What is the difference between a dead-earthed neutral and an isolated one. Requirements for connections of protective and grounding conductors. Measuring the resistance of earthing devices
In electrical installations with a dead-earthed neutral up to 1 kV, when it is not possible to ensure electrical safety only with the help of a protective automatic power off, re-grounding is carried out.
Re-grounding is a deliberate connection in electrical installations up to 1 kV of zero protective conductor(PE) circuit to an earthing device that is electrically connected or not connected electrically to the earthing device of the power supply.
PUE-7 p. 1.7.61
Re-grounding of electrical installations with voltage up to 1 kV, powered by overhead lines, must be carried out in accordance with 1.7.102-1.7.103. The term “Recommended” means that if there is a main potential equalization system to which structures used as natural grounding, then re-grounding is provided by these natural ground electrodes and the electrical installation of an artificial ground conductor is optional. Re-grounding should be performed on overhead lines and branches from them in accordance with PUE-7, clause 1.7.102 and clause 1.7.103
PUE-7 p. 1.7.102
PUE-7 p. 1.7.103
1.7.103. The total spreading resistance of ground electrodes (including natural ones) of all re-groundings of the PEN conductor of each overhead line at any time of the year should be no more than 5, 10 and 20 Ohms, respectively, at line voltages of 660, 380 and 220 V of the source three-phase current or 380, 220 and 127 V source single-phase current. In this case, the spreading resistance of the grounding conductor of each of the repeated groundings should be no more than 15, 30 and 60 ohms, respectively, at the same voltages. At resistivity earth ρ > 100 Ohm⋅m, it is allowed to increase the indicated norms by 0.01ρ times, but not more than tenfold.
Re-grounding wiring is performed to reduce the contact voltage on open conductive parts (metal cases of electrical equipment, etc.), as a result, the risk of damage is reduced electric shock at single-phase faults ground, exposed or third-party conductive parts.
Re-grounding is installed in order to prevent the introduction of induced potentials into the electrical installation of the building through external communications entering the building and to reduce the potential brought to the grounded housings of electrical receivers when the zero working conductor of the supply line is broken.
If re-grounding is installed, then when a separate electrical receiver is shorted to the case, the short-circuit current passes not only through the neutral protective conductor, but also partially through the ground through the resistance of the grounding conductors of the power source and re-grounding. As a result, the voltage relative to the ground on the body of the damaged electrical receiver decreases, and the neutral voltage of the power source rises. The ratio of these voltages is proportional to the ratio of the resistances of the corresponding ground electrodes.
In the distribution networks of cities, factories and industrial enterprises distribution scheme electrical potentials much more difficult, since several electrical installations are often fed from one transformer, where natural grounding conductors are used for re-grounding, the resistance of which is almost impossible to take into account by calculation. Therefore, in accordance with PUE-7 clause 1.7.61, during electrical measurements, the resistance of the grounding conductor of re-grounding is not standardized.
PUE-7
1.7.61. When using the TN system, it is recommended to re-ground the PE and PEN conductors at the input to the electrical installations of buildings, as well as in other accessible places. For re-grounding, natural grounding should be used first. The resistance of the re-grounding earth electrode is not standardized. inside the big and multi-storey buildings a similar function is performed by potential equalization by connecting a zero protective conductor to the main ground bus.
Re-grounding of electrical installations with voltage up to 1 kV, powered by overhead lines, must be carried out in accordance with 1.7.102-1.7.103.
For stand-alone electrical receivers outdoor installation, as well as for buildings or structures with a metal case in their immediate vicinity, re-grounding also performs the function of equalizing the potentials between the conductive parts of these structures accessible to the touch and the ground, and also reduces the possible values of step voltages.
Inside buildings, land is usually not available. The danger of electric shock during single-phase short circuits under these conditions is determined by the value of the potential difference between the conductive parts that are simultaneously accessible to touch, to reduce which it is necessary to carry out potential equalization on the basis of PUE-7, clauses 1.7.82 and 1.7.83.
PUE-7
1.7.82. The main potential equalization system in electrical installations up to 1 kV must interconnect the following conductive parts (Fig. 1.7.7):
- zero protective PE or PEN conductor of the supply line in the TN system;
- grounding conductor connected to the grounding device of the electrical installation, in IT and TT systems;
- grounding conductor connected to the re-grounding conductor at the entrance to the building (if there is a grounding conductor);
- metal pipes of communications included in the building: hot and cold water supply, sewerage, heating, gas supply, etc. If the gas supply pipeline has an insulating insert at the entrance to the building, only that part of the pipeline that is relative to the insulating insert from the side of the building is connected to the main potential equalization system;
- metal parts of the building frame;
- metal parts of centralized ventilation and air conditioning systems. In the presence of decentralized ventilation and air conditioning systems, metal air ducts should be connected to the PE bus of power panels for fans and air conditioners;
- grounding device of the lightning protection system of the 2nd and 3rd categories;
- grounding conductor of functional (working) grounding, if there is one and there are no restrictions on connecting the working grounding network to the protective grounding grounding device;
- metallic sheaths of telecommunication cables.
Conductive parts entering the building from the outside should be connected as close as possible to their point of entry into the building. To connect to the main potential equalization system, all of these parts must be connected to the main grounding bus (see 1.7.119-1.7.120) using the conductors of the potential equalization system.
PUE-7 p. 1.7.83
1.7.83. The system of additional potential equalization must interconnect all open conductive parts of stationary electrical equipment that are simultaneously accessible to the touch and third-party conductive parts, including metal parts accessible to touch. building structures building, as well as neutral protective conductors in the TN system and protective earth conductors in IT and TT systems, including protective conductors socket outlets. For potential equalization, specially provided conductors or open and third-party conductive parts can be used if they meet the requirements of 1.7.122 for protective conductors with respect to conductivity and continuity of the electrical circuit.
PUE-7 p. 1.7.122
1.7.102. At the ends of overhead lines or branches from them with a length of more than 200 m, as well as at the inlets of overhead lines to electrical installations, in which, as a protective measure in case of indirect contact, automatic shutdown supply, re-grounding of the PEN conductor must be performed. In this case, first of all, natural grounding should be used, for example, underground parts of supports, as well as grounding devices designed for lightning surges (see Chap. 2.4). The indicated repeated groundings are performed if more frequent groundings are not required under the conditions of lightning surge protection. Re-grounding of the PEN conductor in networks direct current must be made using separate artificial grounding conductors, which should not have metal connections with underground pipelines. Grounding conductors for re-grounding the PEN conductor must have dimensions not less than those given in Table. 1.7.4.
The main task of re-grounding the zero protective conductor is to reduce the voltage on open conductive parts and in the event of its breakage. The most dangerous case is a break in the neutral conductor with a single-phase short circuit to the body (ground) behind the break. In this case, in the absence of repeated grounding, the voltage on the cases of all power receivers behind the break point will be close to phase for a long time, since such damage cannot be automatically turned off by protection devices.
Content:In the process of production, conversion, transportation, distribution and consumption of electricity, a three-phase symmetrical wire system is used. It became possible to achieve such symmetry by bringing them into the same state. As a result, a uniform current load is formed on all phases, as well as the same phase shift of currents and voltages.
However, during the operation of this entire system, sooner or later, emergency situations arise in the form of a wire break, insulation breakdown and other specific malfunctions that lead to symmetry violations. three-phase system. The consequences of such violations must be remedied as soon as possible. An important role in this is played by the degree of speed of relay protection, the operation of which is affected by isolated and solidly grounded neutral. Each of these modes has its advantages and disadvantages and is used in the most suitable conditions. In any case, normal functioning largely depends on their condition.
Isolated neutral
Isolated neutral has found a fairly wide application in domestic energy systems. This grounding method is used for generators or transformers. In this case, their neutral points are not connected to the ground loop. In distribution networks for 6-10 kilovolts, there may not be a neutral point at all, since the connection of transformer windings is carried out using the triangle method.
In accordance with the PUE, the mode isolated neutral can be limited by the capacitive current, which is the single-phase earth fault current of the network. Its compensation with the help of arc extinguishing reactors is provided for at the following values:
- Current over 30 amperes, voltage 3-6 kilovolts;
- Current over 20 amperes, voltage 10 kilovolts;
- Current over 15 amperes, voltage 15-20 kilovolts;
- Current over 10 amperes, voltage 3-20 kilovolts, with metal and reinforced concrete supports of overhead power lines
- All electrical networks with a voltage of 35 kilovolts.
- In "generator-transformer" blocks at a current of 5 amperes and a generator voltage of 6-20 kilovolts.
Earth fault current compensation can be replaced by resistive neutral earthing with a resistor. In this case, the relay protection algorithm will be changed. For the first time, grounding in the isolated neutral mode was applied in electrical installations with an average voltage value.
Advantages and disadvantages of isolated neutral
The undoubted advantage of the isolated neutral mode is the absence of the need to quickly disconnect the first single-phase earth fault. In addition, a small current is formed in the places of damage, provided that the current capacitance to the ground is small.
However, this mode has a number significant shortcomings, because of which its use is significantly limited.
The main disadvantages of isolated neutral:
- Possible arc overvoltages of the intermittent nature of the arc of low current in the place of a single-phase earth fault.
- Faults can occur in many places due to insulation breakdown at other connections where arc surges occur. For this reason, many cables, electric motors and other equipment fail at once.
- Arc surges affect the insulation for a long time. As a result, defects gradually accumulate in it, which leads to a decrease in the service life.
- All electrical equipment must be insulated line voltage relative to the ground.
- The damage sites are quite difficult to find.
- A real danger of electric shock to people in the event of a prolonged earth fault.
- With single-phase faults, it cannot always be ensured right job relay protection, since the value of the real fault current is completely related to the mode of operation of the network, in particular, to the number of connected connections.
Thus, a large number of shortcomings covers all the advantages of this grounding mode. However, under certain conditions, this method is considered to be quite effective and does not contradict the requirements of the PUE.
Solidly grounded neutral
A more progressive way is the dead-earthed neutral mode. In this case, the neutral of the generator or transformer is directly connected to the earthing device. In some cases, the connection is made using low resistance, for example,. In contrast, such a neutral is called a worker. The resistance value of grounding devices connected to the neutral should not exceed 4 ohms in electrical installations with a voltage of 380/220 volts.
In electrical installations where a dead-earthed neutral is used, the damaged section must be quickly and reliably switched off in automatic mode in the event of a short circuit between the phase and the ground conductor. In this regard, at voltages up to 1000 volts, equipment cases must be connected to earthed neutral installations. Thus, a quick disconnection of the damaged section is ensured in the event of short circuit using an overcurrent relay or fuse.
Features of deaf grounding
Neutral grounding in dead mode is provided for four-wire networks alternating current. In such cases, dead grounding of zero terminals is performed power transformers. All parts to be grounded and a zero grounded terminal are connected. The neutral wire must be solid, without fuses and any disconnecting devices.
As a dead-earthed neutral of overhead lines with a voltage of up to 1 kilovolt, a neutral wire is used, which is laid along with the phase lines on the same supports.
All branches or ends of overhead lines longer than 200 meters are subject to re-grounding neutral wire. The same applies to building entries where there are installations to be grounded. As natural grounding conductors can be used reinforced concrete supports, as well as grounding devices that protect against lightning surges.
Thus, an isolated and solidly grounded neutral provides normal work relay protection of generators and transformers. In addition, they reliably protect people from electric shock.
A network circuit with a solidly grounded neutral serves to protect a person from electric shock. In emergency cases, a dead-earthed neutral equalizes the potentials, as a result of which a person’s touch with the metal parts of electrical equipment becomes safe.
The protective device will also play its role in emergency situations by cutting off the power supply, since during short circuits the current in the network increases.
Device and principle of operation
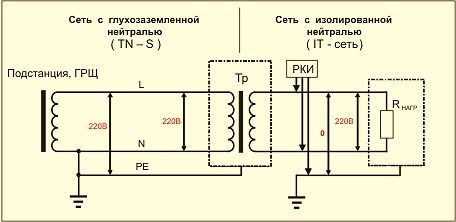
Consumer nutrition electrical energy produced by power transformers and generators. Most often, the windings of the three phases of these devices are connected according to the star scheme, in which common point is neutral. If this neutral is connected to ground through a low resistance, or directly, directly near the power source, then it is called a solidly grounded neutral.
Other modes of operation of the neutral with grounding are also used, depending on the modes of operation of the network during ground faults, the necessary methods for protecting a person from electric shock, methods for limiting overvoltages:
With effectively earthed neutral.
With ungrounded neutral.
Compensated neutral.
These modes are used for electrical devices 6 kilovolts or more. used up to 1 kV, and has not found wide application. It does safe work only mobile devices in which it is impossible to make a ground loop.
Neutral mounting of compensating devices makes it possible to reduce capacitive current closing devices operating with a voltage of more than 1 kV. Compensation is made using inductors, as a result of which the current at the fault point becomes zero. For effective work protection, neutral grounding with a resistor is used. It forms active part current on which the protective relay operates.
A solidly grounded neutral is the most effective way protect people from electric shock. It is used in most electrical networks nutrition. The voltage between phases is called linear, and between phase and zero - phase. The rated voltage of the electrical installation is determined by linear value voltage. It can be 220, 380, 660 volts. In household power networks, the voltage is 380 volts.
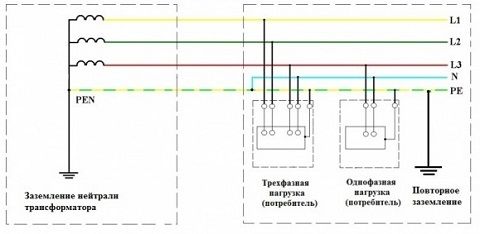
Single-phase consumers are connected between phases and zero evenly. at the substation has a ground loop. It includes metal parts interconnected and buried in the ground. The dimensions of the circuit are determined taking into account the effective distribution of current along the ground during a short circuit.
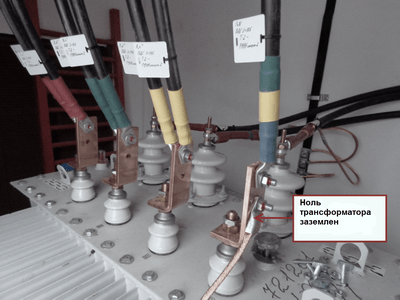
The operability of grounding is determined by the value of current spreading resistance. Permissible values of this parameter are specified in the rules of electrical installations. For electrical substations, ground resistance should not exceed 4 ohms at a voltage of 380 volts.
The ground loop is connected to a neutral bus made in the form of a metal strip. The neutral wire of the transformer is connected to it. Also, cable cores are connected to it, which go to consumers. Phases are connected to circuit breakers, fuse contacts.
The step voltage acts as follows. If wet concrete floor there is an uninsulated conductor under voltage, it is very dangerous to approach it. Tension moves away from him in waves, like circles on water. If a person's feet enter this zone, an electric shock occurs.
To protect people from step voltage, they build in the floor of the room metal mesh, which in different places connected to the ground loop. In this way, the legs of a person are shunted with metal fittings of the grid, and the main part of the electric current passes by the person.
PUE requirements
Ground must be connected to the device with a special conductor. To shorten the path of the flow of electric current and reduce costs, select a place directly next to a voltage source, such as a transformer. There is a limitation that if the existing concrete foundation is the grounding conductor, then the connection to the reinforcement of the concrete base made of metal is made in two or more places.
A similar number of connections are made to metal frames, which are located deep in the ground. Under such conditions, the grounding system is able to effectively protect a person from unpleasant situations.
If transformers located on different floors of the building act as power sources, then the connection to the neutral is made separate wire, which is connected to the metal frame of the entire structure.
The ground connection circuit must not contain fuses, fuses and other components that can break the continuity of this circuit. They also take auxiliary measures that prevent mechanical damage.
Some PUE restrictions
If it is installed on the working, protective or neutral conductors, then the ground electrode wire is mounted immediately after this device, to the neutral conductor.
The resistance of the grounding device in the 220 volt network is limited to the maximum value of 4 ohms, with the exception of the special properties of the earth, which create an increased resistance of more than 100 ohms per meter.
on overhead transmission lines, grounding is installed at the end and at the input of the line for duplication of grounding. This enables the effective operation of the protective devices. This rule is used when there is no need for installation a large number devices that can eliminate overvoltage during lightning strikes.
When choosing conductors for a grounding device, it is necessary to apply the standards for the smallest allowable dimensions and material of conductors used for re-grounding laid in the ground. For example, if a steel corner is used, then its wall thickness must be at least 4 mm. The total cross-sectional area for ground wires connected to the main bus, in accordance with clause 1.7.117 of the PUE, must be:
10 mm 2 - copper wire.
16 mm 2 - aluminum conductor.
75 mm 2 - steel conductor.
The electric machine installed for protection must have a response speed in case of a short circuit of more than 0.4 s at 220 volts.
IN home network according to clause 7.1.36 of the PUE, it is required to lay a network to consumers from common shields with three conductors: phase, working zero and protective earth(solidly grounded neutral). However, in many apartments this requirement is often violated, which is confirmed by the absence of a grounding contact in the sockets.
old regulatory requirements for domestic buildings were determined for insignificant capacities. Today, the power of household electrical devices has increased significantly. The apartments have air conditioners. hobs, ovens which have higher power.
To improve the effectiveness of protection in modern apartments a prerequisite is the presence of grounding. In new housing constructions, a dead-earthed neutral is already included in standard projects. In old buildings, good owners install grounding during major repairs.
A dead-earthed neutral is designed to protect against electric shock to a person. When emergency potential equalization occurs, touching the surface of the equipment case will be safe. Since the current increases at the same time, the residual current device installed in the circuit will quickly operate.
Electrical safety poster "Installations with solidly earthed neutral"
For correct use such a mechanism in practice, it is necessary to know and apply the norms of the current legislation in the field of electrical safety. They are contained in the "Electrical Installation Rules" (PUE, hereinafter referred to as the "Rules"), which were approved by the Ministry of Energy of Russia in an order dated 08.07.2002. The seventh version of this document is currently relevant.
Mechanism of action
In accordance with the Rules, this term is called electrical connection neutral generator (transformer) with a grounding device. For example, a three-wire network is laid from a power source to a residential building. The neutral through the input cabinet is distributed over the shields. Consumer ground loops are connected to it. In these circuits, the installation of fuses or other devices that can disrupt the integrity of the circuit is unacceptable.
Working zero is another conductor. Between it and the third wire, a phase voltage arises, which is used washing machines, microwave ovens and other equipment.
An example of an emergency. Under the influence of vibration inside the equipment, the phase wire was disconnected from the regular attachment point, it touched the metal case. A short circuit will occur, the current will increase sharply. Circuit breaker or the fuse performs its function, the power will be turned off.
The resistance R0 will be less than along the path of the current through the body of a person who accidentally touches phase wire, which excludes electric shock (fig. below). This diagram shows an option for grounding the generator neutral.
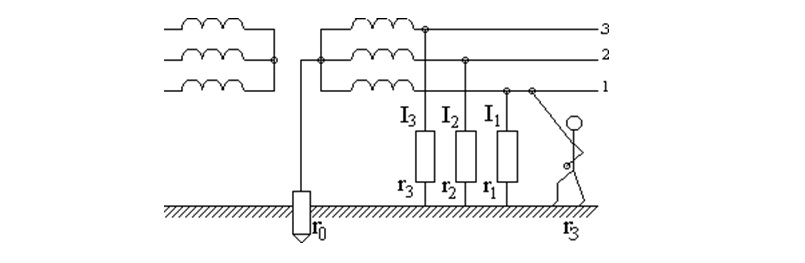
Diagram of a solidly grounded neutral
In order for such a scheme to work quickly and efficiently, it is necessary to comply with the provisions of the Rules. In accordance with them, a high-quality secure network should be created.
PUE requirements
The necessary information is in a separate chapter 1.7 of the Rules. It notes that certain rules apply to electrical installations up to and above one thousand volts. Next, it is worth considering in more detail the household network with a voltage of 220 V.
It uses a single-phase current source. The grounding conductor is connected to one of the electrical terminals of this device using a special conductor. To shorten the current path and reduce costs, choose a location near the generating equipment (transformer).
The following limitation must be taken into account. If the existing foundation is used as a grounding conductor, then to the metal fittings in concrete base connect at least two points.
A similar number of connections are made to metal frames installed deep in the ground. Only in this way will the grounding system work efficiently and reliably enough.
If the device is powered by transformers located on different floors of the building, then the connection to the neutral is made using a separate conductor. It is connected in addition to the metal frame of the building.
When calculating the electrical parameters, the corresponding resistance must be taken into account.

It is allowed to connect grounding to the metal frame of the building
In the first and second versions, fusible links and other elements that can violate its integrity are excluded from the circuit. accept additional measures, preventing accidental or intentional damage with the use of mechanical influences.
Other restrictions noted in the Rules:
- If there is a current transformer in the PEN bus (common neutral conductors, working and protective), then the grounding conductor is attached directly behind this device, to the neutral.
- The electrical resistance of the grounding device in single-phase network 220V is limited to a maximum value of 4 ohms (clause 1.7.104 of the Rules). The exception is the special characteristics of the earth, which create a high resistance ( specific value, more than 100 Ohm per 1 m.).
- If there are overhead power lines, then redundant grounding conductors are installed on the input and end parts. This allows protective system work efficiently. But such a rule is applied only when there is no need to install more devices that can eliminate excessive voltages in the network during lightning strikes.
- In order not to be mistaken, it is necessary to use the standards for the minimum allowable dimensions and materials of conductors used for grounding systems (repeated type) laid in the ground. So, for example, if a black steel angle is used, the wall thickness should be 4 mm or more. The total cross-sectional area is regulated for earthing conductors that are connected to main bus(clause 1.7.117 of the Rules):
- 75 mm 2 if steel is used;
- 16 mm 2 - aluminum;
- 10 mm 2 - copper.
- The machine, which is installed to protect the TN circuit, must have a short circuit speed of at least 0.4 seconds at a voltage of 220 V.
If you study other types of networks, you can find out that when increasing rated voltage, the permitted electrical resistance of the earthing device must be lower. Such a requirement is reasonable, because the main thing is to ensure a good level of security. With less resistance in the event of an accident, a relatively small potential is formed on the grounded case, the protection system will perform its function quite effectively.
Similar reasoning can be used when studying the operation of protective devices. If a corresponding discharge occurs, then significant changes should form in the network. With an increase in the voltage of the power consumption and low operating electrical resistance grounding requirements are stricter. Excessive resistance of this circuit can reduce the amplitude of oscillations in the network, the machines will not be able to work fast enough or will not turn off the power at all.

Machines are selected taking into account network parameters
Now it’s worth moving on to the 220 V household network and paragraph 7.1.36. Rules. It defines the need for laying networks from common shields to consumer devices with three wires (one phase, zero working and protective). The latter is the dead-earthed neutral. Meanwhile, if you conduct an experiment and look at your own sockets in the apartment, then many people will notice the absence of such contact there.
The fact is that the old standards, according to which many domestic buildings are built, are designed for relatively small capacities. Currently, they have grown significantly. Equipping a three-room apartment with air conditioners implies the use of peak loads up to 6-7 kW. About 3 kW consumes an oven, 1.5-2 kW - a hob.
For effective protection under such conditions grounding is required. In new quality houses it is installed as standard. In old apartments, attentive owners install it when performing overhauls. When determining the wiring parameters, the standards of the Rules for conductors made of different metals are used (clause 7.1.45).
Pros and cons of schemes
A careful study of the description of this circuit allows you to understand that it performs its functions efficiently at the level of the rated voltage between phase and neutral. It provides fast response typical devices overload protection. In the event of a short circuit, powerful electromagnetic oscillations are formed that can cause additional accidents and destruction.
Other protective measures
To prevent electric shock, not only neutral grounding is used. Parts of the equipment, conductors, are covered with additional layers of insulation. Special shells are not allowed to touch them directly. Use low voltages that can not cause harm. Industrial plants protected by special barriers, located outside the zone of free access of unauthorized persons.
In everyday life, separate and complex methods are used, you can consider them using the example of a washing machine:
- body and metal carcass connected to the third wire, connected through a socket to a grounded neutral.
- the surface insulated with a thick layer of paint does not conduct current.
- The figure below shows that directly washing machine not equipped in a special way. The power cord has a conductor that, when plugged into a power outlet, is connected to the ground line. In the event of a short circuit, they will work protective devices and turn off the power supply.
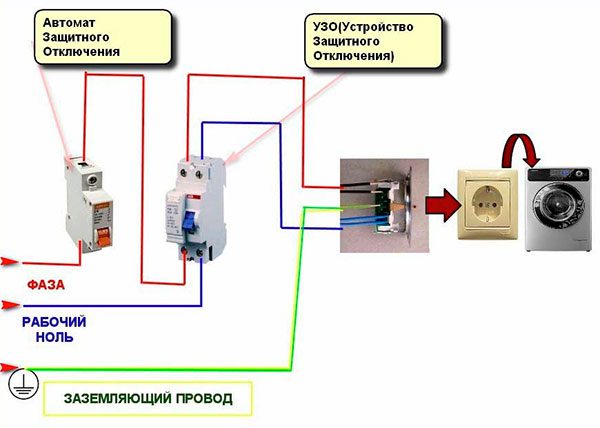
Correct connection to the network of the washing machine
- to reduce the likelihood of electric shock, control knobs are made of plastic, the corner parts of the structure, on which bare metal elements can be seen.
Video about grounding systems
This video provides a description of the grounding systems established by the Electrical Installation Rules.
If the Rules mentioned above are observed, then the created protection system will perform its functions efficiently and quickly enough.




