 7 is hinged on lever 8, connected to armature 3 and pressed to it by a spring. Current supply to moving contact 7 is made from a flexible copper tape. Closing of main contacts 6 and 7 occurs with slipping and rolling, which ensures cleaning of contact surfaces from oxides and carbon deposits.
In contactors and other arc extinguishing devices, a sequential magnetic blowing system is used, in which the circuit current passes from a stationary contact to a movable one through an arc extinguishing coil mounted on a stationary contact in the arc extinguishing chamber. A magnetic field is created inside the chamber, in the area of which there are contacts. The arc formed when the contacts open interacts with magnetic field and is “driven” into the arc-extinguishing chamber. The arcing chambers in this case have a slot design. In AC contactors with low switching frequencies, chambers with an arc-extinguishing grid are used. The arc arising at the contacts is blown onto the grid plates, quickly cools and goes out.
For intensive extinguishing of the electric arc, an arc-extinguishing chamber is used. It has an arc-extinguishing grid in the form of thin metal plates, break the arc into short sections. The plates intensively remove heat from the arc and extinguish it. To force the arc towards the arc extinguishing grid, electromagnetic force can be used, the so-called magnetic blowing. In Fig. Figure 2 shows an arc chute with a narrow slot and magnetic blowing. The slot chamber is formed by two walls 1 made of insulating material.
Therefore, magnetic blowing can also be used in AC contactors. AC contactors differ from DC contactors primarily in that they are usually three-pole. The main purpose of AC contactors is to switch on three-phase asynchronous motors. Therefore they have three main contact points. All three main contact units operate from a common valve-type electromagnetic drive mechanism that returns a shaft with movable contacts mounted on it.
If the power of the contacts is small, then forced arc extinction is not used, but partitions are placed between the contactor poles to prevent the arc from spreading to the contacts of adjacent poles.
The operation of contactors with removed arc chutes is unacceptable.
On cranes, contactors are used in magnetic controllers, as line contactors for protection circuits and in reversers.
Auxiliary contacts are associated with the same pretext. To increase the overall service life of the contactors, it is possible to change the contacts. The most complex and difficult stage of contact operation is the process of opening them. It is at this moment that the contacts melt and an arc appears between them. In these contactors, two thyristors are connected parallel to the main contacts.
In the on position, current flows through the main contacts since the thyristors are in closed state and do not conduct current. The switching wear resistance of combined contactors is several million cycles, while the main contacts of conventional DC and AC contactors usually withstand 150 - 200 thousand switching operations.
The reverser consists of two two-pole contactors installed in a common casing on a rail or panel. The reverser contactors are protected from simultaneous activation by mechanical and electrical interlocks. The circuits of the contactor coils at the reverser are closed by the control contacts of the cam controller, and the main contacts of the contactors are included in the power circuit and with their help the phases of the stator circuits of the motors are switched. Reversers are most often used in conjunction with cam controllers, when the latter control two simultaneously operating, mechanically coupled motors, for example, a crane movement mechanism.
AC Contactor Solenoid Drive low power has an W-shaped core and armature 2, assembled from electrical steel plates. Part of the poles of the core is covered by a short-circuited coil, which prevents vibration of the armature caused by a decrease in the force of electromagnetic attraction to zero during the passage of an alternating current. sinusoidal current through zero. Movable contacts 4 of the bridge type are fixed to the armature 2, which increases the reliability of shutdown due to double opening. Fixed contacts 5 are installed in the plastic case and spring 7 returns contacts 4 to their original position.
A magnetic starter is a small-sized contactor of a special design designed for starting, stopping and reversing asynchronous squirrel-cage motors, as well as for switching (closing and opening) other electrical circuits. The magnetic starter may have built-in thermal relays to protect the closed electrical circuit from overloads.
Auxiliary contacts in fig. 3 not shown. S. - book Electromagnetic mechanisms and automation actuators. Starting and protection of asynchronous motors. Asynchronous electric motors are often used in production technology industrial enterprises, cooling pumps, fans, fire pumps and the like. Their reliable operation It has big influence to ensure quality and adherence to production schedules, safety devices, etc. therefore it is very important that they electrical protection, mutual coordination and blocking of protective and control elements.
On cranes, starters are used to control squirrel-cage motors, in magnetic controllers and for switching other power circuits.
The main component of magnetic controllers, crane (protective) and reversible panels is a contactor - a device that closes and opens power circuits during remote control. In electric crane drives, contractors are used only with electromagnetic drive.
The following article reads the basic devices in relation to traditional direct motor starting, for the star-delta trigger. When considering the design of complete motor starter starters, several basic issues need to be addressed: protection, control and use category, disconnection, type and number of devices making up the starter motor and short circuit conditions in the network. It all depends on the type and parameters of the electric motor and drive equipment, maintenance requirements and financial capabilities.

Rice. 87. Contactor type KT6000:
A - appearance, b - installation of a short-circuited turn; 1 - base, 2 - support, 3 - auxiliary contacts, 4 - contact lever, 5 - fixed contact, 6 - main shaft, 7 - electromagnet, 8 - magnet “yoke”, 9 - short-circuited coil
Movable arc-shaped contacts are assembled on a shaft and, when closed, roll over the surfaces of the fixed contacts. The shaft drive is carried out by an electromagnet installed on the side of the contact group (Fig. 87, a). All KT series contactors (KT 6000 and KT 64) are designed based on the same design principles and operate on alternating current.
It is a combination of all the switching devices required to start and stop the motor combined with appropriate overload protection. Engine starting - 1, 2, 3 or 4 devices? A complete motor starter can be one, two, three or four devices. The choice of the number of devices in a set very often depends on the usage and planning habits of each country, the user's needs for reliable operation, the service life of the instruments and serviceability.
The main functions to be provided are: shutdown, short circuit protection, switching, overload protection. Each solution has its pros and cons. The multi-component engine trigger assembly is more convenient to maintain and is capable of changing individual parts of the starter as they wear out. This is important for contactors and motor starters.
The main contacts have a powerful arc extinguishing system with electromagnetic suppression. Based on the number of simultaneously switched circuits, contactors are divided into single- and multi-pole. AC contactors are available in two-, three- and four-pole versions. In addition to the main contacts, the contactor has a group of auxiliary contacts (make and break), the number of which can be changed during operation in accordance with the circuit diagram of the electrical equipment.

Coordination with short circuit protection devices. To optimize costs, ensure continuity and maintenance, the individual starter components must be functionally coordinated. Type 1 Coordination: Requires that the contactor or trigger will not cause a hazard to persons or be installed in a short-circuit condition and cannot be serviced without repair and replacement of parts. This type of coordination requires skilled maintenance. Acquisition costs are usually slightly lower than for type coordination.
To ensure reliable operation of the electromagnet when powered by alternating current, a short-circuited coil in the form of a brass frame is laid at the ends of the electromagnet yoke, covering part of the magnetic circuit (Fig. 87, b). In a short-circuited turn, a current is induced (as in secondary winding transformer), creating an additional magnetic flux that eliminates vibration of the electromagnet armature. Normal operation of the electromagnet is characterized by a slight hum of the device.
Type 2 Coordination: Requires that the contactor or trigger does not cause a hazard to people or is not installed in a short circuit condition and is suitable for continued use. There is a risk of welding the contacts of these devices. The manufacturer then needs to specify the maintenance procedure. However, maintenance requirements are lower. Using a short circuit protection device that is not recommended and is not a proven solution may de-coordinate coordination.
These combinations have been tested, certified and tabulated by the manufacturer. These devices significantly reduce short circuit and ensure their extremely fast shutdown. This has a positive effect on the service life of the contactor, thermal relay and protection of power cables. No more need to use disconnector and fuses. In addition, in the event of a failure, all phases are switched off simultaneously; this will prevent unwanted two-phase power supply.
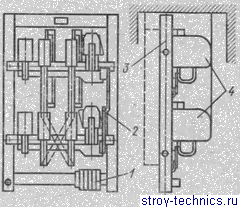
Rice. 89. Reversor DR-160UZ:
1 - terminal board, 2 - mechanical interlock, 3 - housing, 4 - contactor
In crane electric drives, starters of the PME-200 type No. PAE-300 are widely used for an operating current of 25 and 40 A, respectively. The main difference between a PME type starter and a conventional contactor is that its armature does not rotate when the magnet is triggered, but moves forward along with the moving contacts in special guides (Fig. 88).
Exists most of additional engine protection. These are, for example, temperature sensors, current asymmetry detection, stationary motor insulation resistance measurement, insulation insulation detection. 
Stationary motor insulation resistance measurement is mainly used when installed in high humidity or dustiness.
Other additional protection is a protection or monitoring relay that detects small current leaks into the ground due to deterioration of the internal insulation of the motor. This allows you to identify the deteriorating condition of your equipment and inform you about maintenance. In this way, damage or fire to the truck motor or production failure can be prevented.

Rice. 88. Magnetic starter PME-211:
To change the direction of the working movement of crane mechanisms driven by asynchronous motors with a squirrel-cage rotor, special reversing contactors such as TR-160UZ or DR-160UZ are used in combination with cam controllers or start buttons (Fig. 89). The reverser consists of two two-pole contactors, the control circuits of which are closed by a cam controller, and the main contacts switch the phases of the stator circuits of the electric motor. Both contactors are housed in the same housing and have mutual electrical and mechanical interlocks that prevent them from being turned on simultaneously.
Safe and reliable engine operation is a key factor in productivity and economic success in all plants around the world. Also new are four-pole contactors, auxiliary contactors and overcurrent relays.
The contactors themselves are small in size. All contactors are 45mm wide and compared to the previous series of contactors and their content is on average reduced by 6% for AC coil voltage and 32% for DC coil voltage.
On cranes, reversers are usually used to control: power controllers, two simultaneously operating and mechanically connected motors, for example, a crane movement mechanism.

Rice. 90. Devices for infrequent switching of electrical circuits:
a - power distribution box, b - fuse-switch block; 1 - cabinet, 2 - switch, 3 - handle, 4 - fuses, 5 - contact jaws, 6 - lever system, 7 - movable knife - fuse
The number of contactor numbers has been reduced by 90% while maintaining the same number of applications. Significant savings are also achieved by fixing the contactor itself. Therefore, expansions due to fluctuations in network voltage are significantly eliminated. 26 to 38 A contactors are not equipped with any auxiliary contact, but 45 mm width is supported. All contactors can be equipped with a single-pole front auxiliary contact, a four-pole front-mounted auxiliary contact or a double-pole front-mounted auxiliary contact. side mounting.
TO Category: - Crane installation
Why are contactors used in electrical installations and how do they differ from starters? I believe: firstly, large contactors have arc-extinguishing chambers, which means they are used to extinguish the arc; secondly, they have coils for high current (they write about them that they are designed for starting powerful motors). But the question keeps arising early, because there are small contactors without arc-extinguishing chambers and for small currents. How are they different? After all, both of them also have additional block contacts? Or have the concepts become so confused that now they call everything a contactor?
Answer 1
One specialist answered me this way: the difference is design. In a magnetic starter, the core attracts the conductive plate, and it connects two contacts with its plane. And in a contactor, when turned on, one contact hits the other.
Answer 2
If you look at some old reference books, then under the term
“magnetic starter” means a device consisting of a three-phase contactor and a thermal protection relay. There really is confusion at the moment. For example, in the Moeller catalog these devices are called starters, and in Schneider they are called contactors. I adhere to this point of view... The starter is a three-phase contactor... So, according to by and large, both terms are equivalent.
Answer 3
In general, in practice, for some reason everyone calls magnetic starters 0,1,2 magnitude. 3 quantities - some call it a starter, some call it a contactor. And according to theory, a really dark forest. In general, I was only recently able to find out that the abbreviation “PML” is a Licensed Magnetic Starter. No one remembers what kind of license it is, whose it is.
Answer 4
I looked in the old reference book: Contactor - two-position switching device driven by a magnetic drive, etc. Magnetic starter - contactor in combination with a thermal relay.
Here are the definitions from the large reference encyclopedia: “Magnetic starter is a low voltage electrical device designed for remote control(start, stop, change of direction) and protection asynchronous electric motors small and medium power with a squirrel-cage rotor. There are non-reversible and reversible MPs; Special MPs are also produced for switching the windings of multi-speed electric drives. MPs consist of a contactor, a push-button station and a thermal relay. The MP contactor, as a rule, has 3 main contact systems (for inclusion in three-phase network) and from 1 to 5 block contacts"
That is, a hat with a coil and contacts is a contactor, and a magnetic starter is a set of switching devices for starting and protecting the engine - i.e., a thermal relay, a push-button post, and a contactor.
THEORY
“An electromagnetic contactor is an electrical device designed for frequent switching on and off (up to 1500 switchings per hour) of DC and AC electrical power circuits. Widely used for remote control electric machines and devices in direct and alternating current installations at voltages up to 500-650 V and current up to 600 A.”
A contactor is a remotely controlled switching device designed for frequent switching of electrical circuits under normal (nominal) operating conditions. Depending on the type of switched current, direct and alternating current contactors are distinguished. Under certain conditions, the same contactors can switch both DC and AC loads.
Contactors are classified:
· by the type of current of the main circuit and the control circuit (including the coil) - direct, alternating, direct and alternating current;
· according to the number of main poles - from 1 to 5;
· rated current of the main circuit - from 1.5 to 4800 A;
· according to the rated voltage of the main circuit: from 27 to 2000 V DC; from 110 to 1600 V AC with a frequency of 50, 60, 500, 1000, 2400, 8000, 10,000 Hz;
· according to the rated voltage of the switching coil: from 12 to 440 V DC, from 12 to 660 V AC with a frequency of 50 Hz, from 24 to 660 V AC with a frequency of 60 Hz;
· according to the presence of auxiliary contacts - with contacts, without contacts.
Normal operation devices are allowed when the voltage at the terminals of the main circuit is up to 1.1 and the control circuit is from 0.85 to 1.1 rated voltage corresponding circuits.
Contactors can operate in one, several or all of the following modes: intermittent-continuous, continuous, intermittent and short-term (GOST 18311-80). In intermittent-continuous mode, the contactor must allow operation at rated current for no more than 8 hours. The duration of the working period for short-term operating mode is 5, 10, 15, 30 s and 10, 30, 60, 90 min.
The contactor consists of the following main components: electromagnetic or electro-pneumatic drive, main contacts with an arc extinguishing device, auxiliary contacts.
In contactors with an electromagnetic drive, the main and auxiliary contacts are connected directly to the armature of the electromagnet that controls the closing coil.
In contactors with an electro-pneumatic drive, control is carried out using an electromagnetic valve that allows access compressed air to an electro-pneumatic drive.




